In late 2024, a boutique digital marketing agency in Austin, Texas, experienced what seemed like a minor IT hiccup. Their systems froze for six hours. What they didn’t know was that a ransomware attack had quietly encrypted their data. Within 24 hours, the attacker demanded $25,000 in cryptocurrency. The firm, with under 15 employees and no dedicated IT department, had no option but to pay.
This isn’t a one-off tale. It’s a glimpse into a growing epidemic. As we move deeper into 2025, cyberattacks on small businesses are escalating in scale and sophistication, challenging the long-held belief that only large corporations are targeted. This article dives into the statistics that reveal the real scope of the problem and what small enterprises need to know now.
Editor’s Choice
- 61% of small businesses reported being the target of at least one cyberattack in the past 12 months.
- On average, a successful data breach costs a small business $164,000 in 2025.
- Ransomware attacks now account for 37% of all incidents affecting small businesses, an 8% increase year-over-year.
- Only 28% of small firms have a full-time cybersecurity expert or team.
- 45% of small businesses that suffer a cyberattack experience significant downtime, averaging 22 hours of disruption.
- Cloud-based systems were the entry point in 27% of breaches in 2025, especially among remote-first small firms.
- Alarmingly, 19% of small businesses affected by cyber incidents in 2025 had no backup or recovery plan in place.
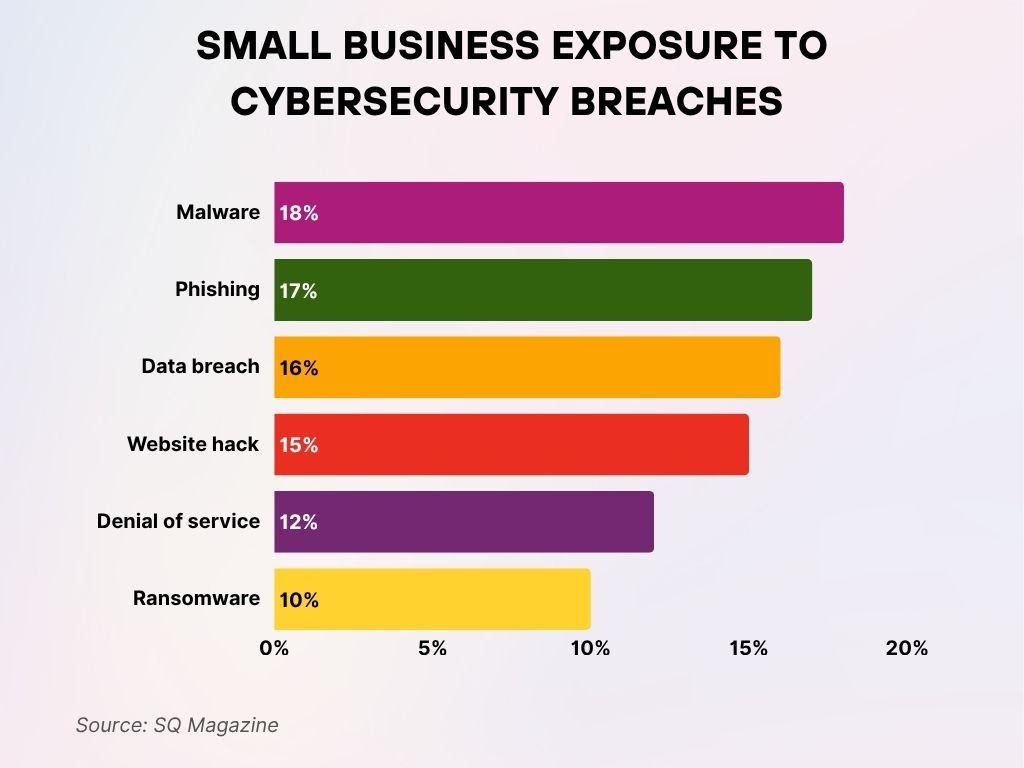
Small Business Exposure to Cybersecurity Breaches
- Malware is the top cybersecurity threat, impacting 18% of small businesses.
- Phishing attacks come close behind, affecting 17% of small businesses.
