In the early hours of a February morning in 2025, power grids flickered across parts of Eastern Europe. It wasn’t a storm. It wasn’t a malfunction. It was a line of code, written thousands of miles away, that turned infrastructure into targets. Cyber warfare is no longer the future; it is our present. From backdoor surveillance to full-scale disruptions of national systems, nation-states now deploy digital arsenals with the same intent and consequence as conventional weapons. This article explores the latest trends, figures, and implications of cyber warfare in 2025, showing how conflict has evolved in our connected world.
Editor’s Choice
- $13.1 billion is the estimated global cost of cyber warfare-related damages in 2025, marking a 21% increase from the previous year.
- 39% of all major cyber attacks in 2025 were state-sponsored, a record high in attribution-confirmed incidents.
- 76 countries were impacted by nation-state cyber operations as of Q2 2025, compared to 62 in the same period last year.
- The United States, China, and Russia together accounted for 61% of all observed cyber warfare activity in 2025.
- Critical infrastructure attacks rose by 34% in 2025, especially targeting energy, water, and transport sectors.
- AI-driven attacks represented 22% of all state-level cyber incidents in 2025.
- In 2025, 47% of global cybersecurity experts surveyed believe cyber warfare is now the primary method of geopolitical confrontation.
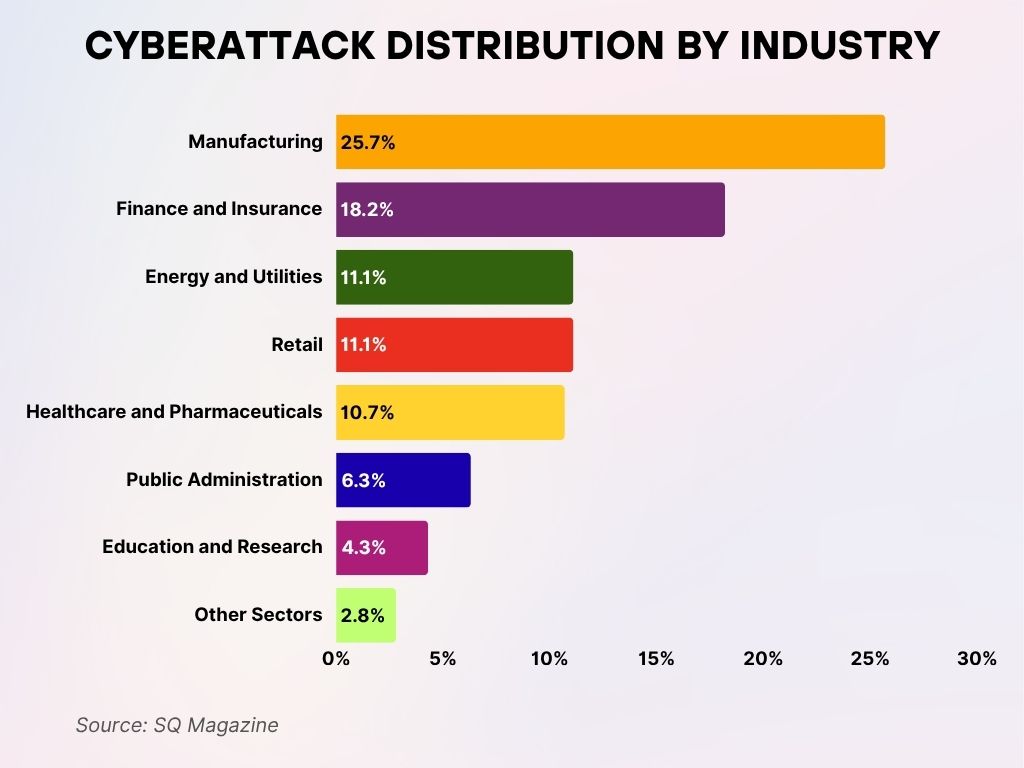
Cyberattack Distribution by Industry
- Manufacturing tops the list, accounting for 25.7% of all cyberattacks, the most targeted industry overall.
