It all started with a laptop on a kitchen table. One device, one user, and a Wi-Fi network not built for enterprise-grade security. Multiply that by millions, and you begin to grasp the scale of the remote work cybersecurity challenge. As the boundaries between home and work blur, so do the perimeters of digital defense. The shift was fast, the adjustment uneven, and the attackers noticed.
In 2025, cybersecurity isn’t just a concern for IT departments. It’s a boardroom priority, a workforce issue, and a frontline of digital survival. This article delves deep into the current statistics, trends, and threats defining remote work security today.
Editor’s Choice
- 78% of organizations reported at least one security incident linked to remote work in 2025.
- The average cost of a remote work-related breach in 2025 rose to $4.56 million.
- 60% of companies in 2025 cite phishing attacks as the top remote work threat vector.
- 73% of remote employees in 2025 use personal devices for work, many lacking enterprise-grade protection.
- 91% of U.S. companies will have adopted at least one form of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote access by 2025.
- 46% of surveyed IT leaders said their cybersecurity posture weakened due to hybrid and remote setups in 2025.
- 36% of businesses in 2025 increased their cybersecurity budgets specifically due to remote work risks.
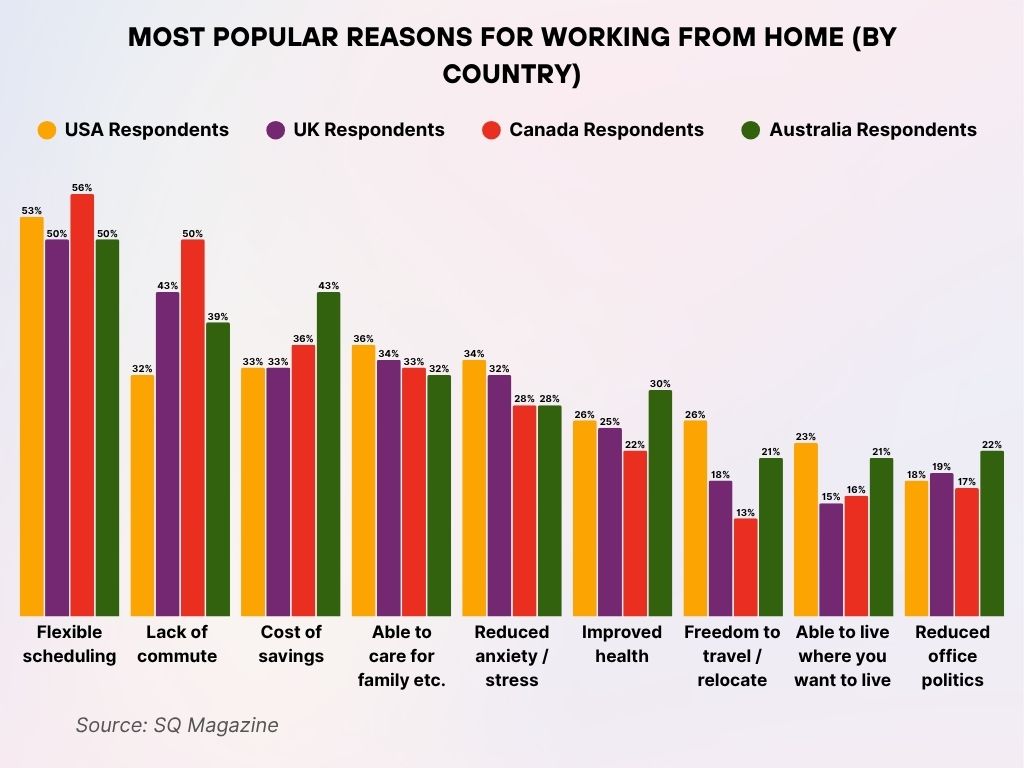
Most Popular Reasons for Working from Home (By Country)
- Flexible scheduling is the top benefit across all countries, especially in Canada (56%) and the USA (53%).
