Grokipedia is the AI‑powered online encyclopedia launched in late October 2025 by xAI, the artificial intelligence company backed by Elon Musk. It aims to serve as a fast, AI‑generated alternative to the long‑standing human‑edited platform Wikipedia. In its first year, Grokipedia has shown rapid growth in article count, global traffic, and debate over content quality. Its development mirrors broader shifts in how people access and trust digital information, with implications for education, research, and AI integration in knowledge systems. From academic comparison studies to real‑world usage trends, the data shows why Grokipedia matters and why readers should dive deeper into this evolving landscape.
Editor’s Choice
- 885,279 articles were live on Grokipedia around launch day in late October 2025, compared with 7+ million Wikipedia articles in English alone.
- By early 2026, over 5.6 million articles were reported, nearing 79 % of Wikipedia’s English‑language corpus.
- Grokipedia received 8.65 million total visits in November 2025.
- Peak weekly traffic topped 2.854 million visits in early November 2025.
- The U.S. accounted for ~14.7 % of traffic, followed by India with ~9 %.
- Third‑party data shows daily U.S. site visits peaked above 460,000 on launch day.
- Academic studies find Grokipedia articles typically have longer text but lower reference density than Wikipedia.
Recent Developments
- Grokipedia launched publicly on October 27, 2025, as version 0.1 of the AI encyclopedia.
- Initial traffic surged on release day, followed by a settling phase with daily visits after early November.
- Within months, the platform expanded its article corpus from ~885,000 to millions, reflecting rapid scaling.
- Version 0.2 updates added features like video summaries and multimedia support in late 2025.
- Major news outlets have covered controversies around content accuracy and AI reliance.
- Academic audits comparing search outcomes between Grokipedia and Wikipedia were published in late 2025.
- Ongoing debates about content bias and source reliability continue in tech and media coverage.
- User‑suggested corrections and editorial workflows are being refined across 2025–2026.
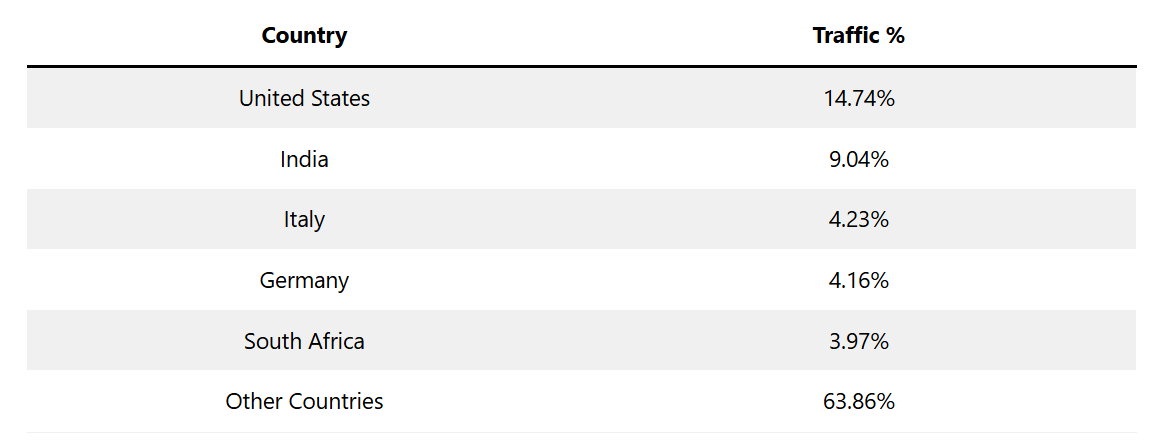
Grokipedia Traffic Distribution by Country
- United States leads Grokipedia traffic with 14.74%, highlighting strong early adoption in mature AI and tech-driven markets.
- India accounts for 9.04% of total visits, reflecting rapid growth among emerging digital knowledge users and students.
- Italy contributes 4.23% of Grokipedia traffic, showing notable uptake across European knowledge platforms.
- Germany follows closely with 4.16%, indicating steady interest from research-focused and academic audiences.
- South Africa represents 3.97% of traffic, signaling growing AI encyclopedia usage in developing regions.
- Other countries collectively dominate with 63.86%, demonstrating Grokipedia’s broad global reach beyond its top markets.
Grokipedia Overview
- Grokipedia is an AI-generated online encyclopedia developed by xAI, powered by the Grok LLM.