- The Finance and Insurance sector follows, hit by 18.2% of cyberattacks, highlighting its high-value data vulnerability.
- Both the Energy and Utilities and Retail sectors experienced 11.1% of attacks each, reflecting threats to essential services and consumer data.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals suffered 10.7% of cyberattacks, emphasizing risks to sensitive health information.
- Public Administration was the target in 6.3% of cases, pointing to continued government-related threats.
- Education and Research faced 4.3% of cyberattacks, likely due to lower security budgets and valuable research data.
- Other Sectors made up the remaining 2.8%, showing that no industry is completely immune to cyber threats.
Global Economic Impact of Cyber Warfare
- In 2025, the total economic losses from cyber warfare are projected to hit $13.1 billion.
- 1.4% of global GDP in 2025 is now attributed to costs stemming from cyber conflict, both direct and indirect.
- The financial services sector bore approximately $2.3 billion in damages from state-linked cyber intrusions in 2025 alone.
- Developing economies saw a 19% increase in economic disruption due to cyber attacks linked to regional rivalries in 2025.
- Supply chain attacks connected to geopolitical tensions have resulted in $890 million in revenue losses globally in 2025.
- Insurance premiums for cyber war coverage surged by 31% in 2025, reflecting both demand and risk assessment changes.
- The cost to recover from a state-sponsored cyber attack now averages $3.6 million per incident globally as of 2025.
- In 2025, export-import systems in six G20 economies experienced partial shutdowns due to offensive cyber actions.
- The UN estimated that the 2025 global cost of cyber-induced disruptions to peacekeeping operations exceeded $160 million.
- International aid deliveries were delayed by up to 6 days on average in 2025 due to cyber threats impacting satellite and logistics coordination.
Nation-State Cyber Attack Trends
- As of mid-2025, China was attributed to 28% of all state-sponsored cyber campaigns targeting foreign governments.
- Russia accounted for 22% of global offensive cyber activity in 2025, with a significant focus on NATO-aligned countries.
- The US launched at least 12 confirmed retaliatory cyber operations in 2025.
- The UK’s cyber command reported a 43% increase in active threat engagements in the first half of 2025.
- In 2025, North Korea resumed coordinated attacks on South Korean crypto exchanges, targeting over $105 million in digital assets.
- Iran’s cyber operations expanded to Latin America in 2025, with 8 confirmed intrusions on national infrastructure.
- A growing number of joint cyber ops were reported, with 17 multinational cyber offensives identified in the first quarter of 2025.
- False-flag tactics were detected in 15% of cyber operations in 2025, increasing the complexity of attribution.
- Election interference attempts rose to 18 countries in 2025, primarily leveraging social engineering and deepfake content.
- Asia-Pacific saw a 37% rise in state-level cyber activity during the first half of 2025, driven by Taiwan Strait tensions.
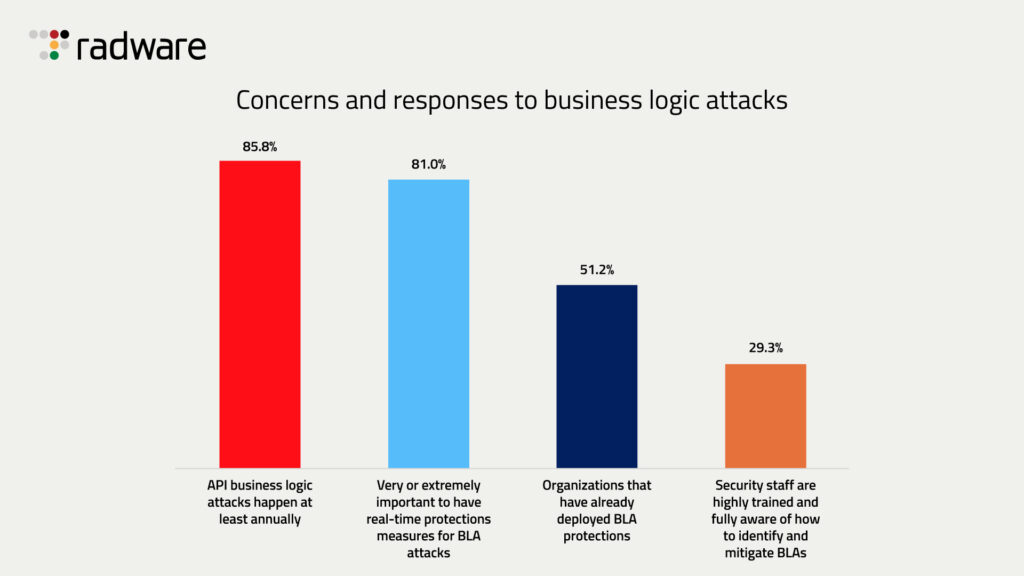
Business Logic Attacks: Concerns and Responses
- 85.8% of organizations report that API business logic attacks occur at least once a year, indicating their high frequency.