- Lack of commute is highly valued in Canada (50%), followed by the UK (43%) and Australia (39%).
- Cost savings resonate most in Australia (43%), compared to Canada (36%), while both the USA and UK report 33%.
- The ability to care for family, pets, or relatives is most important to USA respondents (36%), followed by the UK (34%).
- Reduced anxiety and stress are a notable factor for 34% in the USA, with both Canada and Australia at 28%.
- Improved health (mental, physical, or spiritual) is more emphasized in Australia (30%), ahead of the USA (26%).
- Freedom to travel or relocate is valued by 26% of Americans, while only 13% of Canadians see it as a key benefit.
- Living where you want appeals more to Australians (21%) and Americans (23%), compared to the UK (15%).
- Reduced office politics matters most to Australians (22%), whereas it’s less of a priority in Canada (17%) and the USA (18%).
Rise in Cybersecurity Threats Due to Remote Work
- 92% of IT professionals in 2025 believe remote work has increased cybersecurity threats.
- 38% of cyberattacks in 2025 targeted remote infrastructure specifically, including home routers and VPNs.
- 29% of all ransomware infections in 2025 started from endpoints used in remote environments.
- The average number of attempted remote work cyberattacks per month in 2025 reached 1,000 per organization.
- 54% of CISOs report a spike in credential theft incidents tied to remote access tools in 2025.
- 62% of security breaches exploited weak or stolen remote access credentials in 2025.
- 81% of companies now conduct quarterly risk assessments focused specifically on remote access points in 2025.
Most Common Cybersecurity Incidents in Remote Settings
- Phishing emails remain the most common remote work attack vector in 2025, responsible for 43% of initial breach attempts.
- Unpatched personal devices accounted for 22% of endpoint vulnerabilities exploited in 2025.
- Misconfigured VPNs led to 14% of data leaks in remote work environments in 2025.
- Drive-by downloads from unsecured websites caused 9% of malware infections among remote workers in 2025.
- Remote desktop protocol (RDP) misuse resulted in 11% of unauthorized access incidents in 2025.
- Cloud misconfigurations contributed to 17% of all remote work security events in 2025.
- Social engineering attacks outside phishing, such as voice phishing (vishing), saw a 23% increase in 2025.
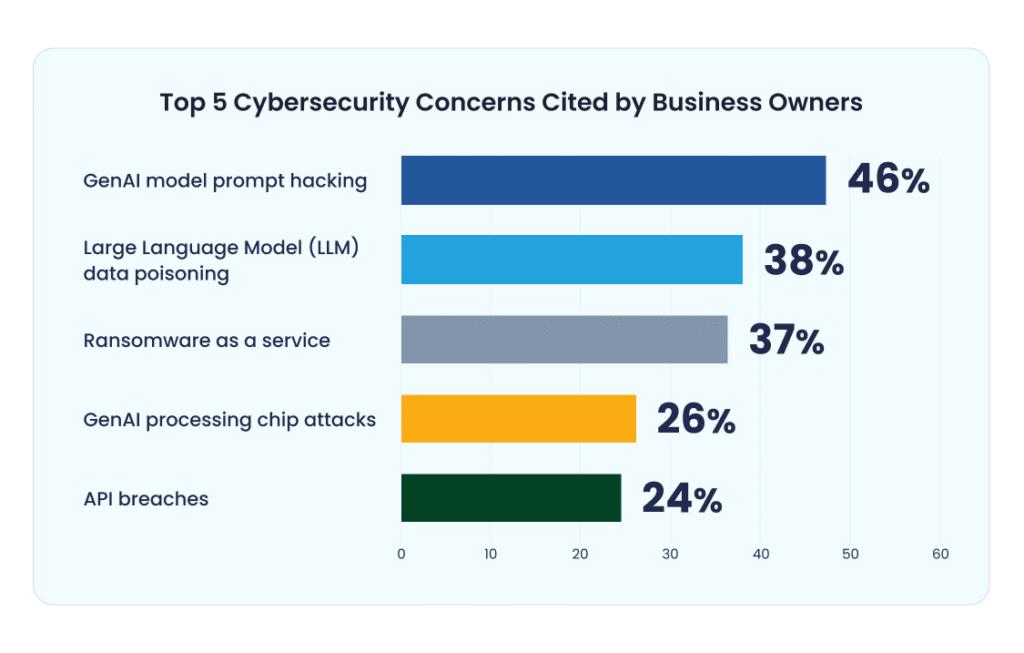
Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- 46% of business owners are concerned about GenAI model prompt hacking, making it the top cybersecurity threat.
