Phishing and wallet drainer attacks have emerged as major threats in the evolving landscape of cybercrime. These attacks not only intensified but also diversified across multiple platforms and threat vectors, targeting both individuals and organizations. Industries such as cryptocurrency exchanges and financial services continue to face mounting losses due to sophisticated phishing lures and automated wallet drainers.
As wallet technologies and phishing kits become more accessible, the risk landscape expands rapidly. This article explores the latest statistics and trends shaping the phishing and wallet draining ecosystem, offering a data-driven snapshot of the current threat environment.
Editor’s Choice
- $1.93 billion in cryptocurrency was stolen through wallet drainers and phishing scams in the first half of 2025 alone.
- Phishing attacks have increased by 31% year-over-year, with wallet-specific lures targeting DeFi and NFT users.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams in 2025 average $4.67 million in losses per attack.
- AI-generated phishing emails saw a 70% increase in 2025, bypassing traditional filters with higher success rates.
- Voice phishing or vishing surged by 449%, indicating the rise of voice-based social engineering scams.
- Over 38% of BEC phishing emails originated from U.S.-based IP addresses in Q3 2025.
- The average cryptocurrency wallet drainer attack leads to losses between $2,000 and $35,000 per victim.
Recent Developments
- Phishing incidents increased by 31% globally in the first half of 2025 compared to the same period in 2024.
- Over 1 million phishing websites were detected in Q1 2025 alone, up from 850,000 in Q4 2024.
- AI-generated phishing content is now involved in more than 17% of phishing campaigns, making detection harder.
- Deepfake videos and synthetic voice calls are increasingly being used in phishing campaigns, particularly in executive impersonation attacks.
- In April 2025, MetaMask users reported more than $10 million in wallet thefts from phishing sites posing as DeFi tools.
- According to blockchain analysis firms, wallet drainer kits were responsible for over $400 million in losses in early 2025.
- Quishing (QR code phishing) attacks grew by 28% as more attackers leveraged mobile-first interfaces.
- Microsoft 365 accounts are frequently targeted, with credential phishing responsible for 60% of account takeovers.
- Telegram, Discord, and other messaging platforms are being used to disseminate phishing links and wallet drainer payloads.
- Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) kits on the dark web have proliferated, making it easier for low-skilled actors to deploy wallet drainers.
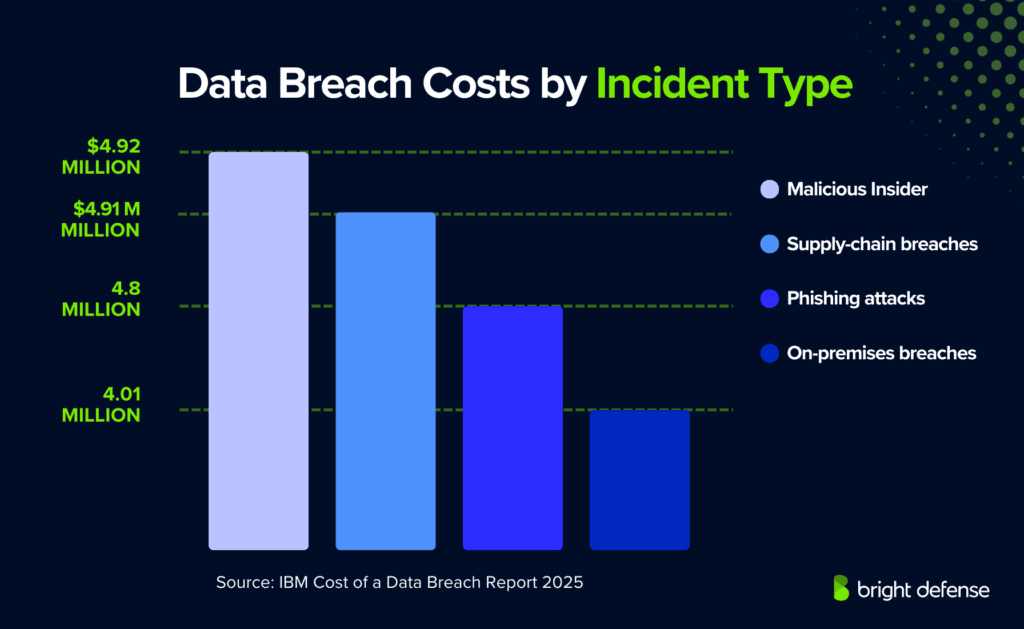
Data Breach Costs by Incident Type
- Malicious Insider breaches are the most expensive, averaging $4.92 million per incident.