- Data breaches are a concern for 16% of small businesses, highlighting risks in data handling.
- Website hacks target 15% of small businesses, making site security a key priority.
- Denial of service (DoS) attacks disrupt operations for 12% of small businesses.
- Ransomware incidents impact 10% of small businesses, often leading to costly consequences.
Percentage of Small Businesses Targeted by Cyberattacks
- In 2025, over 6 in 10 small businesses in the U.S. reported experiencing some form of cyberattack.
- Businesses with fewer than 100 employees are now 2.5x more likely to be targeted than those with 500+ employees.
- Phishing remains the leading attack vector, affecting 42% of small firms.
- Compared to 2024, the incidence rate of cyberattacks on small businesses increased by 14%.
- Retail and healthcare small businesses reported the highest increase in targeting, with healthcare up 19%.
- Approximately 34% of cyberattack victims were repeat targets within the same 12-month period.
- Solo entrepreneurs and micro-enterprises (under 10 employees) accounted for 18% of all reported attacks.
- Startups under 2 years old reported an attack rate of 39%, reflecting their unprepared digital infrastructure.
- Veteran-owned small businesses showed a slightly lower target rate, attributed to higher policy compliance.
Financial Impact of Cyberattacks on Small Enterprises
- The average cost of a single cyber incident for small businesses reached $164,000 in 2025.
- Businesses lost an average of $29,000 in revenue due to downtime and disruption per attack.
- 22% of attacked small businesses reported customer churn as a direct result of breaches.
- Cyber insurance premiums rose by 13% in 2025, pricing out many micro-enterprises.
- Legal fees and compliance penalties from data breaches averaged $18,000 per case.
- Reputation repair and PR management costs averaged $7,500 per breach for U.S. small firms.
- Small healthcare businesses paid the highest average breach cost at $212,000, due to HIPAA compliance issues.
- Over 40% of affected small businesses took out loans or dipped into emergency funds to recover.
- Customer trust scores (measured by online reviews and NPS) dropped by 15% on average post-breach.
- Among firms that experienced a cyberattack in the past 18 months, 17% are no longer operating as of Q2 2025.
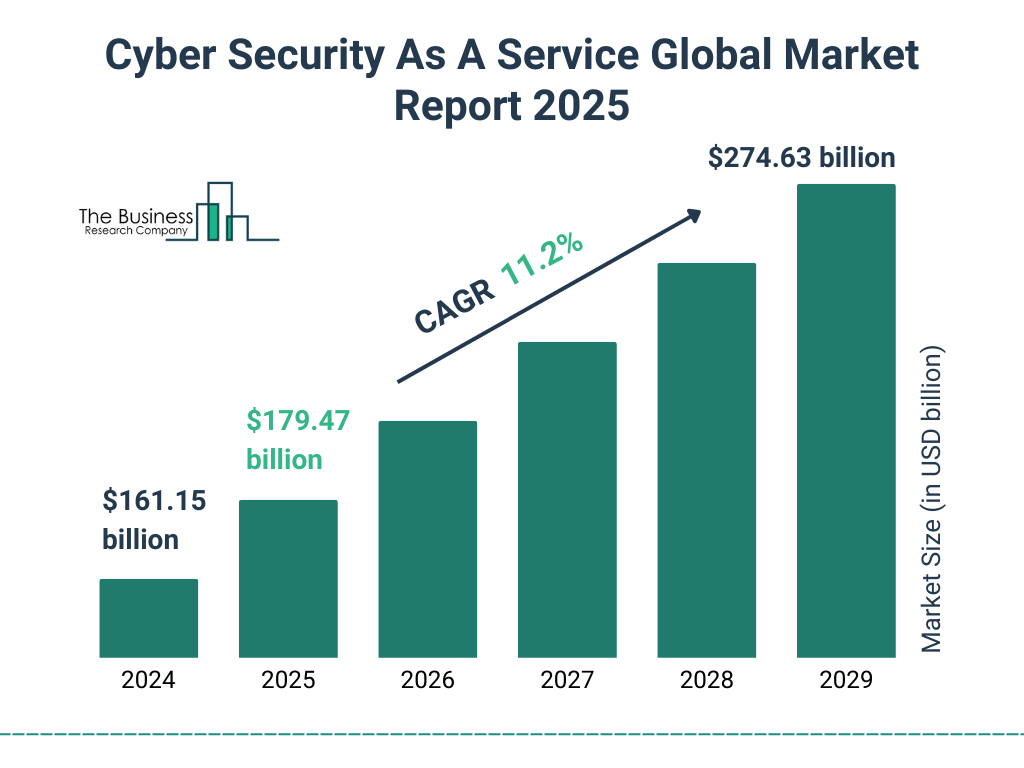
Cyber Security as a Service: Global Market Forecast
- The global market size for Cyber Security as a Service was $161.15 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to grow to $179.47 billion in 2025.
