Imagine waking up and the first thing your hand reaches for isn’t your glasses or a glass of water, but your phone. You’re not alone. For millions around the world, this daily reflex reflects a deeper digital entanglement that’s reshaping our routines, relationships, and realities. As we step into 2025, technology addiction has emerged not just as a buzzword but as a global concern. From compulsive scrolling to gaming marathons, this behavior is backed by rising statistics that demand our attention and action.
Editor’s Choice
- 42% of adults globally reported feeling anxious when separated from their smartphones in 2025.
- 63% of Gen Z users in the U.S. admit to spending more than 6 hours per day on social media platforms.
- 31% of teenagers experience sleep disruption due to late-night device usage.
- 52% of U.S. employees say digital distractions are affecting their productivity.
- 18% of global internet users meet the criteria for internet addiction as defined by the ICD-11 in 2025.
- 76% of parents express concern over their children’s screen time, especially on mobile devices and gaming consoles.
- 1 in 4 college students now exhibit signs of technology dependency, according to behavioral health screenings.
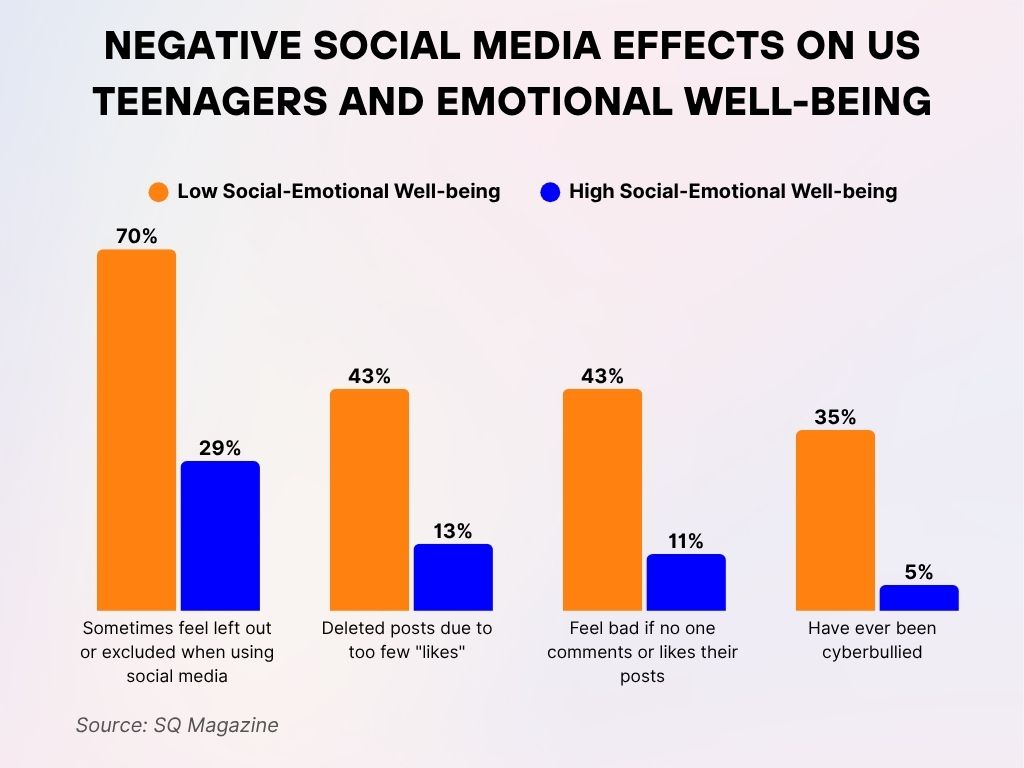
Negative Social Media Effects on US Teenagers and Emotional Well-Being
- 70% of teens with low social-emotional well-being said they feel left out or excluded when using social media, compared to 29% of teens with high emotional well-being.
- 43% of emotionally struggling teens have deleted posts because they received too few “likes”, versus just 13% of emotionally healthy teens.
- 43% of teens with low emotional well-being feel bad if no one likes or comments on their posts, while only 11% of their high emotional well-being peers feel the same.
- 35% of emotionally vulnerable teens have been cyberbullied, compared to only 5% of those with stronger emotional health.