- Supply-chain breaches closely follow at $4.91 million, highlighting elevated third-party risk exposure.
- Phishing attacks cost organizations an average of $4.80 million per breach.
- On-premises breaches remain the least costly yet significant, averaging $4.01 million per incident.
Wallet Drainer Losses
- $1.93 billion in total wallet drainer-related thefts were reported in H1 2025, spanning phishing, malware, and malicious approvals.
- In a single coordinated attack in May 2025, over $60 million in ETH and tokens were drained from users of a popular DeFi platform.
- Phishing links leading to fake MetaMask and Trust Wallet sites caused over $150 million in confirmed losses this year.
- Attackers used fake Discord servers and Telegram groups to mimic legitimate projects, resulting in $72 million in wallet approvals.
- Wallet drainers are now integrated into malicious browser extensions, which caused over $40 million in thefts by June 2025.
- Drainer malware kits are available for as low as $300 on cybercrime forums, democratizing wallet theft capabilities.
- NFT marketplaces were specifically targeted, with $96 million in stolen digital assets tied to phishing drainers in Q1 and Q2 2025.
- Malicious pop-ups imitating wallet connection dialogs drained user assets in over 132 confirmed incidents by mid-year.
- Over 42% of phishing-related crypto losses in 2025 were traced to drainer scripts embedded in fake token airdrop sites.
- The average time from wallet approval to fund loss is under 32 seconds, emphasizing the automation behind drainer tools.
Financial Impact
- The average victim of a phishing-based wallet drainer lost $2,400, while targeted attacks on high-value wallets surpassed $250,000.
- Losses attributed to BEC and phishing scams in the U.S. exceeded $16 billion in 2024 and are projected to surpass $20 billion in 2025.
- Nearly 22% of all cyber insurance claims in 2025 involved phishing or wallet draining as the root cause.
- Cryptocurrency scams, including wallet drainers, account for 63% of total financial cybercrime incidents reported this year.
- Global phishing-related financial losses have surpassed $24 billion in 2025, according to preliminary industry estimates.
- In corporate environments, phishing-linked credential theft caused $4.1 million in operational downtime on average.
- Financial institutions reported a 19% increase in unauthorized crypto transactions, much of it tied to phishing attacks.
- Over 5,100 complaints related to unauthorized wallet access were filed with U.S. law enforcement in the first half of 2025.
- Credential theft losses increased by 160% compared to 2024, correlating with phishing campaign surges.
- Recovery rates from phishing-based financial losses remain below 17%, with cryptocurrency theft among the hardest to reclaim.
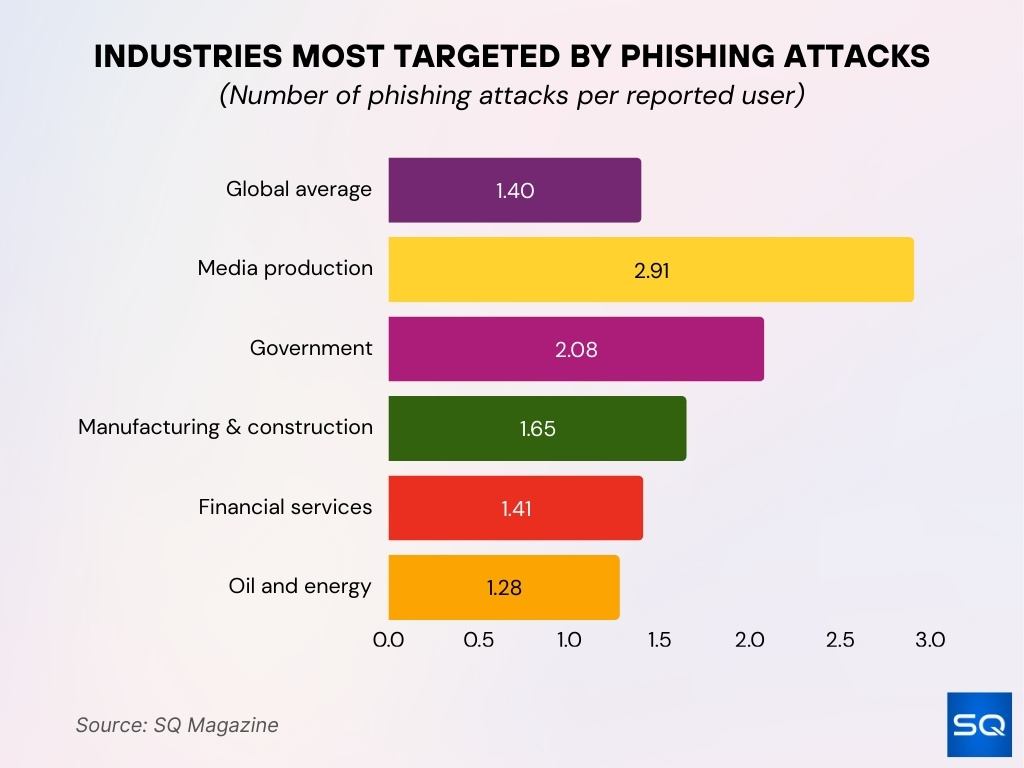
Industries Most Targeted by Phishing Attacks
- Global average exposure stands at 1.40 phishing attacks per reported user.
