In the early hours of January 3, 2025, a mid-sized financial firm in Ohio discovered something chilling: over 1.2 terabytes of client data had been quietly siphoned off over the holidays. The attackers left no ransom demand, no calling card, just a system-wide silence and a massive void in customer trust.
This isn’t an isolated incident. Across the globe, cyberattacks have shifted gears in 2025, not only in volume but also in tactics, targets, and consequences. As digital transformation deepens, understanding these evolving threats isn’t just technical, it’s strategic.
Editor’s Choice
- Cyberattacks have increased by 18% globally in the first quarter of 2025 compared to Q1 2024.
- Ransomware incidents have dropped 7% YoY, but are more targeted and costly.
- Phishing remains the top attack vector, accounting for 31% of all breaches reported by organizations so far in 2025.
- Healthcare and education sectors continue to be high-risk industries, with a 24% spike in reported attacks since January.
- The average data breach cost has climbed to $4.92 million, up from $4.45 million last year.
- 45% of organizations globally now report using AI-driven tools for early detection and response.
- In the U.S., state-sponsored cyber operations are suspected in 22% of confirmed incidents, a growing concern for national infrastructure.
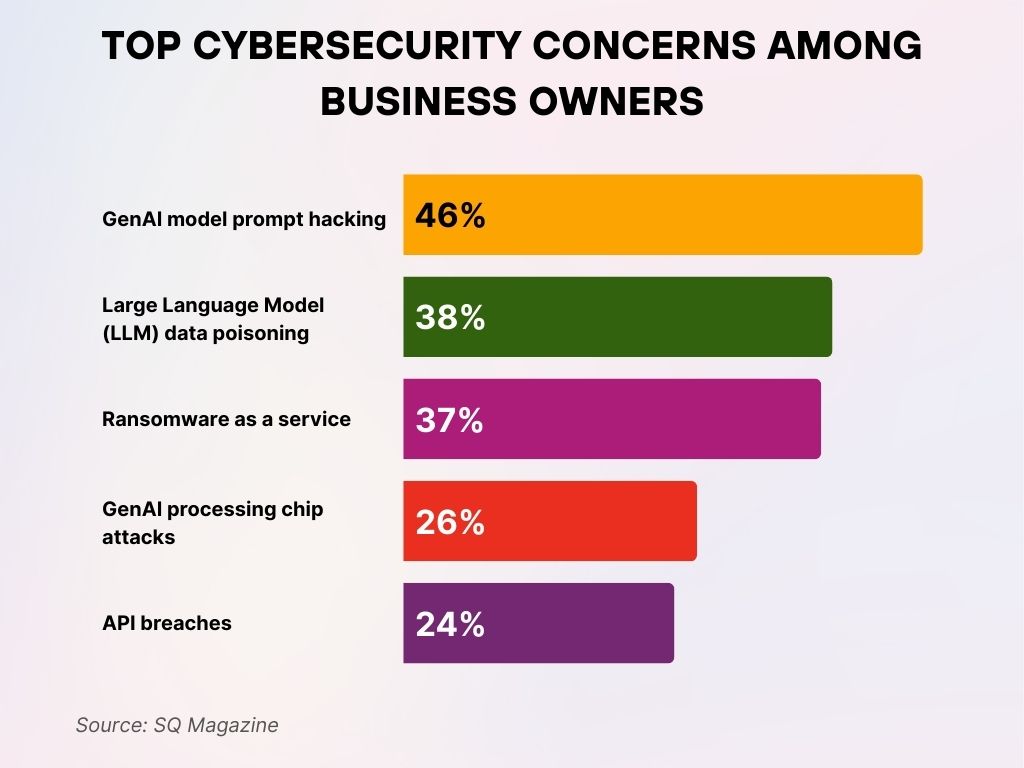
Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- GenAI model prompt hacking is the leading concern, cited by 46% of business owners. This reflects growing anxiety over malicious prompt injection into generative AI systems.
- Large Language Model (LLM) data poisoning is a major issue for 38% of respondents, highlighting risks of corrupting AI training datasets.
- Ransomware as a service worries 37% of business owners, emphasizing the ongoing threat of easily accessible ransomware kits for cybercriminals.
- GenAI processing chip attacks were mentioned by 26%, signaling concerns over hardware-level vulnerabilities specific to AI workloads.
- API breaches are a concern for 24%, pointing to the continued importance of securing integration points in digital infrastructure.
Global Cyberattack Volume Trends
- In 2025 so far, there have been over 7.5 million recorded cyber incidents globally, compared to 6.3 million during the same period in 2024.