- 38% cited Large Language Model (LLM) data poisoning as a major risk to AI-driven systems.
- 37% are worried about Ransomware as a service, reflecting ongoing concerns around evolving cybercrime business models.
- 26% fear GenAI processing chip attacks, highlighting hardware vulnerabilities in AI infrastructure.
- 24% consider API breaches a notable risk, emphasizing the importance of securing integration points.
Remote Work Impact on Corporate Network Vulnerabilities
- 57% of enterprise networks showed increased exposure to vulnerabilities due to remote access in 2025.
- Corporate firewalls are bypassed in 49% of remote connections, exposing internal systems directly to the internet.
- Shadow IT devices grew by 31% in 2025, expanding the unknown surface area vulnerable to attack.
- VPN overloads and downtime contributed to 12% of network disruptions in 2025, leading to exploitable gaps.
- Lateral movement inside corporate networks became 18% more common due to remote entry points in 2025.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities discovered in remote work tools rose by 15% year-over-year in 2025.
- 47% of CIOs reported delays in patch management for systems accessed remotely in 2025.
Cost of Cybersecurity Breaches Related to Remote Work
- The average cost of a breach involving a remote worker in 2025 is $4.56 million.
- Breaches involving remote infrastructure took 58 days longer to contain on average in 2025.
- Regulatory fines stemming from remote work data mishandling grew by 21% in 2025.
- Data loss per breach averaged 22,000 records in 2025.
- Legal expenses tied to remote-related breaches reached a median of $410,000 per incident in 2025.
- Cyber insurance claims for remote work incidents increased by 39% year-over-year in 2025.
- 74% of organizations reported customer trust impact after remote-related security incidents in 2025.
- 37% of remote breaches led to secondary attacks due to inadequate response strategies in 2025.
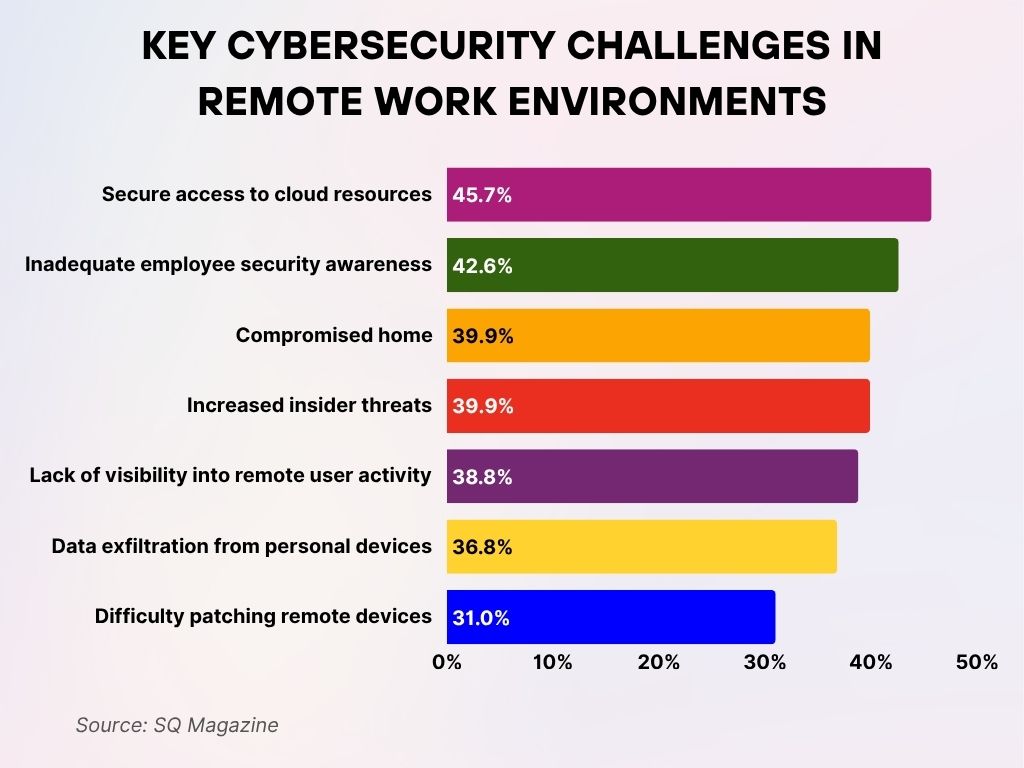
Key Cybersecurity Challenges in Remote Work Environments
- 45.7% of organizations struggle with secure access to cloud resources, making it the most cited challenge in remote work setups.