- Media production faces the highest risk with 2.91 attacks per user, more than double the global average.
- The government sector remains heavily targeted, averaging 2.08 attacks per user.
- Manufacturing and construction industries report roughly 1.65 attacks per user.
- Financial services experience 1.41 attacks per user, slightly above the global benchmark.
- Oil and energy industries face 1.28 attacks per user, below the global average but still notable.
Attack Methods
- In 2025, phishing remains the leading method used in digital credential theft and wallet drain schemes, with attackers combining classic email tactics with modern AI‑assisted nuance.
- Phishing emails bypass traditional filtering in nearly 47% of observed cases, making them a persistent threat vector.
- QR code phishing (“quishing”) has risen sharply, with attacks growing by ~25% year‑over‑year as fraudsters exploit scanning habits.
- Mobile and SMS‑based phishing (smishing) campaigns continue to expand, contributing significantly to wallet drain and credential theft.
- Sophisticated attacks now blend social media impersonation, fake project endorsements, and phishing URLs to lure crypto users into wallet approval dialogs.
- Fake exchange pages and wallet pop‑ups accounted for major phishing vectors in early 2025 crypto losses, leading to hundreds of millions in stolen value.
- Attackers increasingly misuse trusted authentication processes like Microsoft’s OAuth device code to take over accounts without passwords.
- Voice phishing (vishing) and AI‑generated deepfake messages have made attacks more convincing and harder to spot.
- Phishing kit infrastructure and Malware‑as‑a‑Service offerings enable low‑skill actors to deploy credential harvesters at scale.
Credential Theft
- Credential theft incidents surged by ~160% in 2025 compared with prior periods, making stolen credentials a dominant breach factor.
- Compromised credentials now account for about 20% of all breaches in 2025.
- In a single recent month, more than 14,000 employee credentials were exposed through breaches.
- Stolen credentials significantly enable account takeovers, with over 5,100 related complaints to U.S. authorities in 2025.
- Credential harvesting is not limited to emails; attackers also target cloud services, social media, and crypto wallets.
- Legitimate brand impersonations (e.g., Microsoft, Google) are now common lures to capture logins.
- Infostealer malware remains pervasive, extracting passwords and wallet keys used in credential theft campaigns.
- Credentials once stolen often go undetected for an average of 94 days before remediation.