- Articles are generated and continuously updated using AI rather than a volunteer editor community.
- The platform launched on October 27, 2025, with an initial 885,000 articles generated by Grok AI.
- Peaked at over 460,000 US daily visits on October 28, 2025, and later stabilized at 35,000 per day.
- Updated to version 0.2 by early 2026, enabling AI-reviewed user correction suggestions.
- Grew from under 1M articles at launch to over 5.6M in three months through continuous AI updates.
Articles and Content Volume
- Launch version (v0.1) listed ~885,000 articles.
- This figure approaches 79 % of Wikipedia’s English article count.
- Growth from launch to reported millions of entries reflects content generation speeds far exceeding traditional human editing.
- Article length on Grokipedia is often longer than its counterpart, Wikipedia entries.
- Despite volume increases, reference density per word tends to be lower than on Wikipedia.
- Article coverage spans core academic topics, biographies, technology, and popular culture.
- Reports note replication of many Wikipedia pages, sometimes with adaptation or AI rephrasing.
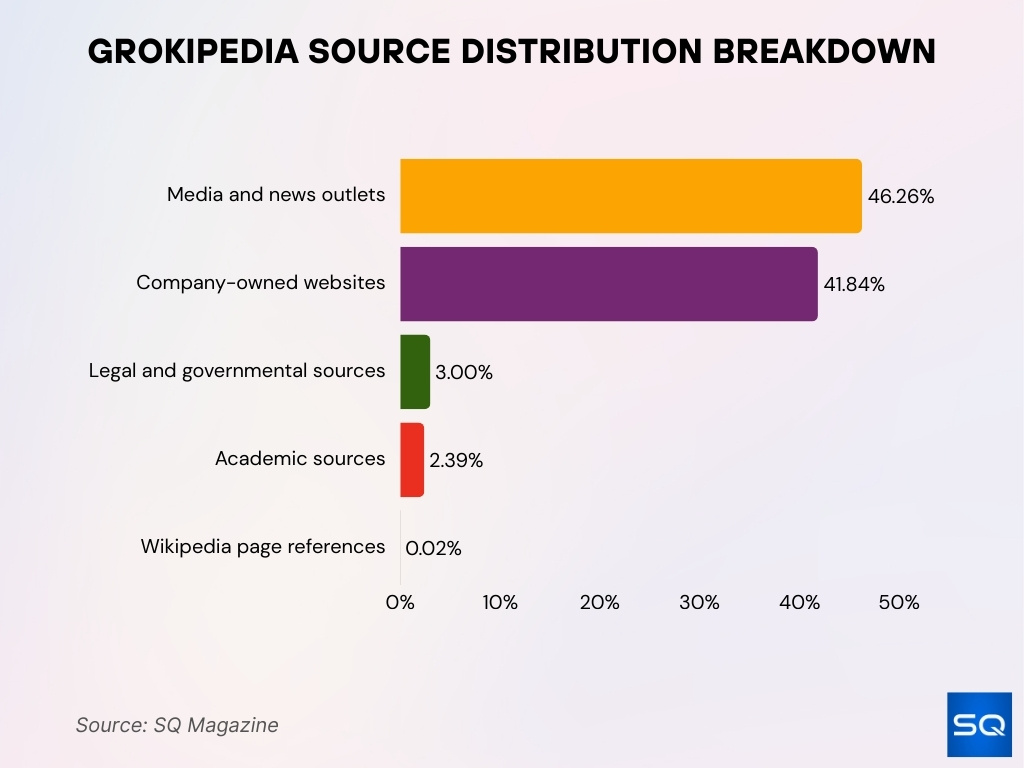
Grokipedia Source Distribution Breakdown
- Media and news outlets account for 46.26% of all references, totaling 2,512 sources, making them the largest citation category.
- Company-owned websites contribute 41.84% of references, equal to 2,272 sources, showing a strong reliance on corporate and proprietary content.
- Legal and governmental sources represent 3.00% of citations, or 163 sources, indicating limited use of official public records.
- Academic sources make up only 2.39%, with just 130 sources, highlighting minimal reliance on peer-reviewed research.
- References to other Wikipedia pages are nearly absent at 0.02%, signaling a deliberate move away from Wikipedia-style internal sourcing.