- The market is expected to expand at a CAGR of 11.2% through 2029.
- By 2029, the market is forecasted to reach $274.63 billion.
This growth reflects the rising demand for scalable, cloud-based security solutions across industries.
Ransomware Attacks and Small Business Vulnerability
- In 2025, ransomware impacted 37% of all small businesses.
- Average ransom demand reached $88,000, though some payments were negotiated down.
- 58% of small businesses that paid a ransom still faced partial or total data loss.
- Healthcare and financial services small businesses were the top sectors targeted by ransomware groups.
- Remote desktop protocol (RDP) exploits were involved in 21% of ransomware infections.
- Double extortion tactics, encrypting and threatening to leak data, were used in 66% of ransomware cases.
- Only 24% of small firms were able to fully recover their data without external recovery assistance.
- Backup systems were compromised in 18% of incidents, especially where backups were not air-gapped.
- The average business downtime due to ransomware reached 16.2 days in 2025.
- New ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) tools made it easier for low-skilled attackers to breach systems.
Employee-Related Cybersecurity Risks in Small Businesses
- In 2025, employee mistakes caused 41% of cybersecurity incidents in small enterprises.
- Poor password hygiene remains a top issue, with 68% of employees reusing passwords across platforms.
- Only 31% of small businesses conduct cybersecurity training more than once a year.
- Phishing simulation tests showed a 38% employee failure rate on average.
- Access mismanagement, such as excessive privileges, contributed to 14% of internal data leaks.
- Unsecured personal devices caused data leaks in 1 in 5 businesses with a BYOD policy.
- Shadow IT, use of unauthorized apps and tools, was detected in 43% of small businesses in 2025.
- Social media scams targeting employees increased by 21%, often impersonating HR or finance roles.
- Contractor or freelancer accounts were involved in 11% of breach incidents due to weak oversight.
- Only 17% of businesses use centralized identity and access management (IAM) systems.
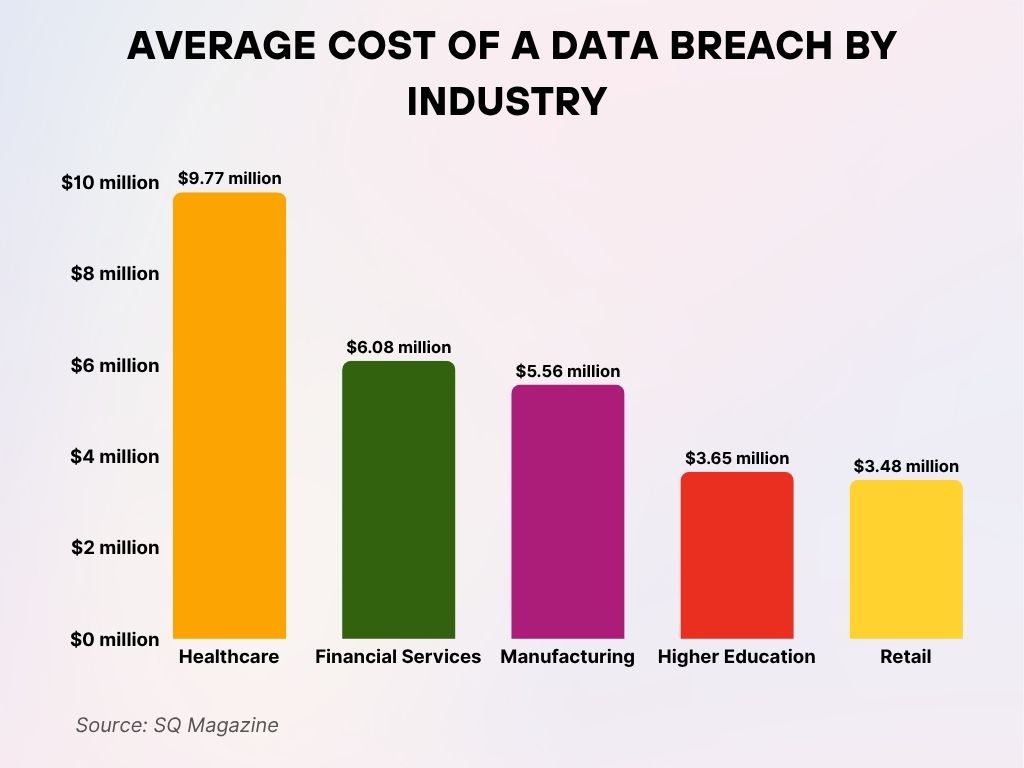
Average Cost of a Data Breach by Industry
- Healthcare faces the highest average cost per data breach at $9.77 million, reflecting the sensitivity of patient data.
- Financial Services follows with an average breach cost of $6.08 million, due to the high value of financial records.