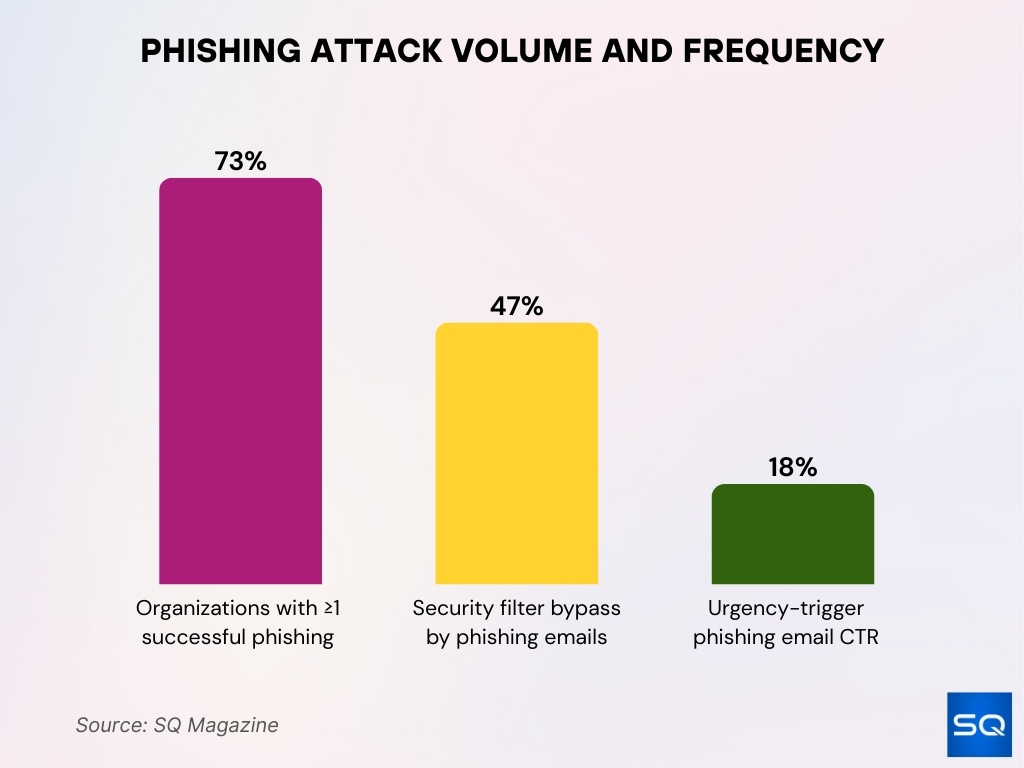
Phishing Attack Volume and Frequency Statistics
- Organizational exposure shows that 73% of organizations worldwide reported at least one successful phishing attack in 2025.
- Email security evasion remains high, with phishing messages bypassing standard filters in 47% of cases.
- Urgency-based phishing tactics drive higher engagement, pushing click-through rates to 18% in 2025.
Brand Impersonation
- Microsoft accounted for 40% of all brand impersonation phishing campaigns in Q3.
- Google represented 9% of global brand spoofing attempts in phishing attacks during Q3.
- Apple comprised 6% of brand impersonation incidents in phishing scams in Q3.
- Tech giants Microsoft, Google, and Apple together made up over 50% of all brand-related phishing activity in Q3.
- Credential theft incidents surged by 160% compared to prior periods.
- Phishing emails contributed to 36% of all data breaches.
- Wallet drainer scams caused nearly $500 million in losses.
- Phishing and social engineering led to $594.1 million stolen in H1 from the total $3.1 billion crypto losses.
- Infostealers harvested 1.8 billion credentials from 5.8 million devices.
- APWG recorded 1,130,393 total phishing attacks in Q2, many involving brand impersonation.
Social Engineering
- Social engineering remains a core component of phishing and wallet draining, exploiting human trust and urgency triggers.
- Attackers typically use urgency cues (e.g., “account locked”) to push users into hasty actions, raising click rates to ~18%.
- Deepfakes and AI‑generated voice scams have contributed to hundreds of millions in losses.
- Scammers craft tailored narratives, such as fake job offers or support tickets, to extract credentials or wallet approvals.
- Fake project endorsements and social media hype around Web3 initiatives attract victims to malicious wallet interactions.
- Social engineering via phishing appears in email, SMS, voice calls, and third‑party messaging platforms.
- Humans are often the weakest link, with 60%+ of breaches involving human error enabling social engineering success.
- Wallet drain scams exploit misplaced trust in online personalities and influencers promoting fake crypto opportunities.
