Tesla is more than just a car company; it’s a global employer with tens of thousands of people driving its mission forward. From manufacturing lines in Texas to software labs in Palo Alto and energy teams in Germany, Tesla’s workforce plays a pivotal role in shaping the future of electric vehicles, energy storage, and autonomous technology. For instance, Gigafactory Texas alone employs over 20,000 workers, while Tesla’s engineering teams have been central to breakthroughs in AI and battery systems.
How Many People Work At Tesla?
- 125,665 employees, that’s Tesla’s global headcount as of December 31, 2024, down ~10.54% from 2023.
- Tesla cut 14,808 jobs in 2024 alone.
- In May 2024, Tesla began laying off staff from software, services, and engineering units.
- The 2024 headcount decline reversed a prior trend; Tesla peaked at 140,473 employees in 2023.
- Elon Musk authorized cuts of roughly 10% of the global workforce in 2024.
- Tesla operates large manufacturing sites employing 20,000+ people (like Fremont, California).
- In acquisitions, Tesla may absorb staff, e.g., ~300 employees from German parts maker Manz in 2025.
Recent Developments
- In April 2024, Musk confirmed Tesla would cut about 10% of its workforce to reduce overhead.
- The layoffs stretched over multiple waves, affecting engineering, software, and service teams.
- Charging‑team staff (Supercharger unit) were also subject to cuts in mid‑2024.
- Tesla’s “Dojo” supercomputer division has been scaled back, and key team members departed in early 2025.
- Tesla acquired parts of Germany’s Manz AG in 2025, gaining ~300 jobs at the Reutlingen site.
- As of 2025, there is ongoing senior staff turnover attributed to burnout and internal tensions.
- In 2025, Tesla’s stock and operations face pressure from reduced sales, especially in Europe and China.
Tesla’s Current Team (Key People)
- Elon Musk – Chief Executive Officer. Musk continues to serve as CEO and lead product architect, overseeing long-term vision, product roadmap, and strategic decisions across automotive, energy, AI, and robotics divisions.
- Vaibhav Taneja – Chief Financial Officer. Appointed in 2023, Taneja oversees Tesla’s global financial operations, investor relations, and compliance. He also continues to serve as Chief Accounting Officer.
- Andrew Baglino – SVP of Powertrain and Energy Engineering. A Tesla veteran, Baglino leads teams responsible for powertrain systems, battery tech, and Tesla’s energy products. He is also frequently involved in investor calls and product briefings.
- Tom Zhu – Senior Vice President, Automotive. Formerly the head of Tesla China and Gigafactory Shanghai, Zhu now oversees global automotive operations, including manufacturing, delivery, and quality control across Tesla’s vehicle programs.
- Lars Moravy – VP of Vehicle Engineering. Moravy plays a pivotal role in vehicle design, structural engineering, and model development, especially for the Cybertruck and next-gen platforms.
- Ashok Elluswamy – Director, Autopilot Software. Elluswamy leads Tesla’s Autopilot and AI software teams, managing the development of Full Self-Driving (FSD) technologies.
- Drew Baglino (former) – Previously a key figure in battery development and engineering, Baglino stepped down from his executive role in early 2024 during internal restructuring.
- Rebecca Tinucci – (Departed). Formerly leading Tesla’s Supercharger division, Tinucci was among several senior executives who exited during the 2024 wave of layoffs.
- Roshan Prasad – Legal Affairs (Acting). Tesla’s legal operations continue under internal leadership, with shifting roles following the departure of multiple legal execs since 2023.
- Kirkhorn and Musk Family Office. Zach Kirkhorn, Tesla’s previous CFO, stepped down in 2023 but remains influential within Musk’s broader network, including his family office operations.