- 81.0% believe it’s very or extremely important to implement real-time protection measures against business logic attacks (BLAs).
- Only 51.2% of organizations have already deployed BLA protection, suggesting many remain unprepared.
- Just 29.3% of security teams are highly trained and fully aware of how to identify and mitigate business logic attacks.
Frequency of State-Sponsored Attacks by Country
- The United States endured 227 major state-sponsored cyber incidents in 2025, the highest of any nation.
- India reported 93 incidents tied to foreign state actors, primarily attributed to regional adversaries, in 2025.
- Germany experienced 74 confirmed intrusions by hostile states in 2025.
- Ukraine saw 118 cyber incidents linked to Russian-backed groups in the first five months of 2025 alone.
- In 2025, South Korea reported 61 state-level cyber intrusions, many targeting defense and telecom sectors.
- Israel disclosed 45 cyber warfare incidents in 2025, half of which originated from neighboring state actors.
- Brazil encountered 39 state-originated cyber attacks in 2025, an emerging trend in Latin America.
- Japan saw a 19% rise in attacks tied to Chinese and North Korean sources, totaling 68 incidents in 2025.
- France blocked over 220 million intrusion attempts in 2025, many traced back to coordinated international campaigns.
- Australia classified 53 cases as “cyber warfare-related” under new national threat protocols by mid-2025.
Military and Defense Sector Vulnerabilities
- In 2025, 61% of military cyber breaches occurred via third-party software vulnerabilities.
- 21 countries reported successful intrusions into classified defense networks during Q1–Q2 of 2025.
- The average dwell time for undetected breaches in military systems dropped to 41 days in 2025.
- $5.2 billion is the estimated global military sector spending on emergency cyber response operations in 2025.
- Satellite command and control systems were targeted in at least 9 high-level campaigns during H1 2025.
- 68% of NATO members confirmed attempted intrusions into defense logistics software during the first half of 2025.
- In 2025, unmanned aerial systems (UAS) in 7 countries were briefly hijacked through state-originated code injection attacks.
- Defense contractors reported a 38% increase in spear-phishing attempts traced to foreign intelligence services in 2025.
- A coordinated attack against military IoT devices impacted three Baltic states in March 2025.
- Zero-day exploits used in military cyber campaigns rose by 46% in 2025, highlighting persistent supply chain weaknesses.