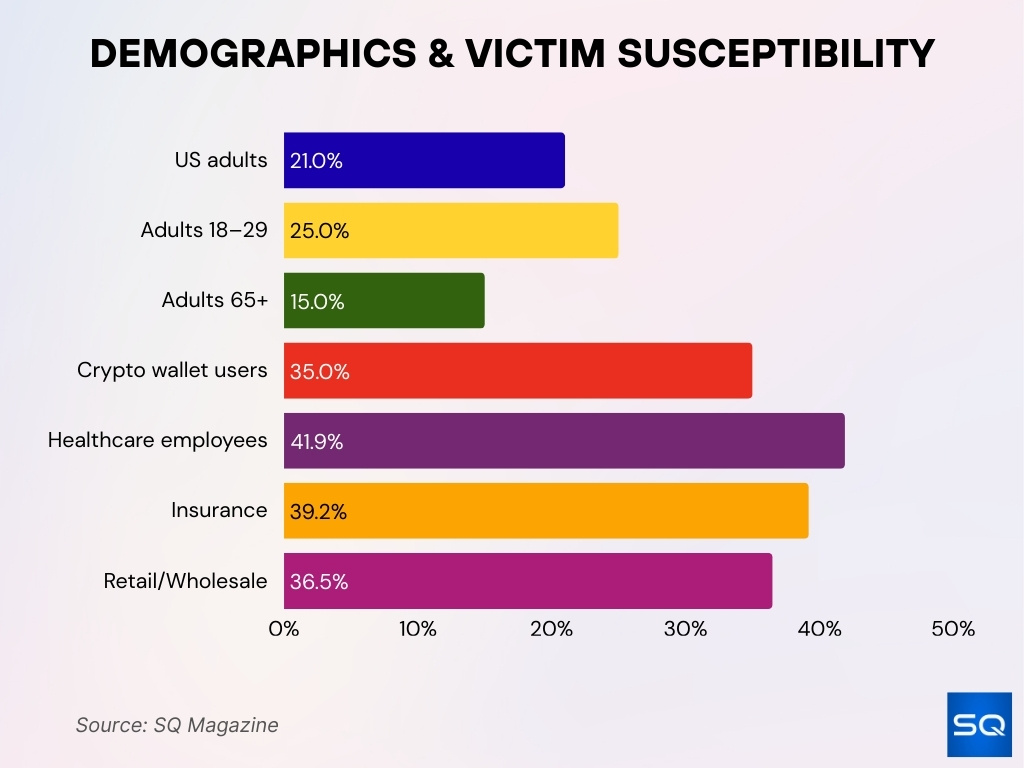
Phishing Victim Demographics and Susceptibility
- Financial loss prevalence shows 21% of U.S. adults have lost money to online scams or attacks.
- Age-based vulnerability indicates 18–29 year olds report losses at roughly 25%, compared with about 15% among adults aged 65+.
- Racial and ethnic exposure gaps reveal that Black, Hispanic, and Asian adults experience multiple online attack types more often than White adults.
- Income-linked risk patterns show that lower-income households report more frequent exposure to multiple scam attempts.
- Crypto wallet security gaps persist, with 35% of users failing to properly back up secret recovery phrases.
- Industry susceptibility rates are highest in healthcare at 41.9%, insurance at 39.2%, and retail and wholesale at 36.5%.
- Brand impersonation tactics remain effective, with many victims deceived by fake communications mimicking trusted services.
- Demographic correlation factors confirm that age, occupation, and digital literacy strongly influence phishing response likelihood.
Multi‑Channel Attacks
- Phishing attacks no longer rely solely on email, SMS, voice, and QR code channels are widely used in 2025.
- Smishing accounts for a growing share of credential theft and account takeover incidents.
- Quishing (QR code baiting) campaigns have increased by ~25%.
- Attackers send coordinated phishing across platforms, email, followed by SMS to increase chances of user compliance.
- Voice phishing with AI‑generated audio impersonations enhances believability and success rates.
- Social media, direct messages, and chat apps serve as vectors for malicious links pushing users to phishing sites.
- Fake ads on search engines and social platforms redirect to credential‑stealing or wallet‑approval pages.
- Multi‑channel approaches increase the likelihood of bypassing single‑layer defenses like email filters alone.
Targeted Wallets
- Crypto wallet drainers impersonate legitimate services to trick users into authorizing transactions that drain all assets.
- Nearly $410.7M in phishing‑related crypto losses were recorded across just 132 incidents in early 2025.
- MetaMask reported hundreds of victims losing funds due to malicious wallet connection pop-ups.
- Wallet drainers are commonly deployed via fake exchange and dApp connection pages.
- Fraudsters embed malicious JavaScript in trusted sites to trigger wallet connection dialogs, leading to asset theft.
- Wallet attacks often combine brand impersonation and social engineering to lower user suspicion.
- Losses from wallet drainers are part of broader crypto crime, which saw nearly $1.93 billion stolen in the first half of 2025.
- Wallet targeting continues to evolve alongside decentralized finance and Web3 adoption, expanding the potential victim pool.
BEC Statistics
- In 2025, Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks cost companies an average of about $4.67 million per incident, making them one of the most financially damaging phishing variants.
- BEC attacks accounted for roughly 8.5% of all data breaches in 2025, underscoring their role in broader cybersecurity risk.
- A 37% increase in BEC attack volume was observed in June 2025 compared to May 2025, illustrating escalating attacker activity.
- About 70% of BEC attacks in October 2025 were sent from free webmail providers such as Gmail and Microsoft accounts, highlighting the misuse of trusted platforms.