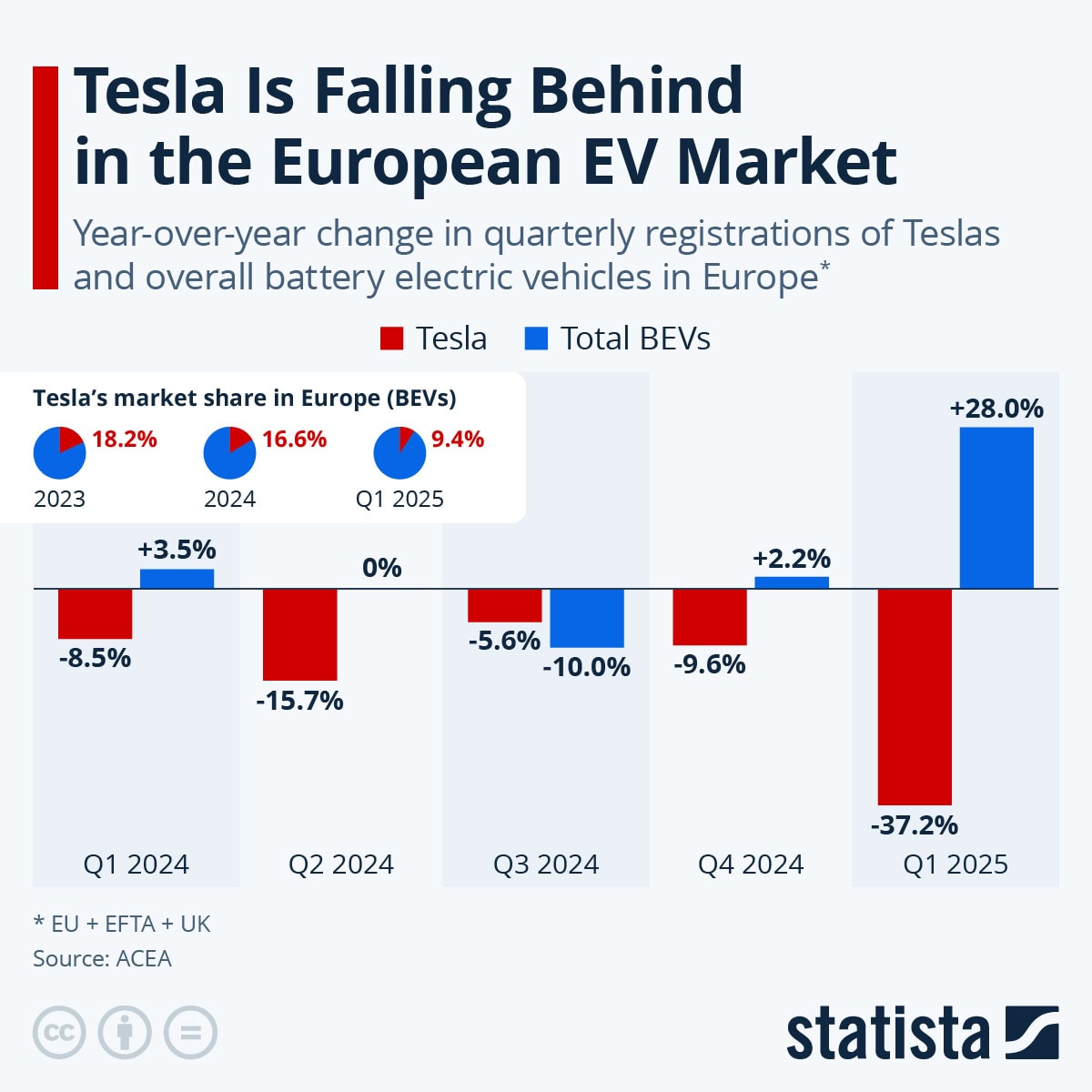
Tesla’s Performance in the European EV Market
- Tesla’s market share in Europe dropped from 18.2% in 2023 to 16.6% in 2024, and further down to 9.4% in Q1 2025.