Global Prevalence of Technology Addiction
- In 2025, approximately 1.08 billion people worldwide will be affected by some form of technology addiction.
- Asia accounts for the highest regional prevalence, with over 480 million reported cases.
- In the United States, nearly 19% of adults are identified as having moderate to severe digital dependency.
- Europe follows closely, with 16.5% of the population showing signs of problematic tech use.
- Brazil and India have seen a 9% year-over-year increase in digital addiction rates, driven by mobile gaming and video content.
- Technology addiction among urban populations globally is 28% higher than among rural counterparts.
- Women aged 18–34 have shown the fastest growth rate in daily screen time addiction, now averaging 7.3 hours per day.
- Australia reports a 12% increase in tech-related anxiety disorders compared to 2024.
- Global rehabilitation programs have reported a 21% increase in enrollments for technology-related behavioral issues.
Internet and Gaming Addiction Trends
- Online gaming addiction affected 9.5% of youth aged 10–18 globally in 2025.
- Massively multiplayer online games (MMOs) see the longest average session times, with players logging 3.7 hours per session.
- 47% of gamers report feeling irritable or anxious when unable to play.
- South Korea, China, and the United States top the list for most time spent on online games, averaging 6.3 hours/day.
- Women aged 25–34 represent the fastest-growing gaming demographic.
- Game streaming platforms like Twitch and Kick saw a 26% increase in daily viewers year-over-year.
- Mobile gaming now constitutes 58% of total gaming revenue globally, signaling increased accessibility and engagement.
- Virtual reality gaming participation increased by 22%, with overuse concerns emerging in younger players.
- In-game spending addiction rose, with 17% of teen gamers spending money impulsively on digital rewards.
- A UK survey found 12% of online gamers aged 18–24 have skipped meals or hygiene due to extended gameplay.
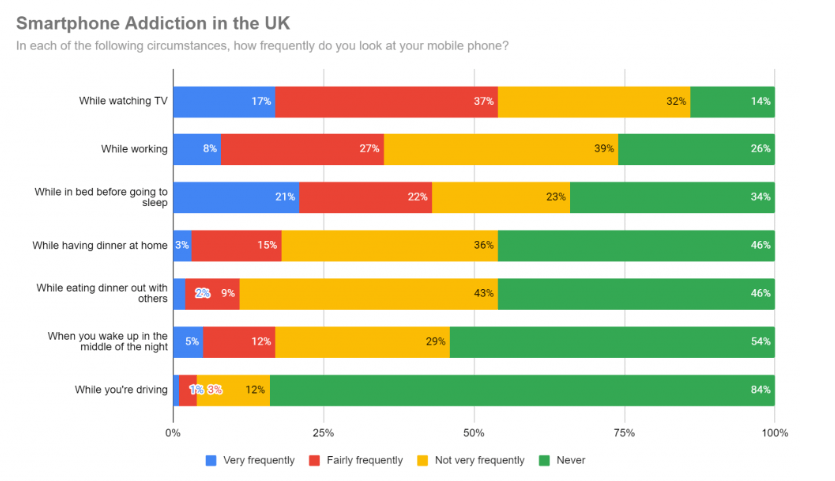
Smartphone Addiction in the UK: Usage Habits by Situation
- 54% of people never check their phones when they wake up in the middle of the night, but 5% still do very frequently.
- 84% say they never check their phones while driving, yet 1% do it very frequently and 3% fairly frequently.
- 46% of respondents never use phones while eating dinner, whether at home or with others, though 2–3% still do it very frequently.
- 34% say they always check their phones in bed before sleep (21% very frequently, 22% fairly frequently).
- While working, 35% (8% + 27%) check their phones frequently, while 26% say they never do.
- The most common time to use a phone is while watching TV, with 54% checking it very or fairly frequently.
Impact of Technology Addiction on Mental Health
- 52% of young adults report feeling “mentally drained” from digital overexposure.
- Tech fatigue syndrome, characterized by cognitive dulling and irritability, was cited in 23% of workplace wellness reports.
- Digital detox programs increased in enrollment by 37% in 2025.
- Social media overuse is linked to a 35% higher risk of anxiety and depressive symptoms in adolescents.
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out), driven by social platforms, affects 64% of Gen Z users regularly.