- Average wire transfer amounts requested in BEC scams hovered around $48,252 in October 2025, slightly lower than earlier months.
- Credential phishing was the most common cash‑out method in BEC scams, used in over 43% of observed attacks.
- United States‑based IP addresses accounted for around 38% of BEC threat actor locations tracked in October 2025.
- Specialty banks were the primary institution used in payroll diversion scams, making up 26% of such BEC schemes in late 2025.
- Deepfake CEO fraud tactics contributed to more than $200 million in BEC‑related losses as attackers impersonated top executives.
- Organization surveys show that over 94% experienced phishing attacks in 2024, with BEC frequently cited as the method used, demonstrating widespread exposure.
Regional Trends
- The United States remains a primary target for BEC and phishing attacks, given its large economic footprint and reporting volume.
- Phishing and email compromise incidents are reported globally, with Australia and Europe also seeing notable increases.
- In Australia, BEC incidents grew by about 7% year‑over‑year and are part of a broader 22% rise in advanced email threats.
- Phishing attacks frequently cause other fraud vectors, identity fraud, and online banking scams remain top-reported threats in multiple regions.
- Phishing incidents vary by geography but often correlate with internet penetration and digital transaction rates across regions.
- APWG reports millions of phishing attacks globally in early 2025, highlighting that threats are not confined to a single territory.
- U.S. losses from internet crime, including phishing, spoofing, and BEC, exceeded $16 billion in 2024 and continue to grow.
- Regions with strong reporting frameworks tend to show higher documented incident counts, suggesting visibility differences rather than purely risk disparities.
- Credential theft impacts countries across the globe, with exposure rates reported across Brazil, India, the U.S., and others in 2025.
- Phishing‑linked ransomware and credential theft trends also vary regionally, often reflecting local cybersecurity maturity.
Emerging Trends
- Vishing attacks increased by 449% in 2025, indicating that voice‑based social engineering is rapidly gaining traction alongside traditional email phishing.
- A notable 70% uptick in attacks sent from legitimate platforms was observed, complicating detection efforts.
- AI‑generated phishing content made emails harder to differentiate from legitimate communications.
- BEC campaigns increasingly use deepfake audio and CEO impersonation, causing substantive financial losses.
- Phishing delivered via social media and collaboration platforms continues to rise as attackers exploit user trust in these channels.
- AI‑assisted spear‑phishing campaigns are more personalized and harder for standard filters to catch.
- Multi‑vector attacks combining SMS, email, and voice are becoming more frequent in sophisticated campaigns.
- Attackers increasingly exploit supply chain and third‑party vendor relationships to launch BEC and phishing scams.
- Credential theft remains central to many attacks, suggesting that identity‑centric defenses are more critical.
- Phishing is evolving with the successive use of generative AI, deepfakes, and automation to scale attacks globally.
Recovery Rates
- Over 50% of BEC victims recovered at least 82% of stolen funds through rapid bank recalls.
- 73% of wire fraud victims recovered all or most funds per CertifID’s report.
- Industry recovery firms achieved 94%–98% success rates in select crypto cases.
- Most victims recover only 15–20% of funds lost to phishing and crypto scams.
- FBI’s Recovery Asset Team secured a 71% success rate on $538.39 million of $758.05 million in wire fraud.
- 25% of cyber insurance claims for BEC saw meaningful recovery.
- 14% of BEC scam victims recovered none of their financial losses.
- Coordinated operations froze over $300 million in stolen crypto assets.
- Victims acting within 24 hours had substantially better recovery outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Investors lost nearly $2.5 billion to crypto scams and hacks in the first half of 2025.
Approximately $1.71 billion was lost from compromised wallets and $410.75 million from phishing attacks.
Wallet drainer and phishing incidents caused about $3.1 billion in losses in the first half of 2025.
Losses from wallet draining are projected to exceed $4.3 billion by the end of 2025.
Conclusion
Phishing, BEC, and wallet drainer threats continue to evolve rapidly, driven by AI, social engineering, and multi-channel strategies. Notably, BEC remains among the costliest attack types, with millions lost per incident. At the regional level, data shows the United States leading in documented activity, while, globally, trends point to the spread of increasingly sophisticated attack vectors across email, voice, and emerging platforms.
Despite growing awareness and improved defensive tools, recovery rates continue to lag behind attack volumes, thereby underscoring the need for stronger defenses and faster reporting. As a result, as cybercriminals continue to innovate, organizations must adapt their security posture and increasingly prioritize identity-centric protections to mitigate risk and limit financial impact.