- In Q1 2024, Tesla registrations fell 8.5%, while the overall BEV market grew 3.5%.
- In Q2 2024, Tesla declined by 15.7%, while the BEV market recorded 0% growth.
- In Q3 2024, Tesla dropped 5.6%, compared with a 10.0% fall in the total BEV market.
- In Q4 2024, Tesla fell 9.6%, while BEVs still managed a 2.2% growth.
- By Q1 2025, Tesla plunged 37.2%, even as the total BEV market surged 28.0%.
Total Number of Tesla Employees
- At year-end 2024, Tesla’s global employee count stood at 125,665.
- In 2023, Tesla had 140,473 employees.
- That means a drop of ~10.54% year‑on‑year from 2023 to 2024.
- Some sources suggest Tesla’s workforce was ~121,858 by mid‑2024, following additional reductions.
- The 2024 figure reflects all global staff, corporate, manufacturing, R&D, and service.
- Tesla’s own “About” page states it employs “over 100,000 employees” in its global operations.
- Market‑analysis platforms confirm ~125.67 K employees in their fundamentals listings.
Headcount by Year
- 2024: 125,665 employees, –10.54% from 2023.
- 2023: 140,473 employees, +9.87% from 2022.
- 2022: 127,855 employees, +28.77% from 2021.
- 2021: 99,290 employees, +40.33% from 2020.
- 2020: 70,757 employees.
- Earlier years: 2019 (48,016), 2018 (48,817), 2017 (37,543).
- Note how growth was steep in 2021–22, but in 2024, Tesla reversed with a net reduction.
Workforce Reduction and Layoffs
- In 2024, Tesla eliminated approximately 10% of its global headcount.
- That meant roughly 14,808 jobs were cut in one year.
- Tesla’s engineering, software, and service departments were explicitly named in layoff reports.
- The Supercharger, charging infrastructure team, also faced reductions.
- Some cuts are linked to Musk’s memo that roles had become duplicated due to fast growth.
- Analysts argue the layoffs aim to redirect resources toward core innovation and R&D.
- As of mid‑2024, Tesla’s internal email lists suggested ~121,000 employees, implying continued cuts beyond year‑end.
- Some critics highlight the risk of morale decline and institutional knowledge loss.
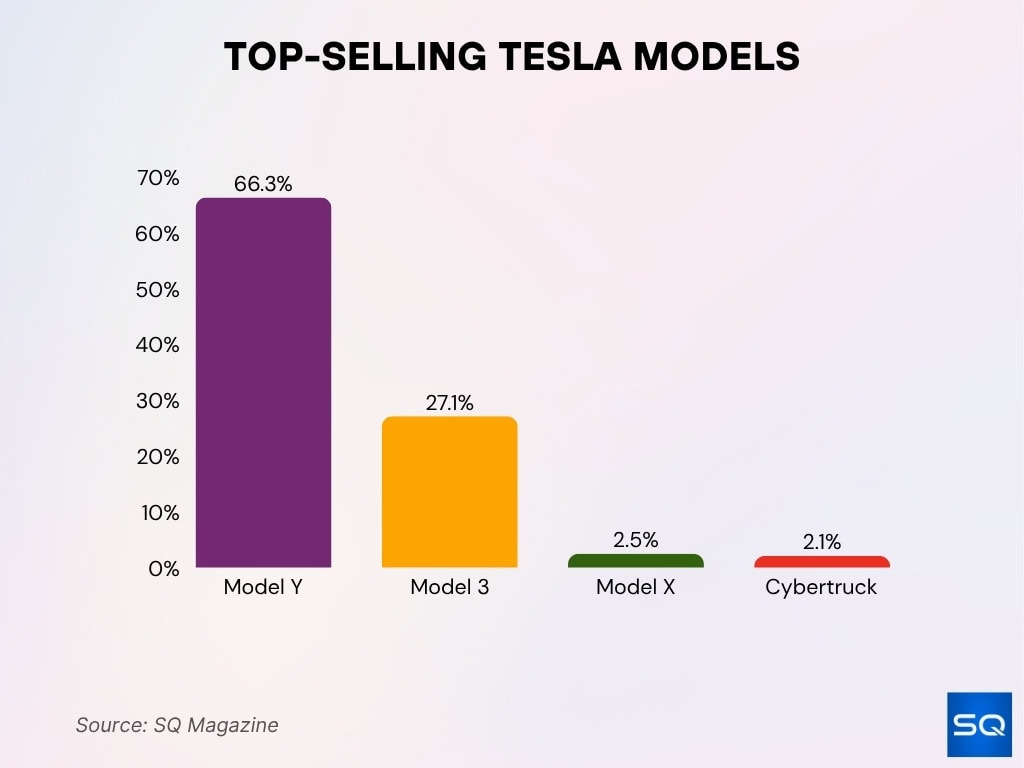
Top-Selling Tesla Models
- Model Y leads with 1,185,757 units sold, capturing 66.3% of total Tesla sales.