Account and Registration Metrics
- As of early 2026, 210,751 approved edits were recorded from user suggestions reviewed by Grok.
- Platform surpassed 200,000 approved edits by mid-January 2026, with over 6 million articles hosted.
- Registration is optional but enables edit suggestions, with higher engagement among logged-in users.
- Version 0.2 rollout in late 2025 introduced user-proposed edits and transparent edit history.
- Traffic peaked at over 460,000 US daily visits on October 28, 2025, and dropped to 35,000 per day by November.
- No official total registered user count disclosed, but patterns suggest a substantial casual base.
- Early data shows registration rates increased post-version 0.2, boosting community interaction.
Content Quality and Reliability
- Cornell study identified 12,522 citations to low-credibility sources and 1,050 self-citations across Grokipedia.
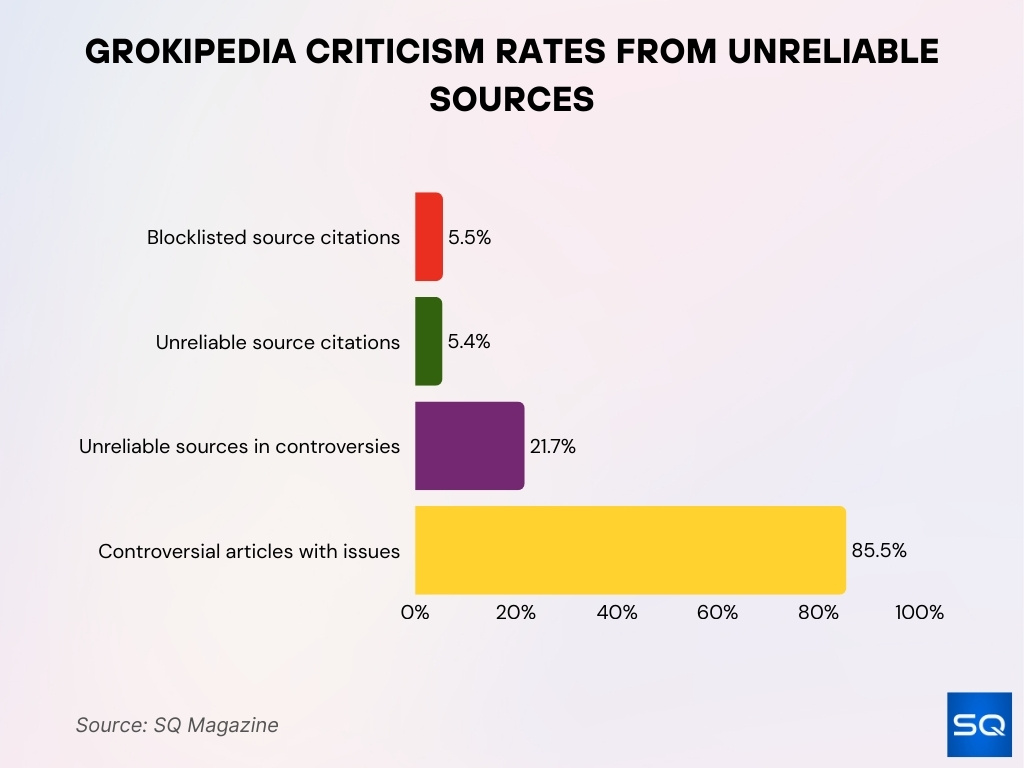
- 5.5% of articles cite Wikipedia-blocklisted sources, compared to near-zero on Wikipedia.
- Grokipedia articles are 3.2x more likely than Wikipedia to cite “generally unreliable” sources in non-CC content.
- 0.1% of citations from blocklisted sources, a 275% relative increase over Wikipedia.
- Includes 42 citations to Stormfront and 34 to InfoWars, absent on Wikipedia.
- 5.4% of citations are “generally unreliable,” an 86% relative increase from Wikipedia.
- 85.5% of controversial topic articles contain unreliable source citations.