- Psychiatrists now list tech addiction among the top five behavioral health issues in urban populations.
- Blue light exposure is tied to delayed melatonin production, affecting sleep in 46% of nightly device users.
- Cyberbullying via apps caused 1 in 5 teenagers to experience emotional breakdowns in the past 12 months.
- Mental health apps saw a 40% rise in downloads, showing a self-awareness trend but also a screen paradox.
- Among professionals, 43% report burnout associated with being “always online” and unable to disconnect after work hours.
Technology Dependency Among Adolescents and Children
- 65% of children aged 6–12 in the U.S. use tablets or smartphones for more than 3 hours a day, excluding school-related activities.
- 41% of parents report that arguments over screen time occur daily in their households.
- Video platforms like YouTube Kids account for 43% of total screen time in children under 10.
- Teenagers aged 13–17 are spending an average of 7.6 hours per day on screens, not including educational usage.
- Screen time tracking apps usage by parents has increased by 33%, reflecting elevated oversight concerns.
- 1 in 5 adolescents shows signs of withdrawal, irritability, and restlessness when denied access to devices.
- Online learning platforms contributed to longer screen exposure, especially post-pandemic, with 29% of students using them beyond homework requirements.
- Gaming among minors has reached 4.5 hours/day on average, with multiplayer titles driving most of the engagement.
- 62% of middle school counselors** cite technology overuse as a major concern in student behavior and attention span issues.
- Digital reward systems in educational apps have led to increased compulsive behavior in 23% of users under 15.
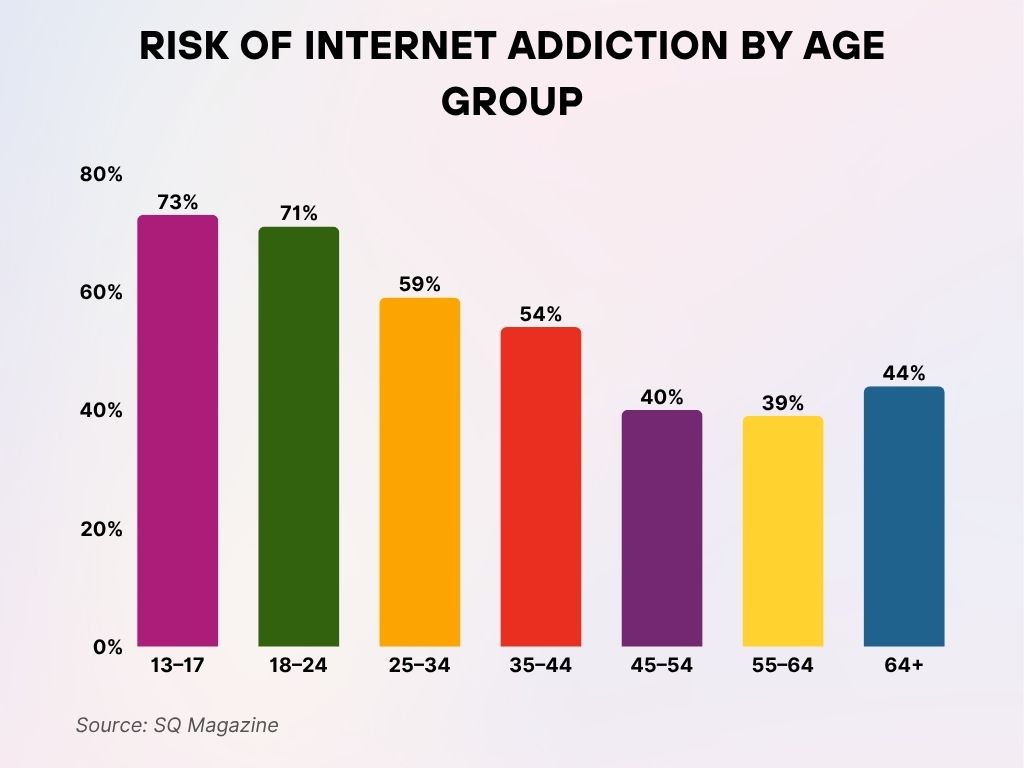
Risk of Internet Addiction by Age Group
- Teens aged 13–17 have the highest risk, with 73% at risk of internet addiction.