- Model 3 follows with 484,026 units sold, accounting for 27.1%.
- Model X holds a smaller share at 2.5% of sales.
- Cybertruck contributes 2.1%, reflecting its early adoption phase.
Operations and Manufacturing Staff
- Tesla’s Fremont factory employs over 20,000 people as of recent reports.
- Gigafactory Texas, near Austin, had plans to staff 20,000 workers or more in 2023.
- The Berlin‑Brandenburg gigafactory reportedly employs 11,500 staff.
- Tesla’s manufacturing operations span multiple gigafactories, including Nevada, Shanghai, Texas, and Berlin, each with several thousand workers.
- In 2024, Tesla laid off 693 employees at its Sparks, Nevada, facility as part of broader cuts.
- In Austin, Tesla’s local headcount fell by 7% from 2023 to 2024, reflecting layoffs in the manufacturing hub.
- The Austin headcount as of late 2024 was reported at 21,191, down from 22,777 the prior year.
- Some production roles are outsourced, including contractors, suppliers, and are not included in Tesla’s direct‑employee counts; estimating full operations headcount is complex.
Gender Distribution of Tesla Employees
- About 21% of U.S. Tesla employees are women.
- In older Tesla DEI reports, men made up ~79% of the U.S. workforce.
- Among leadership roles, reports show ~83% male composition in U.S. operations.
- Women accounted for ~23% of promotions in some earlier years.
- Tesla’s UK data shows that women are more represented in the upper pay quartile, ~21.1%, vs the middle quartiles.
- In bonuses, awards, UK women’s mean incentive was ~22.7% higher, median 71.3% higher than men.
- Across global operations, the female share likely varies by geography, e.g., the U.S. vs Europe, but non-U.S. data is less disclosed.