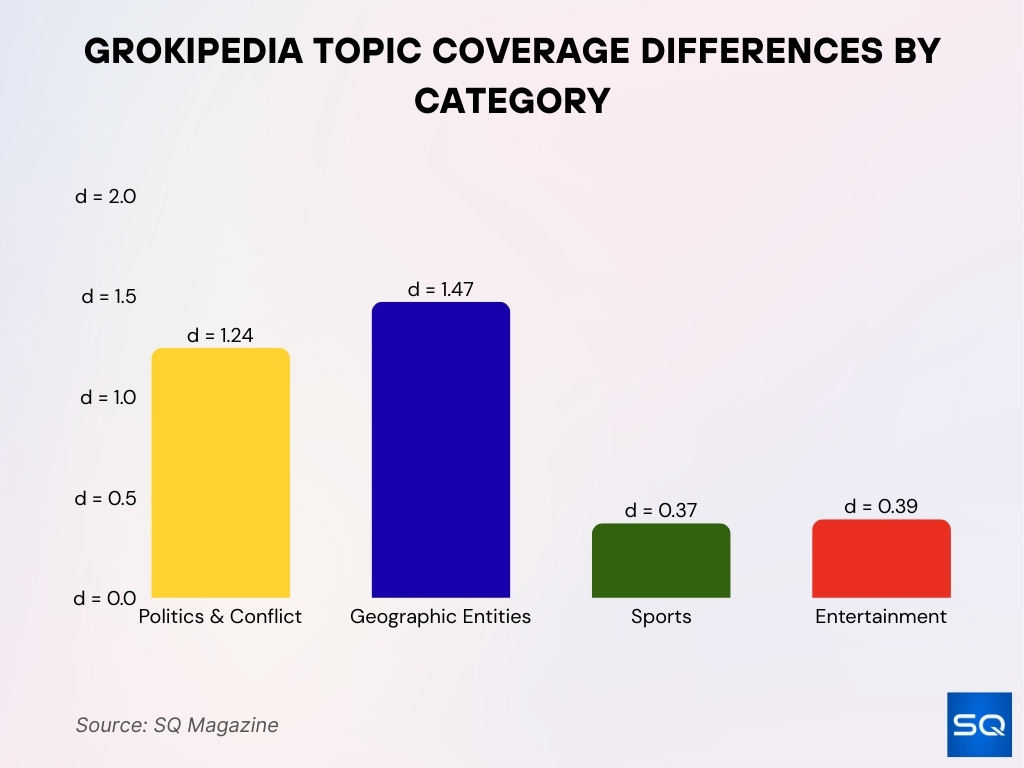
Topic Coverage and Categories
- Politics & Conflict (d=1.24), Geographic Entities (d=1.27) show the largest sourcing divergence from Wikipedia.
- Sports (d=0.37), Entertainment (d=0.39) exhibit the smallest effect sizes in epistemic profile differences.
- Covers 885,279 articles at launch across popular topics, mirroring 69% of Wikipedia’s October 2025 pageviews.
- 5.6 million total articles by January 2026, spanning history, science, culture, technology, biographies, and politics.
- Tech articles garnered 8 million views in recent months, wellness 5.2 million pageviews.
- 3,152 controversial articles analyzed, with the lowest similarity to Wikipedia in politics, geography, and history.
- Analyzed 30,000 articles using the WMF topic model covering geography, history, politics, biography, and science.
- Average article length 7,662 words versus Wikipedia’s 6,280 across 17,000 matched pairs.
Editorial Process and AI Generation Model
- Content generated by Grok 4.1 LLM, released November 2025, with reduced hallucinations and advanced reasoning.
- Launched October 27, 2025, with 885,000 articles automatically produced by Grok AI.
- Version 0.2 introduced user edit suggestions evaluated solely by Grok, with over 22,000 approvals.
- 210,751 approved edits by early 2026 via AI-reviewed user proposals.
- Studies confirm 3.2x more low-credibility citations than Wikipedia due to machine-selected references.
- No human oversight or community consensus; Grok acts as sole arbiter for all content changes.
- Growth to 1.7M articles by December 2025 via AI prioritizing coverage breadth.
- Epistemic profile differs with higher user-generated source reliance versus Wikipedia’s scholarly focus.
Search, Discovery, and SEO Metrics
- Google clicks surged from 19 per month in November 2025 to 3.2 million monthly by January 2026.
- Ranks for 6 million keywords with server-side rendering and Wikipedia-like interlinking.
- Peaked at 460,000 US daily visits on October 28, 2025, and fell to 35,000 daily by November.
- 900,000 AI-generated pages were indexed by Google shortly after the October 2025 launch.
- Entered the top 11-17 most recommended wikis by LLMs like ChatGPT, up from 18-24.