- 71% of young adults aged 18–24 are also highly vulnerable to developing addictive internet behavior.
- Among those aged 25–34, the risk stands at a notable 59%.
- 54% of individuals aged 35–44 face a significant risk of internet addiction.
- Risk levels begin to drop in older age groups, with 40% of those 45–54 and 39% of those 55–64 affected.
- Interestingly, 44% of adults aged 64+ still show signs of risk, indicating internet addiction isn’t limited to youth.
Workplace Productivity and Technology Overuse
- Digital distractions account for a 22% drop in productivity, according to U.S. workforce analytics in 2025.
- Smartphone use during meetings has increased by 31%, even in industries with strict device policies.
- 44% of employees report checking personal social media during work hours multiple times daily.
- Remote workers cite a 38% increase in multitasking between work apps and personal media.
- Virtual burnout, characterized by fatigue from constant video calls, affected 26% of remote professionals.
- Productivity apps and trackers have seen a 19% surge in usage, suggesting attempts to manage distractions.
- Instant messaging overload was the top complaint in HR reports, noted by 56% of employees.
- Tech breaks, like scheduled no-screen intervals, were implemented by 22% of companies in 2025 as part of wellness initiatives.
- Online procrastination costs U.S. businesses an estimated $98 billion annually.
- Millennials and Gen Z workers report higher stress levels due to the inability to disconnect from work tools outside business hours.
Screen Time by Region
- North America leads globally with an average screen time of 7.2 hours/day per user in 2025.
- Europe follows with an average of 6.5 hours/day, driven by remote work and digital media consumption.
- Asia-Pacific has the highest growth rate in screen usage.
- South Korea reports the highest per capita mobile device engagement globally, averaging 5.9 hours/day.
- In Africa, screen time remains relatively lower at 4.1 hours/day, though smartphone penetration is increasing.
- Latin America users average 6.2 hours/day, with Brazil leading regional usage trends.
- Middle Eastern countries show a 9% increase in video content streaming compared to 2024.
- Canada’s youth (ages 12–17) clock an average of 8.3 hours daily, the highest in its national history.
- Urban populations globally average 23% higher screen time than rural regions.
- Device multi-tasking (using multiple screens simultaneously) was most common in Japan and the U.S., with over 39% of users reporting regular behavior.
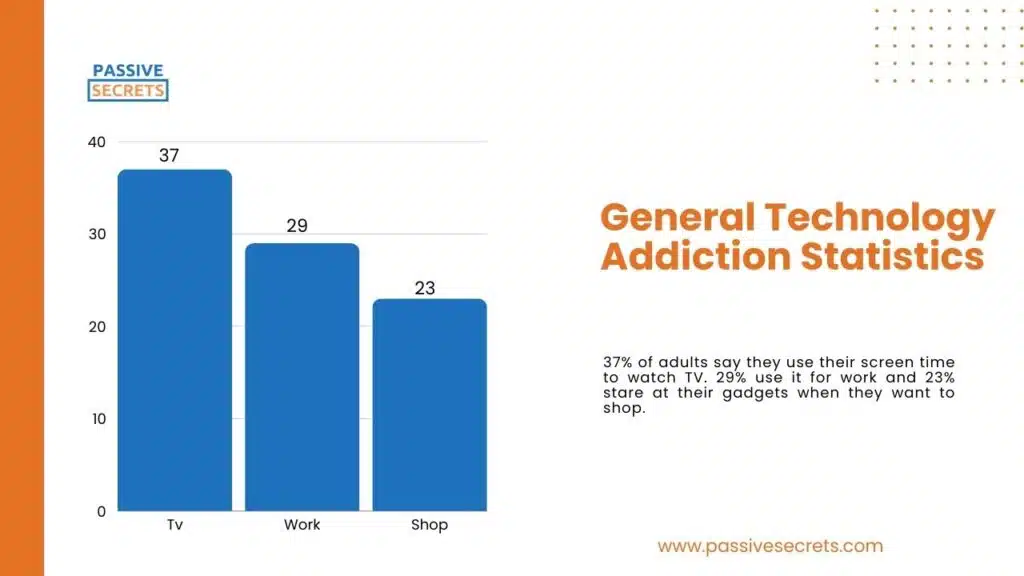
General Technology Addiction Usage
- 37% of adults say they primarily use their screen time to watch TV.