Employee Demographics
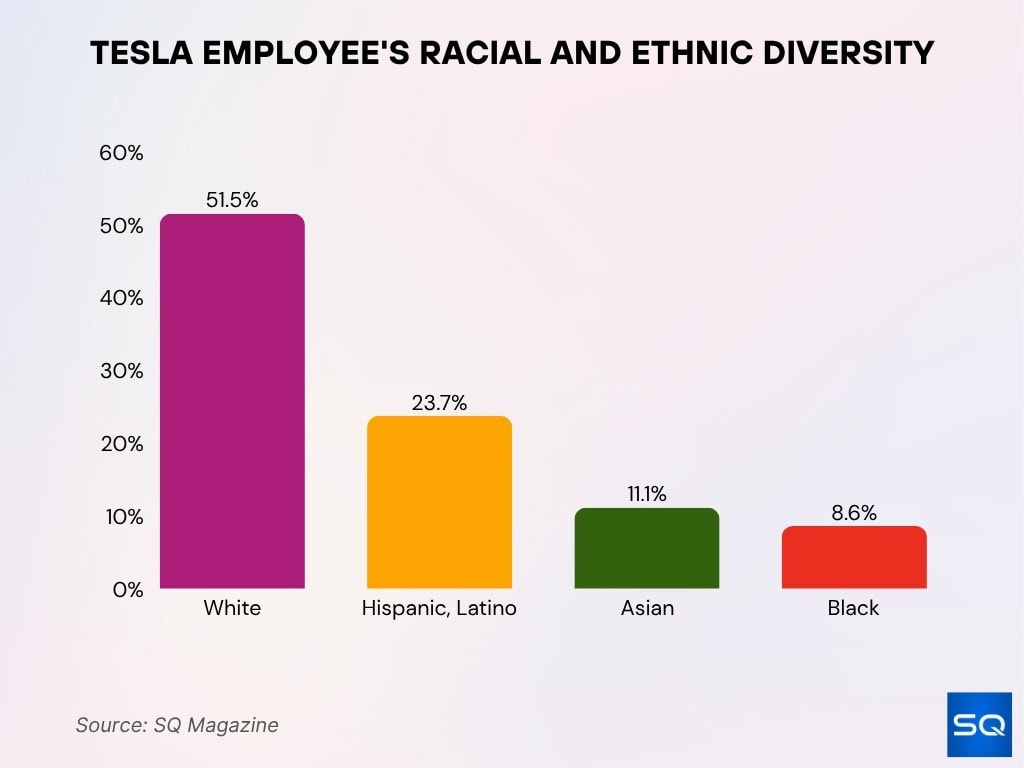
- Racial, ethnic breakdown, U.S., approximates, 51.5% White, 23.7% Hispanic, Latino, 11.1% Asian, 8.6% Black, African American.
- Women make up roughly 21% of Tesla’s U.S. workforce.
- Some sources report a 22% female total workforce proportion.
- Tesla’s leadership, U.S., is more heavily male and White, reports cite ~83% male leadership and ~59% White leadership.
- Women held ~17% of director, VP roles in Tesla’s U.S. operations.
- Asian employees reportedly held ~25% of senior management roles versus ~21% of the overall workforce.
- Tesla’s UK gender pay report, 2023, shows female mean base pay ~2.6% higher than male average, median base pay ~1.1% lower.
Racial and Ethnic Diversity
- Tesla reports ~51.5% White, ~23.7% Hispanic, Latino, ~11.1% Asian, ~8.6% Black, in some aggregated data.
- In older U.S. DEI disclosures, Black, African American employees made up ~10% of the workforce, leadership proportion was ~4%.
- Hispanic, Latino employees held ~22% of U.S. roles per earlier reports, but lagged in management ranks, ~4%, at that time.
- Asian employees ~21% of the U.S. workforce in earlier Tesla reports, ~25% of leadership in those periods.
- Tesla’s first U.S. diversity report showed ~59% of leadership was White.
- Critics have pointed to the underrepresentation of Black employees in leadership and recurring discrimination lawsuits.
- Some Tesla commentary suggests the company intends to boost minority representation, but progress has been gradual.
Employees by Location
- Tesla’s U.S. operations, factories, offices, and service house a large share of its workforce; the international count is less transparent.
- Fremont, California, employs ~20,000+ staff at the vehicle assembly plant.
- Gigafactory Texas, Austin area, had ~21,191 employees in late 2024.
- In Berlin, Tesla’s Gigafactory employs ~11,500 people.
- Tesla’s Shanghai gigafactory likely employs many thousands, but I could not find a reliable recent count.
- Regions such as Germany, China, and Europe may have local R&D, engineering, and sales offices supporting local operations.
- Some manufacturing and battery plants, e.g., in Nevada, Germany, contribute to location-based staff.
- Tesla’s stake in the global workforce means the U.S. may still dominate in proportion, but precise percentages are not published.