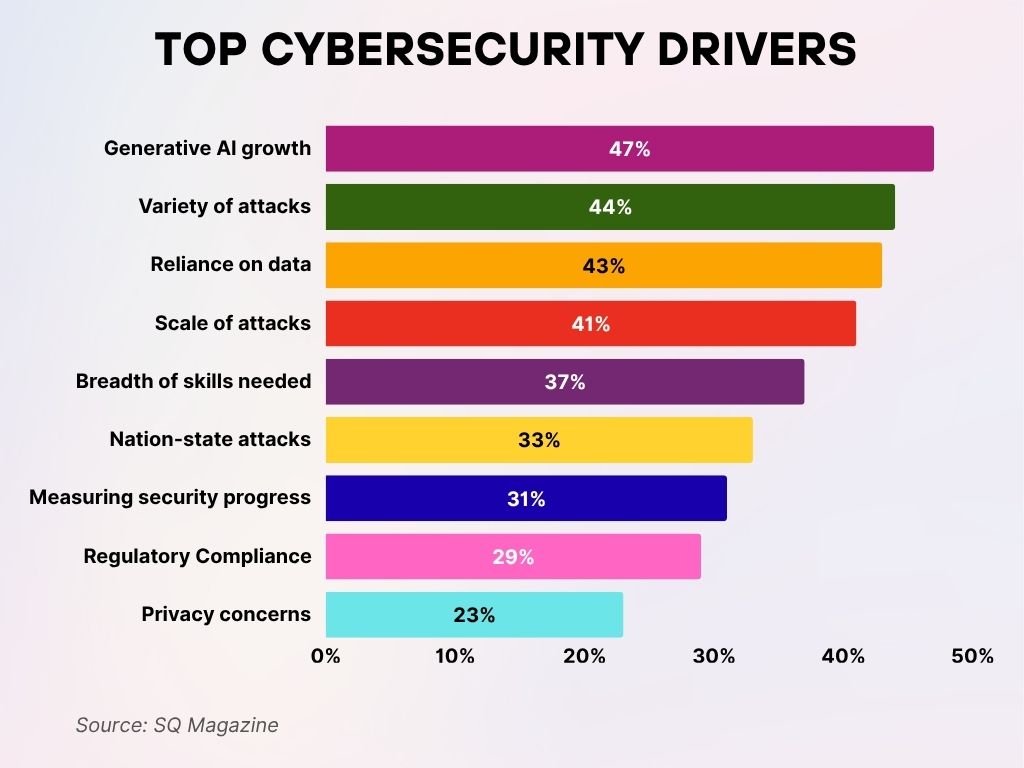
Top Cybersecurity Drivers
- 47% of respondents cite Generative AI growth as the top cybersecurity driver, highlighting its dual role in innovation and threats.
- 44% point to the variety of attacks, emphasizing the increasing complexity of cyber threats.
- 43% are driven by the reliance on data, showing the high stakes in data protection.
- 41% recognize the scale of attacks as a pressing concern requiring stronger defenses.
- 37% highlight the breadth of skills needed, underscoring ongoing talent gaps in cybersecurity.
- 33% are concerned about nation-state attacks, indicating rising geopolitical cyber tensions.
- 31% focus on measuring security progress, reflecting the need for better performance tracking.
- 29% see regulatory compliance as a key motivator for cybersecurity investment.
- 23% mention privacy concerns, showing ongoing public pressure to safeguard personal data.
Cyber Espionage Incidents and Growth Rate
- 2025 saw a 32% year-over-year increase in confirmed cyber espionage campaigns globally.
- Intellectual property theft through cyber espionage resulted in over $1.9 billion in global economic loss in 2025.
- South Asia and Eastern Europe were hotspots, comprising 44% of global espionage cases in the first half of 2025.
- Journalists and dissidents were targeted in 11% of state-sponsored spyware deployments in 2025, especially in authoritarian regimes.
- Quantum-resilient encryption was bypassed in two test environments by espionage actors during simulation events in 2025.
- In 2025, university research networks were among the top targets, involved in 19% of all corporate espionage breaches.
- Remote access trojans (RATs) used in stealth campaigns increased by 61% globally in 2025.
- Cyber espionage linked to economic policy leaks disrupted trade negotiations in at least 7 countries during Q2 2025.
- Deep packet inspection tools were discovered embedded in telecom hardware in 3 G20 nations in 2025, traced to a hostile state actor.
- A multi-national probe in 2025 revealed 12 years of stealth surveillance on transnational companies by a single foreign APT group.
Cyber Weapon Development and Deployment
- In 2025, over 27 new offensive cyber tools were identified originating from state military labs worldwide.
- Modular malware frameworks became the standard for state deployment, seen in 73% of incidents in early 2025.
- AI-generated payloads used in offensive tools rose by 190% between 2023 and 2025.