42.6% report issues due to inadequate employee security awareness, exposing vulnerabilities through human error. - 39.9% face risks from compromised home networks, where security controls are weaker than in-office environments.
- 39.9% also cite increased insider threats, underscoring trust and monitoring concerns in dispersed teams.
- 38.8% mention a lack of visibility into remote user activity, hindering threat detection and response.
- 36.8% are concerned about data exfiltration from personal devices, as employees mix work and personal tech.
- 31.0% struggle with difficulty patching remote devices, delaying critical security updates across remote endpoints.
How Remote Working Led to the Increase in Shadow IT Environments
- 61% of IT leaders in 2025 said shadow IT has increased since the remote shift began.
- 35% of employees in 2025 admit to using unapproved applications for work-related tasks.
- 23% of data breaches in 2025 involved unauthorized cloud platforms introduced by staff.
- File-sharing apps not vetted by IT were in use in 42% of remote teams by 2025.
- Shadow SaaS tools grew by 28% year-over-year due to the decentralization of tech stacks in 2025.
- 67% of remote workers said convenience outweighs security when selecting tools in 2025.
- 19% of organizations uncovered high-risk shadow IT activity during annual audits in 2025.
- Slack bots, browser extensions, and unauthorized APIs contributed to 16% of security alerts in 2025.
Percentage of Companies Updating Security Policies Post-Remote Shift
- 84% of organizations revised their cybersecurity policies to address remote work by 2025.
- 57% of these updates included formal bring-your-own-device (BYOD) frameworks.
- 41% added or expanded zero trust architecture guidelines in 2025.
- 63% created new training protocols specifically for home office security by 2025.
- 28% now require remote workers to pass annual cybersecurity compliance tests.
- 46% of companies introduced new incident response procedures tailored for remote threats.
- 22% of updates focused on third-party risk linked to remote collaboration tools in 2025.
- Cyber insurance policy revisions due to remote work were implemented by 31% of firms in 2025.