Employee Tenure and Experience
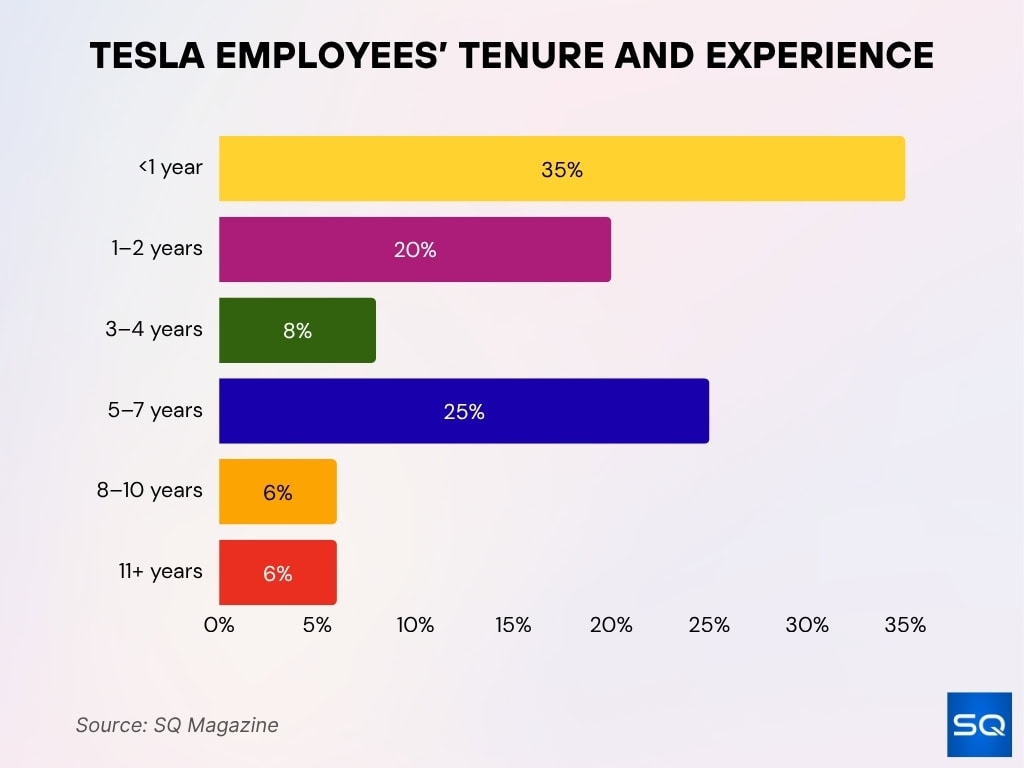
- The average Tesla employee tenure is 3.7 years.
- A plurality, ~35%, of employees stay less than 1 year.
- Percent breakdown by tenure brackets,
• <1 year: 35%.
• 1–2 years: 20%.
• 3–4 years: 8%.
• 5–7 years: 25%.
• 8–10 years: 6%.
• 11+ years: 6%.
Educational Background of Tesla Employees
- About 48.4% of Tesla employees hold a bachelor’s degree as their highest credential.
- 18.4% have a high school diploma as their top education level.
- 15.0% hold an associate degree.
- The most common major is business, accounting for ~22% of Tesla employees.
- Engineering majors also figure prominently, ~9.2% in electrical engineering and ~8.5% in mechanical.
- Tesla states that it does not require a college degree for many roles.
- Tesla offers tuition assistance, covering up to $5,250/year.
- Tesla’s Manufacturing Development Program allows high school graduates to begin career paths while gaining an education.
- Some job listings still expect bachelor’s or equivalent experience.
Revenue and Profit Per Employee
- Tesla’s revenue per employee is about $660,056.
- Alternate sources estimate $777,380 revenue per employee in 2024, up from ~$688,910 in 2023.
- Tesla registers ~$740,000 revenue per worker, placing it among the high‑efficiency peers.