- 29% of adults use their devices mainly for work-related tasks.
- 23% of users admit they stare at their gadgets when they want to shop online.
Economic Costs of Technology Addiction
- The global economic impact of technology addiction in 2025 is estimated at $296 billion, including lost productivity and healthcare costs.
- U.S. companies alone face over $125 billion in annual losses due to tech-related inefficiencies.
- Healthcare costs for treating digital addiction symptoms in the U.S. crossed $3.1 billion.
- Employee turnover linked to digital burnout costs employers an estimated $27,000 per lost worker.
- Insurance claims related to mental health from tech overuse rose 17% year-over-year.
- Government-funded awareness programs against technology addiction received over $610 million globally in 2025.
- Youth rehab programs for digital addiction increased funding by 21%, with an average cost of $13,400 per treatment cycle.
- The average household in the U.S. spends $1,240 annually on mobile apps and digital subscriptions per person.
- Corporate wellness programs now allocate 23% of their mental health budgets to tech-related issues.
- Tech industry lobbying around screen time legislation has reached a record $92 million in 2025.
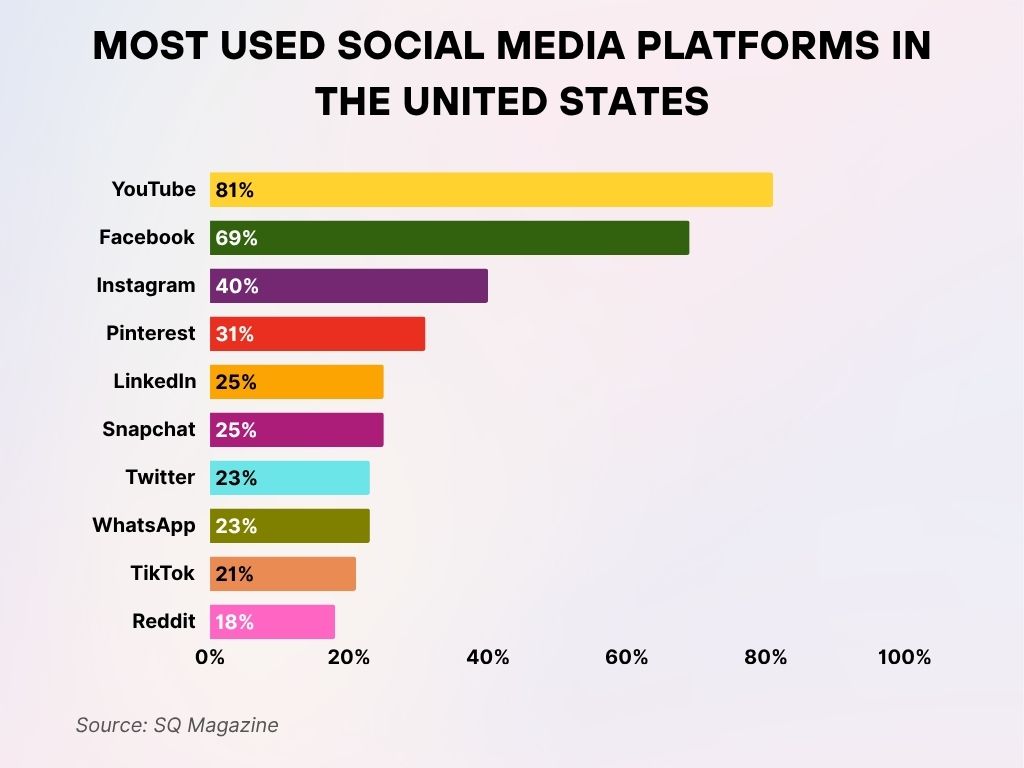
Most Used Social Media Platforms in the United States
- YouTube is the most used platform, with 81% of Americans actively using it.
- Facebook ranks second, used by 69% of the population.
- 40% of users are on Instagram, showing its strong popularity.
- Pinterest is used by 31%, especially favored for visual inspiration and shopping.
- Both LinkedIn and Snapchat have an equal user base of 25%.
- Twitter and WhatsApp each have a usage rate of 23% among US users.
- TikTok, despite its rapid growth, is used by 21% of Americans.