- Manufacturing incurs an average loss of $5.56 million per breach, impacting operations and supply chains.
- Higher Education institutions see average breach costs of $3.65 million, with increasing threats to academic data.
- Retail ranks fifth, with an average breach cost of $3.48 million, often linked to compromised customer payment data.
Adoption Rates of Cybersecurity Measures Among Small Businesses
- As of 2025, only 34% of small businesses have a formal cybersecurity policy in place.
- Use of endpoint protection software stands at 61%, showing slight growth.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adoption among small firms increased to 47%.
- Firewall and network monitoring tools are used by just 29% of businesses with under 20 employees.
- Cybersecurity awareness training is conducted quarterly by only 9% of small businesses.
- Email filtering solutions are active in 42% of small firms to reduce phishing threats.
- Regular vulnerability scanning is performed by 22% of businesses, mostly those in regulated sectors.
- Only 1 in 5 small firms conducts annual penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks.
- Patch management protocols are lacking in 39% of businesses, with critical updates often delayed.
- Despite improvements, 26% of small firms still use unsupported or legacy software systems.
Role of Cloud Security in Small Business IT Environments
- In 2025, 71% of small businesses use cloud-based apps as part of their daily operations.
- 27% of data breaches in small businesses originated from misconfigured cloud settings.
- Cloud storage solutions like Google Drive and Dropbox were common entry points in phishing-led breaches.
- Shared credentials across cloud tools were found in 35% of audited security assessments.
- Unauthorized third-party integrations were responsible for 11% of cloud-related incidents.
- Only 22% of small businesses audit cloud access logs regularly.
- Cloud-based ransomware attacks have risen by 14%, often via email-linked file sync.
- Data sovereignty concerns prompted 19% of small firms to switch to region-specific cloud providers.
- Serverless environments, while scalable, presented new risks; 28% of breaches involved misconfigured permissions.
- Cloud access security broker (CASB) tools are used by just 6% of small businesses, mostly tech startups.
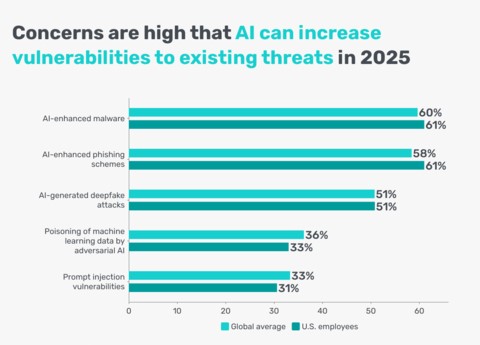
AI-Driven Cyber Threat Concerns
- AI-enhanced malware is the top concern, cited by 60% globally and 61% of U.S. employees.