- Zero-click exploits in mobile cyber tools became widespread, with at least 9 countries confirmed to use them in Q1 2025.
- The first confirmed use of a drone-to-cyber relay weapon occurred during a regional conflict in April 2025.
- Nuclear-adjacent systems were targeted using a newly identified exploit codenamed “AshFall” in 2025.
- Offensive cyber programs are now operated in at least 38 countries, according to 2025 data.
- Remote firmware corruption tools were deployed by 3 advanced persistent threat (APT) groups in 2025.
- An experimental quantum-based intrusion detection bypass was tested and failed containment in two scenarios in 2025.
- Command-and-control (C2) architectures in state-built malware became more decentralized in 2025, with multi-node routing across 5 continents.
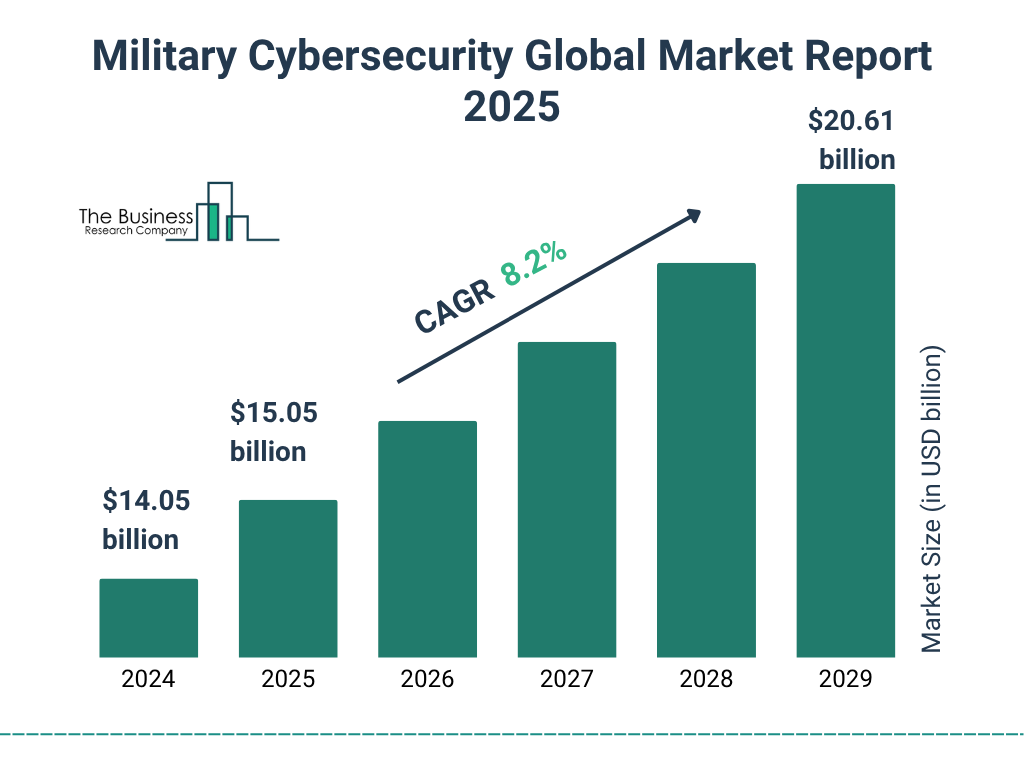
Military Cybersecurity Market Growth Forecast
- The military cybersecurity market is projected to grow $20.61 billion by 2029.
- In 2025, the market is expected to reach $15.05 billion, marking steady expansion.
- The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is estimated at 8.2%, indicating a strong and sustained upward trend.
- This growth reflects increasing global investments in defense digital infrastructure and threat protection.
- By 2029, the market size will have grown by over $6.5 billion, showing the rising importance of cybersecurity in national defense.
Ransomware and Malware Usage in Geopolitical Conflicts
- In 2025, 43% of ransomware incidents had geopolitical motivations, not financial.
- Wiper malware campaigns tied to state objectives rose by 51% in the first half of 2025.