- Tesla’s revenue per employee figure surpasses many traditional automakers.
- Data from Finbox shows Tesla’s total revenue per employee in recent years averaged ~0.62 million.
- Tesla’s productivity metrics are often cited in investment and valuation analyses.
- Profit per employee is less publicly broken out; margin levels and operating income must be applied to headcount for estimates.
- Because Tesla’s operations include energy, battery, infrastructure, and software, “per employee” metrics can mask internal variation across divisions.
Market Capitalization Per Employee
- Tesla’s market capitalization in 2025 is roughly $800 billion.
- With an employee count of ~125,665, this yields ~$6.4 million market cap per employee.
- In bull markets, this per‑employee figure can shift dramatically.
- Some equity analysts track this metric to compare capital intensity across sectors.
- Legacy automakers tend to have a lower market cap per employee due to lower margins.
- Tesla’s high market cap per employee reflects investor expectations in autonomy and energy.
- Market cap per employee does not reflect debt, liabilities, or capital equipment.
- If headcount declines, this ratio may improve, even if valuation declines.
Tesla’s Global Workforce Distribution
- Tesla’s reported global workforce in 2024 is 125,665 employees.
- Tesla operates major plants in the United States, China (Shanghai), Germany (Berlin), and other.
- U.S. revenue in 2024 totaled $47.73 billion, followed by China at $20.94 billion, and other countries at $29.02 billion
- Tesla manufacturing facilities span three continents: North America, Asia, and Europe.
- Some headcount estimation services suggest region and department breakdowns, but figures are not always verified.
- Tesla’s acquisition of Manz AG may expand the European staff.
- Workforce distribution shifts with plant expansion, supply chain localization, and geopolitical pressures.
H‑1B Visa Employees and Trends
- In FY 2024, Tesla had 742 approved H‑1B petitions for initial employment, up from 328 in FY 2023.
- The denial rate for new H‑1B petitions was about 2.5 % in 2024.
- Tesla had 1,025 approvals for continuing employment H‑1B petitions in 2024.
- In 2025, Tesla filed 2,475 LCAs for H‑1B, with 2,449 approved.
- Tesla’s cumulative LCAs from 2022 to 2024 totaled 4,854, and 523 green card certifications.
- A lawsuit in 2025 claims Tesla hired ~1,355 visa holders in 2024 while laying off over 6,000 U.S. workers.
- Tesla ranked 16th in new H‑1B approvals among U.S. companies in 2024.
Comparison With Previous Years
- 2023: 140,473 employees.
- 2024: 125,665 employees, a decline of ~10.54 %.
- 2024 layoff rounds cut approximately 14,000 jobs.
- Tesla’s headcount rose sharply between 2021–2023.
- Revenue per employee increased from ~$688,910 in 2023 to ~$777,380 in 2024.
- H‑1B filings increased year over year.
- 2024 reductions affected engineering, service, and infrastructure departments.
- The 2024 drop represents a pivot away from sustained growth.
- Market cap per employee was higher in 2023 due to a larger valuation and higher headcount.
- 2024 marks a turn toward cost control and consolidation after years of expansion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How many employees did Tesla have at the end of 2024?
Tesla eliminated approximately 10.54 % of its workforce in 2024.
Tesla’s headcount declined by 14,808 employees from 2023 to 2024
Some sources estimated Tesla had 121,858 employees by June 2024, reflecting a ~14% drop from December 2023.
Conclusion
Tesla’s workforce remains a dynamic reflection of its ambitions, challenges, and evolutionary path. From a headcount to increases in productivity, revenue per employee, and heightened reliance on H‑1B talent, Tesla’s employee metrics reveal much about its direction. The firm balances broad hiring flexibility, including non‑degree roles, with engineering rigor, global distribution, and intensive restructuring. As Tesla pursues electrification, autonomy, and energy expansion, the composition, location, and capabilities of its workforce will continue to shift in tandem.