- AI-enhanced phishing schemes worry 58% globally and 61% in the U.S., showing rising fears around deception technologies.
- AI-generated deepfake attacks raise alarm for 51% of both global and U.S. respondents.
- Poisoning of machine learning data by adversarial AI is a concern for 36% globally and 33% in the U.S..
- Prompt injection vulnerabilities are noted by 33% globally and 31% of U.S. employees.
Industry-Wise Breakdown of Cyberattack Frequency
- Healthcare small businesses top the list, with 65% reporting at least one breach in the past 12 months.
- Retail businesses followed closely at 59%, largely due to POS system vulnerabilities.
- Financial services SMEs were targeted in 57% of cases, mainly via email spoofing and credential theft.
- Legal and consulting firms saw a breach rate of 48%, often through document-sharing platforms.
- Construction and manufacturing firms had a 36% breach rate, with notable growth in supply chain attacks.
- Education and tutoring businesses experienced a 32% breach rate, often involving student data.
- Marketing and media firms were hit in 29% of cases, often through social media impersonation.
- Real estate agencies faced a 27% incident rate, commonly involving wire transfer fraud.
- Hospitality and small travel agencies reported cyberattacks in 24% of businesses, mostly targeting booking systems.
- Nonprofit organizations also saw a rise, with 31% experiencing attacks.
Insurance Coverage and Cyber Risk Management Practices
- In 2025, only 38% of small businesses carry cyber insurance, despite the rising risk landscape.
- Cyber insurance premiums rose by 13%, driven by increased claims from ransomware payouts.
- 47% of businesses with insurance filed a claim in the past 18 months.
- Of those, 62% received partial coverage, citing gaps in policy language and exclusions.
- Third-party liability coverage is included in only 29% of standard small business cyber policies.
- 14% of insured firms faced claim denial due to non-compliance with policy-mandated security practices.
- Cyber insurance bundling with general liability policies grew by 22% among small businesses in 2025.
- Risk assessments are conducted annually by only 18% of small firms, despite insurer recommendations.
- Premiums for businesses in healthcare and finance are typically 40% higher due to data sensitivity.
- Claims processing time averages 74 days, leading to financial strain for smaller firms awaiting reimbursement.
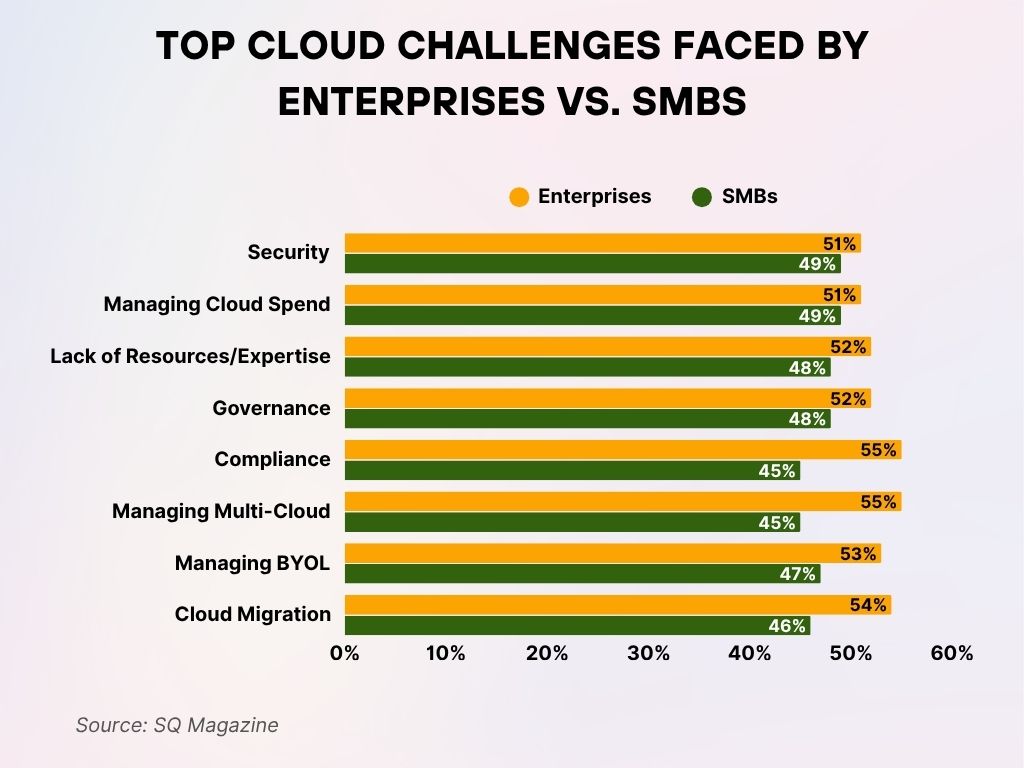
Top Cloud Challenges Faced by Enterprises vs. SMBs
- Security is the leading concern, with 51% of enterprises and 49% of SMBs identifying it as a top cloud challenge.