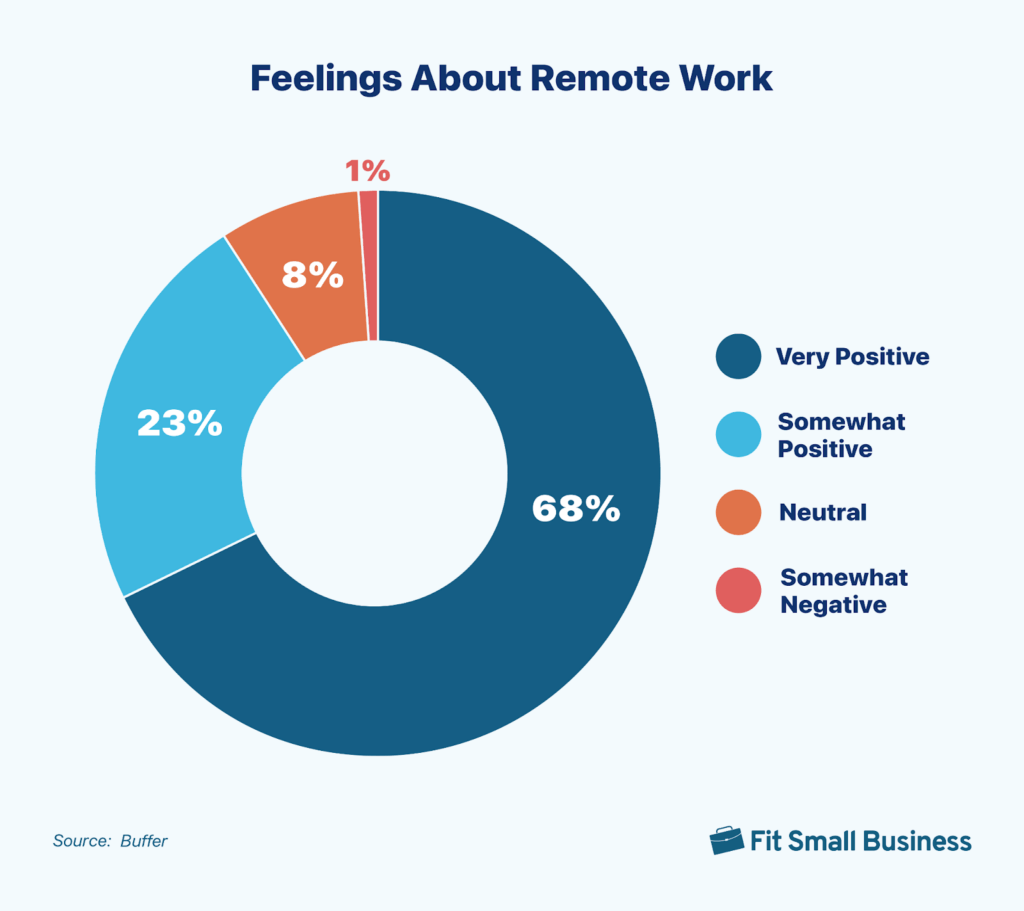
Employee Sentiments Toward Remote Work
- 68% of respondents feel very positive about remote work, indicating overwhelming support.
- 23% reported somewhat positive experiences, showing general satisfaction with minor reservations.
- 8% feel neutral, suggesting no strong opinion either way.
- Only 1% view remote work somewhat negatively, reflecting minimal dissatisfaction.
Adoption Rates of VPNs, Zero Trust, and MFA for Remote Employees
- 91% of businesses deployed multi-factor authentication (MFA) for remote systems in 2025.
- 78% adopted VPNs organization-wide for remote access protection in 2025.
- 63% of large enterprises implemented a zero-trust framework to support secure remote work.
- 32% of mid-sized companies adopted cloud-native security tools, replacing traditional VPNs.
- 49% of organizations using VPNs reported concerns over scalability and latency in 2025.
- 69% of firms said endpoint verification was central to their 2025 zero trust strategy.
- 25% of security teams use software-defined perimeters (SDPs) instead of legacy firewalls for remote access.
- 36% of businesses upgraded their identity and access management (IAM) platforms in 2025.
Employee Cybersecurity Training and Awareness
- 58% of remote workers in 2025 received formal cybersecurity training in the past 12 months.
- 41% of phishing simulation campaigns had a click rate over 15%, indicating persistent risk in 2025.
- 73% of companies conduct mandatory cybersecurity refreshers every 6 months for remote teams.
- 19% of employees admitted to sharing work passwords with family or friends in 2025.
- 29% failed basic awareness tests on phishing and data handling policies in 2025.
- Gamified training modules improved retention rates by 23% compared to passive learning in 2025.