- Reddit rounds out the list with 18% usage.
Treatment and Intervention
- Digital addiction clinics in the U.S. have grown to over 420 facilities as of 2025.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) remains the most common treatment, used in 68% of digital dependency cases.
- App-based interventions like screen limiters and mindfulness prompts saw a 32% growth in user adoption.
- Online therapy platforms report a 26% increase in sessions dealing with tech-related stress.
- Family counseling referrals due to device overuse conflicts rose by 18%.
- School-based awareness programs are now mandated in 21 U.S. states.
- VR exposure therapy has shown promise, with a 60% success rate in reducing compulsive digital habits.
- Peer support groups for social media detox and gaming addiction are expanding rapidly, with thousands of new members weekly.
- Insurance coverage for technology addiction treatment is now offered by 34% of major U.S. health providers.
- Mindfulness training programs in schools and workplaces have increased by 42% as a proactive intervention tool.
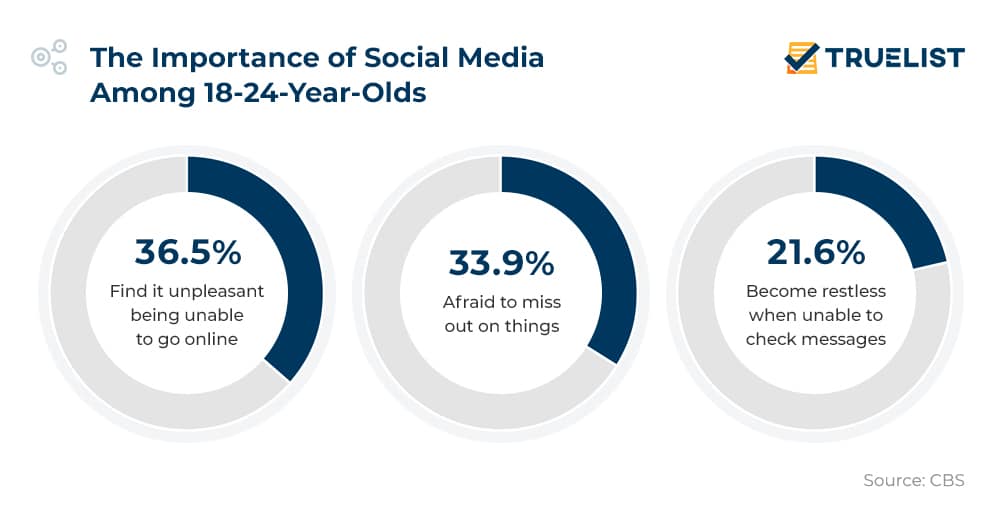
How Social Media Impacts 18–24-Year-Olds Emotionally
- 36.5% of young adults find it unpleasant when they’re unable to go online.
- 33.9% are afraid of missing out (FOMO) when not connected to social media.
- 21.6%become restless if they can’t check their messages.
Recent Developments in Technology Addiction Research
- A 2025 MIT study found that overuse of AI-generated content increases decision fatigue by 36%.
- Researchers identified dopamine spikes from social media scrolling similar to those from gambling in a study by Stanford.
- Neurofeedback tools are being tested for self-regulation of screen behavior, with early trials showing 47% efficacy.
- Wearable devices that track screen exposure are helping researchers measure tech-induced stress with greater accuracy.
- A Harvard study links compulsive app use with shortened attention spans in adolescents, down by 23% over the last decade.
- A multi-year project in Finland revealed that tech-free weekends improved emotional stability scores by 29%.
- Chatbot therapists are under ethical review, with concerns over their potential to enable, rather than reduce, device reliance.
- New genetic research indicates certain dopamine receptor variations may make individuals more prone to digital addiction.
- Interdisciplinary studies are now merging neuroscience, behavioral economics, and design to combat addictive tech patterns.
- AI content moderation tools are being explored to reduce exposure to harmful or compulsive-triggering digital material.
Conclusion
Technology addiction in 2025 is no longer a fringe concern; it’s a full-fledged public health, economic, and cultural issue. With nearly every age group affected in some way, addressing this problem requires a mix of personal awareness, educational outreach, workplace policy shifts, and scientific intervention. The data shows a world waking up to its screen time, but the question remains: will we take back control or continue scrolling?