- A state-backed ransomware strain dubbed “GlacierLock” targeted critical power infrastructure in 3 nations during Q1 2025.
- $730 million in cumulative ransom demands were linked to politically motivated cyber groups in 2025.
- Cryptojacking malware was deployed to secretly fund state proxies, detected in 18 cases across 4 continents in 2025.
- In 2025, 39% of all ransomware payloads were deployed via compromised remote desktop protocols in governmental systems.
- Hacktivist-aligned groups with nation-state ties were responsible for 62% of anti-government website defacements globally in 2025.
- Hybrid malware, capable of encrypting and stealing data simultaneously, became common in state-led operations by 2025.
- Healthcare ransomware attacks in conflict zones were up 28% in the first half of 2025.
- Supply chain ransomware events orchestrated by state proxies impacted over 210 vendors across 8 countries in Q1–Q2 2025.
Cost of Cyber Warfare Prevention and Mitigation
- Global government and private sector combined spending on cyber warfare prevention is projected at $28.6 billion in 2025.
- The average incident response time has improved to 17 hours globally in 2025.
- $6.7 billion was spent on cyber threat intelligence platforms in 2025, reflecting growing demand for proactive defense.
- The cost of cyber range simulations increased by 40%, with 53 nations now running joint-response training in 2025.
- Red-teaming services tailored to nation-state scenarios are projected to generate $1.1 billion in revenue in 2025.
- The average organizational spend on military-grade endpoint protection hit $740,000 per entity in 2025.
- Cloud-based cyber defense platforms saw a 63% adoption rate among Fortune 500 government contractors in 2025.
- Cyber drills involving multi-sector participants increased by 22% globally in 2025, a key part of the mitigation strategy.
- In 2025, retainer agreements for breach response services became standard across 72% of public institutions.
- Organizations reporting zero-day readiness policies jumped from 39% in 2023 to 66% in 2025.
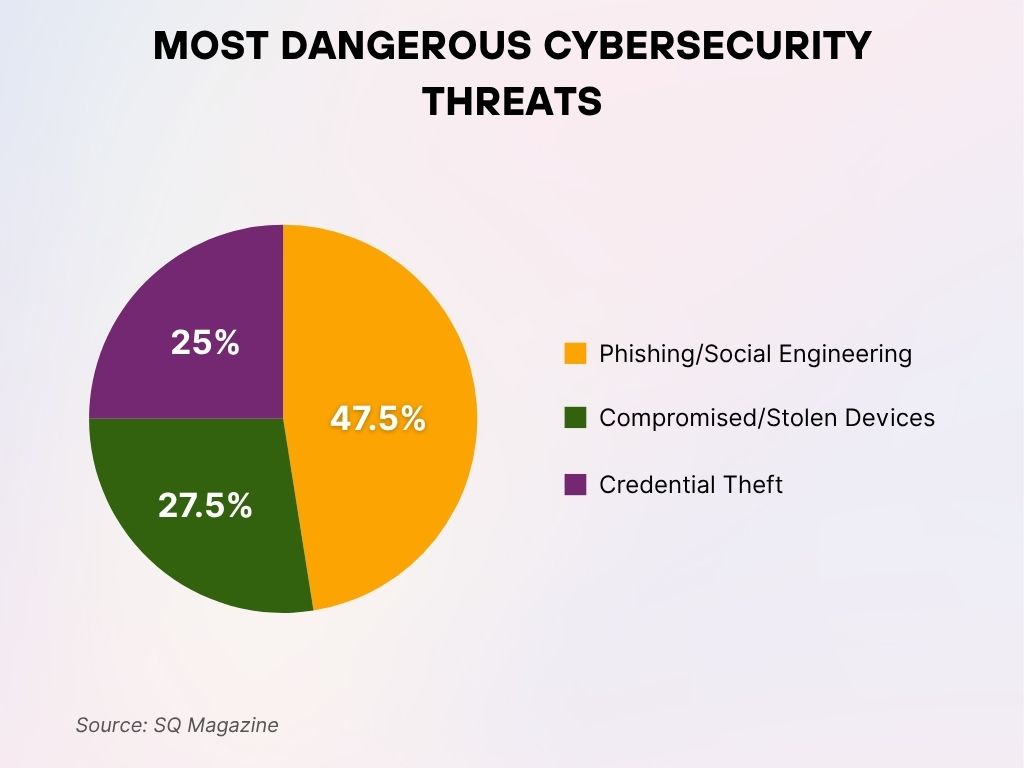
Most Dangerous Cybersecurity Threats
- 47.5% of attacks stem from phishing and social engineering, making it the most dangerous and common threat vector.