- Managing cloud spend equally challenges both groups, with 51% of enterprises and 49% of SMBs being split.
- Lack of resources or expertise is more pressing for enterprises (52%) compared to SMBs (48%).
- Governance issues are cited by 52% of enterprises versus 48% of SMBs.
- Compliance requirements pose greater difficulty for 55% of enterprises, while 45% of SMBs struggle similarly.
- Managing multi-cloud environments challenges 55% of enterprises and 45% of SMBs.
- BYOL (Bring Your Own License) is more of a concern for 53% of enterprises than for 47% of SMBs.
- Cloud migration remains a key issue, with 54% of enterprises and 46% of SMBs identifying it as a top hurdle.
Small Business Compliance with Cybersecurity Regulations
- In 2025, only 27% of small businesses claimed full compliance with applicable cybersecurity laws and frameworks.
- HIPAA compliance among small healthcare firms is at 51%, still lagging behind expectations.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) impacts 18% of U.S. small businesses directly.
- 23% of firms report confusion over whether they fall under GDPR compliance based on their clientele.
- Compliance fines averaged $8,900 per violation for noncompliant small businesses in the past year.
- PCI DSS compliance among small retail businesses dropped slightly to 58%, due to stricter authentication updates.
- New FTC Safeguards Rule updates in 2024 caused compliance expenses to spike by 19% in some sectors.
- Cybersecurity audits were conducted proactively by just 13% of small firms.
- Legal consultants specializing in data compliance were retained by only 6% of small businesses.
- Many businesses still treat compliance as a checkbox activity, rather than a proactive defense framework.
Impact of Remote Work on Small Business Cybersecurity
- As of 2025, 53% of small businesses maintain hybrid or fully remote work setups.
- Remote work security breaches increased by 17%, often due to unsecured home Wi-Fi networks.
- Use of personal devices for work contributed to 32% of security incidents.
- VPN usage among small businesses grew to 49%, though only 33% enforce mandatory use.
- Work-from-anywhere policies were exploited in 9% of breach incidents, involving geo-fencing blind spots.
- Remote access tools like TeamViewer and AnyDesk were linked to 7% of unauthorized access cases.
- Email phishing targeting remote workers spiked by 24%, often exploiting HR-related lures.
- Only 22% of remote employees use company-issued devices exclusively.
- Remote collaboration tools (Slack, Zoom, MS Teams) were involved in 12% of credential leaks.
- Employee cybersecurity awareness was significantly lower in remote teams not trained monthly.
Use of AI and Automation in Small Business Cyber Defense
- In 2025, 19% of small businesses use AI-driven cybersecurity tools.
- Automated threat detection systems reduced incident response time by 31% on average.
- AI-powered email filters blocked 3.8x more phishing emails than traditional rules-based systems.
- Behavioral analytics using machine learning is deployed by 8% of small businesses to flag anomalies.
- Chatbot impersonation and AI-generated phishing have increased attack sophistication by 22%.
- AI-enabled endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools are adopted in 13% of high-risk sectors like fintech.
- Cybersecurity automation platforms helped small teams cut labor hours by 42% on average.