- 47% of employees said cybersecurity training helped them avoid real threats in 2025.
- Cyber hygiene habits, such as regular software updates and strong password use, rose by 18% among trained staff in 2025.
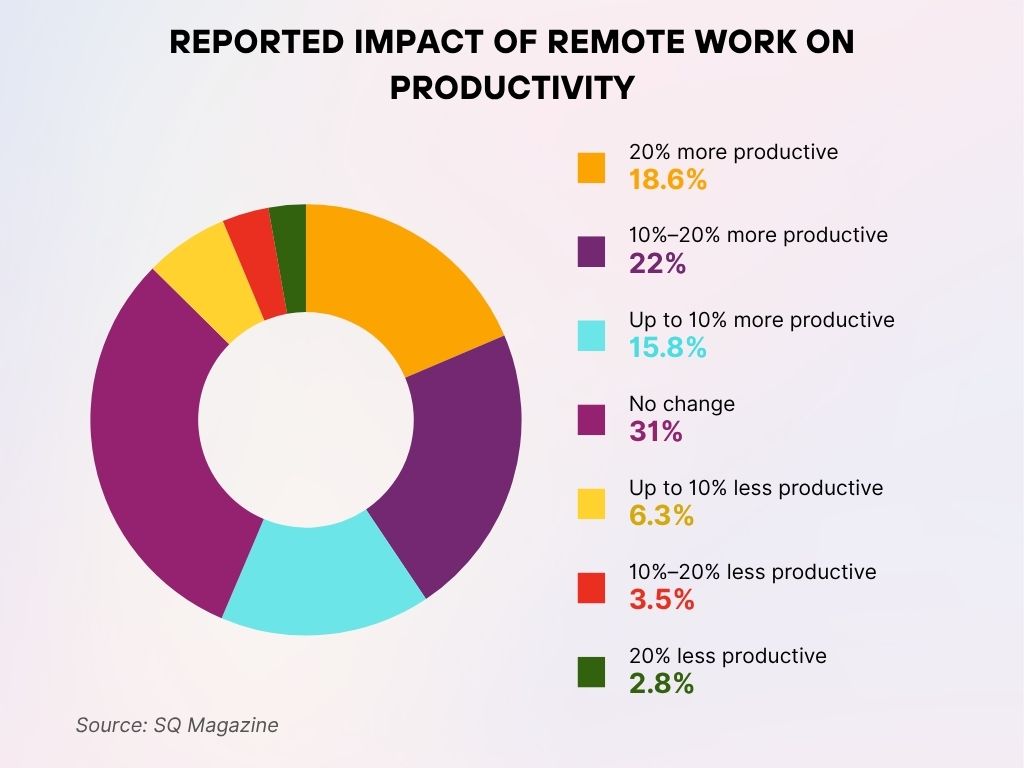
Reported Impact of Remote Work on Productivity
- 31% of professionals reported no change in productivity since switching to remote work.
- 22% said they became 10%–20% more productive, showing a moderate boost.
- 18.6% experienced a 20% increase in productivity, a strong positive impact.
- 15.8% noted up to 10% more productivity, indicating smaller gains.
- 6.3% felt up to 10% less productive, showing mild declines.
- 3.5% reported a 10%–20% drop in productivity.
- 2.8% experienced a significant decline, becoming 20% less productive.
Industries Most Affected by Remote Work Cyber Threats
- The financial services sector saw the highest incident rate, with 74% reporting breaches linked to remote work in 2025.
- Healthcare organizations faced a 63% rise in endpoint security breaches tied to telehealth and remote workforces.
- Technology firms experienced 29% of total ransomware cases originating from remote employees in 2025.
- Educational institutions reported a 34% increase in phishing attacks targeting remote faculty and students.
- Retail and e-commerce experienced a 21% surge in card skimming and session hijacking attacks in 2025.
- Legal and professional services firms identified data leakage as the most prevalent threat, affecting 49% of respondents.