- 27.5% are caused by compromised or stolen devices, underscoring the importance of securing physical and remote access.
- 25% involve credential theft, emphasizing the critical need for robust authentication systems.
Government Cybersecurity Budgets and Allocations
- In 2025, global governments collectively allocated $59.4 billion to cybersecurity defense budgets.
- The United States Department of Defense dedicated $13.8 billion to cyber warfare initiatives in its 2025 budget.
- China’s digital defense budget for 2025 reached $9.2 billion, with a growing share invested in AI-based security platforms.
- NATO cyber programs received a combined allocation of $5.6 billion in 2025, a 22% increase year-over-year.
- India earmarked $2.1 billion for military-grade cybersecurity and threat intelligence infrastructure in 2025.
- UK’s National Cyber Security Centre received a $590 million allocation in 2025, primarily focused on critical infrastructure.
- Australia’s federal cyber funding expanded to $980 million in 2025, with 30% dedicated to offensive capabilities.
- Germany increased its cyber defense allocation by 26%, hitting $1.8 billion in 2025.
- The UAE announced a $420 million commitment in 2025 to establish its first state-backed cyber warfare command.
- In 2025, over 48% of governments surveyed globally indicated that cybersecurity makes up 10% or more of their total defense budget.
Role of AI and Automation in Cyber Warfare Tactics
- AI-enabled cyber operations accounted for 34% of all documented nation-state incidents in 2025.
- Machine learning accelerated threat detection and adaptive response times by 41% in deployed defensive networks in 2025.
- Autonomous exploit generation systems were identified in 11 confirmed nation-state toolkits in 2025.
- Adversarial AI models designed to mimic target behaviors bypassed 38% of behavioral firewalls in test simulations in 2025.
- AI-powered deepfake content was deployed in at least 14 influence operations linked to election interference in 2025.
- In 2025, 60% of cyber operations teams in military and intelligence communities reported AI integration in both offense and defense.
- Robotic process automation (RPA) was weaponized in at least 3 coordinated attacks on satellite ground stations during 2025.
- AI-authored phishing emails had a click-through success rate of 43% in simulated red team exercises in 2025.
- Natural language processing (NLP) bots were used in automated misinformation campaigns across 8 regional conflicts in 2025.
- Quantum-safe AI models began rolling out in select NATO-aligned networks as part of pilot deployments in 2025.
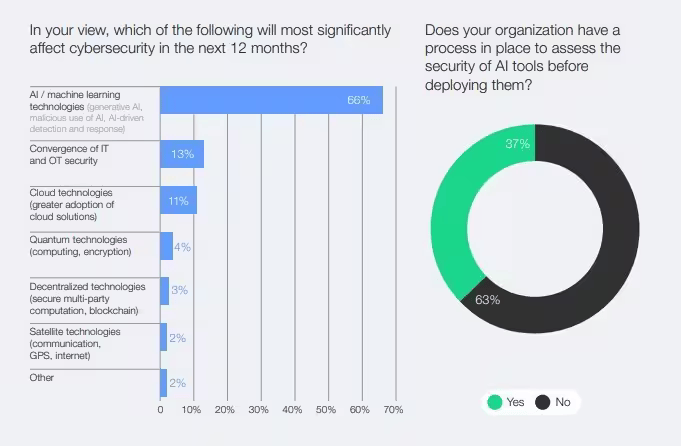
AI’s Growing Role in Cybersecurity
- 66% of experts believe AI/Machine Learning technologies will have the greatest impact on cybersecurity in the next 12 months.