- AI search traffic grew 527% YoY, with 60% queries answered without clicks.
- 35% of US Gen Z uses AI chatbots for searches, boosting platforms like Grokipedia.
- Organic traffic comprises 47% of all site traffic, down 3.65% in 2025.
Criticisms and Controversies
- 5.5% of articles cite Wikipedia-blocklisted sources.
- 5.4% “generally unreliable” sources, 86% relative increase over Wikipedia.
- 21.7% controversial topic entries cite “generally unreliable” sources.
- 85.5% controversial articles contain unreliable source citations.
- 12,522 citations to very low credibility domains (quality 0.0–0.2), 3x Wikipedia’s share.
- 34 citations to InfoWars in the analyzed content.
- PolitiFact review found non-existent sources and misleading claims.
Device, Platform, and Session Behavior
- Mobile accounts for ~60% of worldwide web sessions, desktop ~39% per industry benchmarks.
- Desktop AI search traffic exceeds 90%, with AI Overviews 39% more frequent than mobile.
- Peak 460,000 US visits on October 28, 2025, split across desktop and mobile devices.
- Mobile app loads 1.4–1.9s for medium queries, faster than desktop 1.6–2.1s and web 2.4s.
- Industry average engaged session duration is 4.2 minutes, healthy engagement rate 60–70%.
- Desktop AI Overviews allocate 1,110 pixels versus mobile 617, an 80% difference.
- Articles with interactive elements see 60% longer sessions than plain text.
- Desktop users from AI search convert at 11x higher rates than mobile.
Referral Sources and Traffic Channels
- 80.18% direct traffic (122.7M visits), 8.86% organic search (13.6M), 8.63% referrals (13.2M).
- 2.2% organic social referrals, ranking fourth among traffic channels.
- AI platforms generated 1.13B referrals to top 1K sites in June 2025, up 357% YoY.
- ChatGPT drove over 80% of AI referrals to the top 1K websites.
- 47% overall site traffic from organic sources in 2025.
- Facebook led social referrals at 7.75% total global traffic.
- X.com appeared only 14 times in 18,759 Grokipedia citations.
Monetization and Revenue Indicators
- xAI 2025 revenue run-rate nears $3.2 billion consolidated with the X platform.
- xAI standalone revenue guidance at $500 million for 2025.
- xAI plans a $15 billion funding round at $230 billion pre-money valuation.
- Wikimedia donations were $185 million in 2024 for comparison.
- Grok Premium+ $16 monthly, SuperGrok API up to $300.
- Potential $100 profile fee for 1 million subscribers, yielding $1.2 billion annual revenue.
- Premium tiers are estimated at $10–$25 monthly for higher limits.
- Previous Series B $6 billion funding to support products like Grokipedia.
Community and Feedback Insights
- 210,751 approved edits from user suggestions by early 2026.
- 22,319 approved edits recorded shortly after version 0.2 rollout.
- Over 60,000 approved edits by late 2025, with public verification logs.
- 1,000,000 articles reached amid real-time edit transparency rollout.
- Tech articles received 8 million views, wellness 5.2 million in the past month.
- 35% higher engagement for tech articles between 7 PM and 10 PM.
- 40% of wellness views between peak times, 2x shares for how-to content.
- 5x higher visibility for content published within 24–48 hours of trends.
- Reddit r/EnoughMuskSpam post rejecting Grokipedia garnered 244 upvotes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
As of January 14, 2026, Grokipedia’s article count has grown to approximately 6,092,140 articles.
Grokipedia’s daily visits peaked at ~460,400 on October 28, 2025.
The United States contributed 14.74% of Grokipedia’s traffic share as of November 2025.
A Cornell study found 12,522 instances of citations to sources deemed low‑credibility.
Conclusion
In its first year, Grokipedia has sparked significant attention as an AI‑generated encyclopedia aiming to rival traditional models like Wikipedia. While data shows rapid content expansion and substantial early traffic, the platform faces serious questions about search visibility, editorial integrity, and content reliability. AI‑driven discovery trends now shape how users locate information, challenging Grokipedia’s SEO and referral pathways. The controversies over sourcing, bias, and editorial transparency highlight why researchers and general users alike should approach AI encyclopedia outputs critically. As the ecosystem evolves, stakeholders will need to balance innovation with trust, accuracy, and accountability in the age of algorithmic knowledge systems.