- Manufacturing companies with remote-capable roles reported a 27% vulnerability increase in their supply chains.
- Government agencies saw 22% of their cybersecurity incidents traced to home-based endpoints and third-party access.
Role of Personal Devices in Remote Work Security Risks
- 73% of remote employees in 2025 use personal devices for work-related tasks at least once per week.
- Only 38% of organizations enforce mobile device management (MDM) on employee-owned hardware.
- 44% of security breaches in 2025 involved unmanaged personal devices.
- 23% of surveyed workers in 2025 admitted to disabling antivirus software on personal laptops used for work.
- 14% of infected endpoints in 2025 were traced to shared home devices accessed by family members.
- 65% of CIOs rated personal devices as their highest-risk asset class in the remote work environment.
- Biometric authentication adoption on personal work devices increased by 19% in 2025.
- 34% of organizations now offer subsidies or stipends for employees to purchase secure devices.
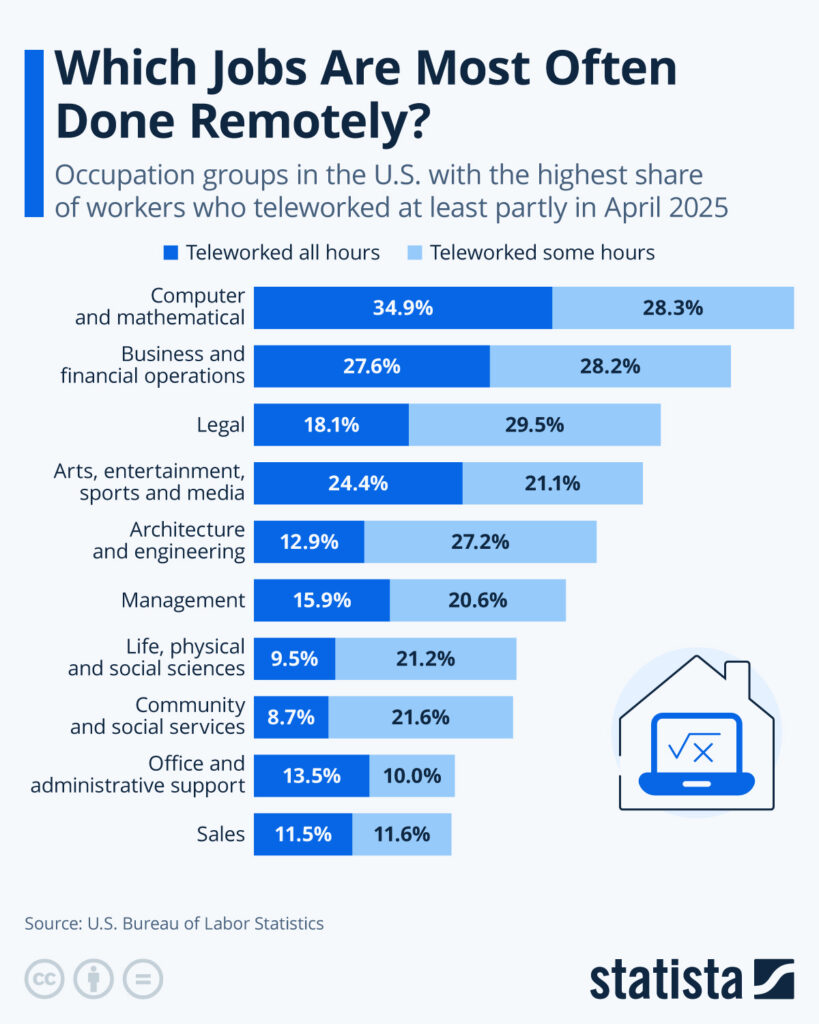
Jobs Most Frequently Done Remotely in the U.S.
- Computer and mathematical roles lead in remote work, with 34.9% teleworking all hours and 28.3% for some hours.
- Business and financial operations follow closely: 27.6% worked all hours remotely, and 28.2% for some hours.