- Only 37% of organizations have a security assessment process in place for AI tools before deployment, 63% do not.
- 13% cite the convergence of IT and OT security as a significant cybersecurity driver.
- 11% say greater cloud adoption will shape upcoming cybersecurity challenges.
- Emerging risks include quantum technologies (4%), decentralized tech (3%), and satellite technologies (2%).
- Just 2% attribute a significant impact to “other” technologies, indicating a concentrated concern around AI and cloud systems.
Attribution Challenges and False Flag Operations
- 2025 saw a 29% increase in cyber operations using false flag tactics, complicating global attribution efforts.
- In 31% of all major incidents, initial attribution was incorrect or delayed due to deliberate obfuscation by the attacker in 2025.
- Attribution lag time averaged 19 days in 2025, due to the use of global proxies and language mimicry.
- Seven nation-state actors were identified using off-the-shelf malware tools intentionally to mask their origins in 2025.
- AI-based deception was used to generate fake telemetry logs in 23 major campaigns during 2025.
- Code fragmentation tactics increased, with threat actors breaking payloads into up to 80 distributed pieces to evade forensic tracing in 2025.
- Attribution databases grew by 18% in 2025, yet accuracy metrics remained stagnant due to adversarial counterforensics.
- A joint task force reported that 12 of 48 nation-state groups engaged in attribution spoofing techniques in 2025.
- Attribution confusion delayed sanctions or retaliation decisions in 9 international incidents during Q1–Q2 2025.
Public-Private Partnerships in Cyber Defense
- In 2025, 74 countries reported active public-private cyber alliances, a record high.
- Microsoft, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud partnered with 16 governments on real-time cyber incident response in 2025.
- The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) expanded its cooperative framework to include 238 private vendors by Q2 2025.
- Public-private simulations rose by 48%, with cross-sector drills held across 43 countries in H1 2025.
- Information sharing platforms like ISACs facilitated 3.2 million alerts between governments and industry players in 2025.
- Cyber emergency response teams (CERTs) co-managed by public-private entities resolved 8,700 incidents in 2025 alone.
- In 2025, 38% of all proactive threat intelligence was first detected by private companies before government response.
- Legal frameworks enabling real-time collaboration between defense and tech firms were ratified in 27 countries in 2025.
- Insurance and cybersecurity firms formed coalitions to handle state-sponsored ransomware aftermath in 17 nations by mid-2025.
Recent Developments in Cyber Warfare
- 2025 marked the first international cyber arms embargo, passed by a UN digital security subcommittee in March.
- Stuxnet-like malware v2.0 targeting modern ICS systems was identified in 2 countries’ nuclear programs in Q1 2025.
- South Korea revealed its newly developed autonomous cyber interceptor, tested successfully in early 2025.
- A pan-African cyber threat coalition was formed in May 2025, aiming to share intelligence and standardize digital defense policies.
- Germany’s federal police announced the use of AI-based behavior profiling tools for real-time threat response in April 2025.
- In 2025, Turkey became the fifth country to declare offensive cyber response as an official act of war in its national defense doctrine.
- A massive deepfake-driven disinformation campaign disrupted local elections in three EU states during spring 2025.
- The “Digital Geneva Convention” draft proposal gained support from 68 nations by June 2025, pushing for cyber conflict regulations.
- Cybercrime-as-a-Service (CaaS) offerings tailored to state actors appeared on darknet markets with enterprise-level support models in 2025.
- Biometric spoofing techniques were deployed in five high-level diplomatic breaches, confirmed in Q2 2025.
Conclusion
Cyber warfare in 2025 isn’t confined to theory or dark rooms full of hackers. It’s active, escalating, and entrenched in national defense strategies. This year has seen more innovation, both defensive and offensive, than any previous period. Nations now face a complex battlefront where attribution is murky, AI acts faster than humans, and private sector partnerships are essential to national resilience. As the digital battlefield continues to evolve, policymakers, military leaders, and civil society must stay alert, adaptive, and above all, collaborative.