- AI tools misclassified threats in 7% of cases, often leading to overlooked advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Automated compliance checks have been adopted by 6% of firms to meet regulatory standards more easily.
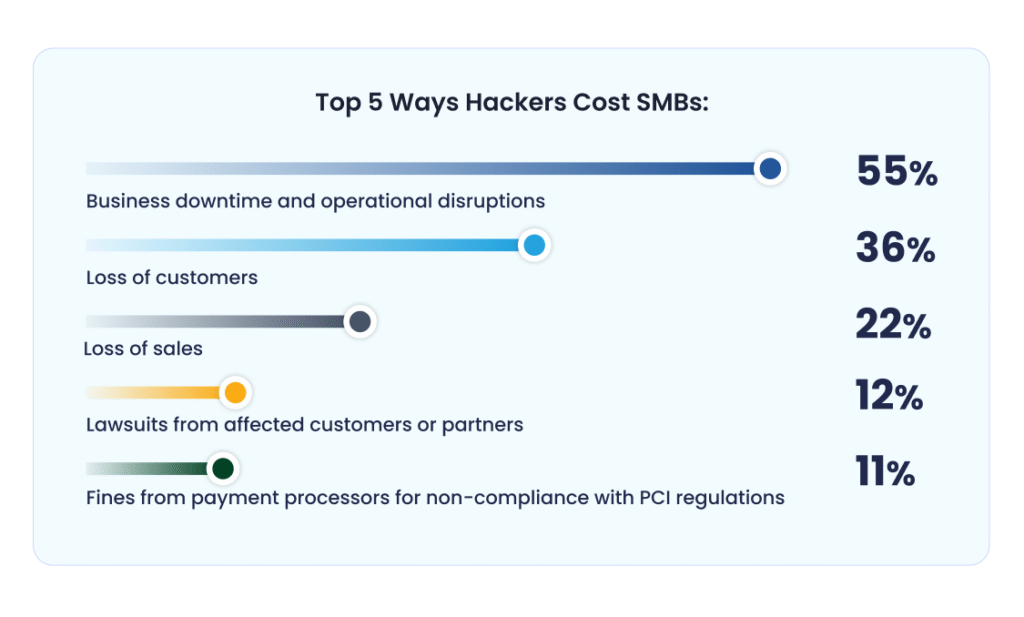
Top 5 Ways Hackers Financially Impact SMBs
- 55% of SMBs suffer from business downtime and operational disruptions after a cyberattack.
- 36% experience a loss of customers, damaging long-term business growth.
- 22% report a loss of sales, directly affecting revenue streams.
- 12% face lawsuits from affected customers or partners due to breaches.
- 11% incur fines from payment processors for failing to comply with PCI regulations.
Recent Developments in Small Business Cybersecurity
- Quantum-safe encryption trials have begun in select small healthcare and law firms.
- Zero-trust architecture is gaining traction, now used by 12% of small businesses.
- Cybersecurity as a service (CSaaS) offerings are growing, with adoption rates hitting 21% in Q2 2025.
- Microsoft’s Security Copilot is being piloted by small tech firms to detect and analyze threats faster.
- Passwordless authentication (e.g., biometrics, passkeys) was deployed in 17% of SMBs by mid-2025.
- State-funded cybersecurity grant programs supported over 9,000 small businesses in the U.S. in 2025.
- Decentralized identity solutions are being explored in fintech and legal startups.
- Collaboration between local governments and SMBs to establish community cyber-response protocols grew by 24%.
- Open-source cybersecurity tools like Snort and Zeek are increasingly used to avoid licensing costs.
- Virtual CISO (vCISO) services are now used by 16% of small firms that can’t afford full-time security leadership.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is no longer a concern just for enterprise IT departments. For small businesses in 2025, it’s a critical survival issue. Whether it’s the rising tide of ransomware, the persistent threat of phishing, or the growing complexity of remote work vulnerabilities, small businesses must treat cybersecurity as a foundational investment, not a luxury. With attack vectors evolving and compliance expectations tightening, small businesses that remain reactive rather than proactive may find the cost too steep, not just in dollars but in trust, continuity, and reputation.