- Legal occupations saw 18.1% working fully remote, and 29.5% for some hours, the highest partial telework rate.
- In arts, entertainment, sports, and media, 24.4% worked fully remotely, with 21.1% doing so part-time.
- Architecture and engineering professionals reported 12.9% full remote work and 27.2% part-time.
- Management roles show a split: 15.9% full-time remote, 20.6% part-time.
- Life, physical, and social sciences reported 9.5% fully remote and 21.2% partially.
- Community and social services had 8.7% full remote work and 21.6% partial, a strong presence despite being a people-centric field.
- Office and administrative support roles saw only 13.5% fully remote, with just 10.0% working partially.
- Sales had the lowest figures: 11.5% fully remote and 11.6% partially.
Cloud Security Concerns for Remote Teams
- 89% of organizations said cloud applications are critical to remote work but pose ongoing security risks.
- Misconfigured access controls in cloud systems were the root cause of 24% of breaches in 2025.
- 51% of IT managers reported difficulty monitoring data flows across remote team cloud tools.
- Unauthorized file sharing via cloud platforms contributed to 17% of data exposure incidents.
- Third-party integrations within cloud ecosystems caused 13% of indirect access breaches in 2025.
- Data residency compliance issues affected 28% of U.S. companies using international cloud providers.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools saw a 32% increase in deployment to manage remote setups.
- Shadow cloud accounts, untracked logins to services like Google Drive, grew by 26% in 2025.
Compliance and Regulatory Trends in Remote Cybersecurity
- 71% of U.S. firms reported new compliance requirements affecting their remote work policies in 2025.
- GDPR enforcement actions related to remote data handling increased by 15% among U.S.-EU operations.
- CISA guidelines in 2025 now explicitly mandate remote endpoint monitoring for federal contractors.
- State-level privacy laws, such as California’s CPRA, impacted 43% of U.S. companies’ remote compliance practices.
- PCI-DSS 4.0 updates in 2025 require additional controls for remote payment processing environments.
- SOX audits flagged 24% more remote system access violations.
- 32% of U.S. companies underwent remote-specific compliance assessments from third-party auditors.
- 21% faced penalties due to improper cloud and VPN logging during security investigations.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Workforces
- Zero trust adoption became a cornerstone of remote strategy for 63% of firms in 2025.
- Mandatory MFA was enforced by 91% of companies for all remote access endpoints.
- Regular patching cycles (weekly or biweekly) were adopted by 44% of remote-first organizations.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions were deployed across 57% of remote fleets.
- Phishing simulations and gamified training were used by 76% of businesses to improve awareness.
- Secure browser-based environments, like virtual desktops, gained a 34% market share for remote users.
- IT asset inventory tracking was a top priority for 58% of security leaders managing hybrid setups.
- User behavior analytics (UBA) were introduced by 39% of firms to identify insider threats in real-time.
Recent Developments in Remote Work Cybersecurity
- AI-based threat detection tools for remote endpoints grew in adoption by 46% in 2025.
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) implementations surged by 35% to streamline remote network security.
- Cloud-native SIEM platforms now handle remote log analysis for 62% of mid-to-large enterprises.
- Work-from-anywhere models accelerated demand for location-independent IAM by 31%.
- Quantum-resilient encryption trials began in 11% of high-security organizations in 2025.
- Home office hardware tokens, such as FIDO2 keys, gained traction in 28% of remote workforces.
- Continuous authentication technologies, including keystroke biometrics, entered pilot phases in 19% of large firms.
Conclusion
Remote work has permanently changed the cybersecurity landscape. With expanded threat surfaces, shadow IT growth, and evolving attack vectors, organizations must rethink how they secure distributed teams. The 2025 statistics are clear: proactive defense, policy evolution, and employee education are no longer optional; they’re survival tools. Cybersecurity leaders who adapt with speed and rigor will define the resilience of tomorrow’s remote-first enterprises.