- Asia-Pacific leads in volume, contributing to 34% of all attacks, largely targeting financial institutions and supply chain networks.
- North America saw a 15% rise in attacks compared to Q1 2024, with increased activity targeting cloud services and municipal systems.
- Mobile-related attacks have surged by 22% globally due to the proliferation of hybrid work models and device vulnerability.
- DDoS attacks make up 16% of global attack methods, with volumetric attacks becoming shorter yet more frequent.
- Europe recorded a sharp rise in cyber incidents against government networks, up 28% YoY, due to geopolitical tensions.
- SaaS platforms have reported a 13% uptick in targeted breaches, primarily through credential stuffing and token hijacking.
Most Common Types of Cybersecurity Attacks
- Phishing remains dominant, comprising 31% of known attack vectors in 2025.
- Credential theft accounts for 21% of all cyber breaches, mainly due to poor password hygiene and weak MFA setups.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) schemes rose by 11% YoY, causing significant financial and reputational damage.
- Zero-day exploits increased by 27%, especially affecting unpatched enterprise software and proprietary APIs.
- Malware deployment fell slightly to 14% of incidents, largely due to improved endpoint detection and response systems.
- Ransomware incidents declined to 9%, yet the average ransom demand grew to $2.3 million in 2025.
- Supply chain attacks saw an alarming 35% spike, especially in open-source dependency attacks.
- IoT attacks surged by 19%, mainly targeting smart factory devices and home automation hubs.
- Insider threats accounted for 6% of incidents, many due to a lack of access control policies.
- Cryptojacking activity doubled compared to early 2024, with attackers embedding mining scripts in compromised ad networks.
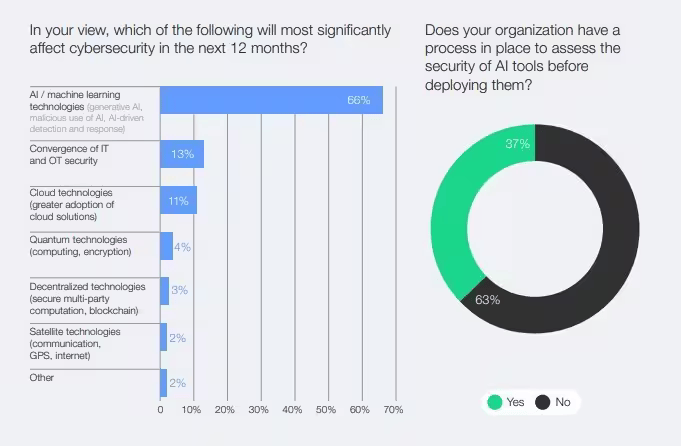
AI and Cybersecurity Threat Outlook for the Next 12 Months
- 66% of respondents believe AI/machine learning technologies (e.g., generative AI, AI-driven detection) will most significantly affect cybersecurity in the coming year.
- Convergence of IT and OT security was cited by 13%, showing growing concern about integrating operational and information technology.
- 11% pointed to cloud technologies, reflecting the impact of expanded cloud adoption.
- Emerging risks include quantum technologies (4%), decentralized technologies (3%), and satellite technologies (2%).
- Only 37% of organizations have a process in place to assess the security of AI tools before deployment, while 63% do not, revealing a critical security gap.
Industry-Wise Breakdown of Cyber Incidents
- The healthcare industry faced a 26% increase in breaches, many involving sensitive patient data and ransomware strains.
- Financial services accounted for 17% of total incidents, driven by credential stuffing and phishing-led frauds.
- The education sector saw a 21% rise, with many K-12 institutions lacking modern cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Retail and e-commerce platforms reported a 16% surge in bot-based attacks, impacting both web and mobile apps.
- Manufacturing sector breaches grew by 13%, often through exploited industrial control systems (ICS).
- Government organizations worldwide have seen a 30% YoY rise, largely attributed to targeted geopolitical attacks.
- Media and telecommunications providers experienced an 18% uptick, particularly around election coverage and public broadcasting.
- Energy and utilities infrastructure reported 12% more attacks, many attempting SCADA and OT system infiltration.
- Technology companies, particularly startups, reported a 15% increase, often due to third-party vulnerabilities.
- Legal and consulting firms saw a 10% rise in targeted data theft, often involving confidential client information.
Financial Impact of Cyberattacks
- The average cost of a data breach in the U.S. reached $5.18 million in Q1 2025.
- Global cybercrime damages are projected to hit $10.5 trillion annually by the end of 2025.
- SMBs reported median losses of $87,000 per attack, often due to ransomware and business email compromise.
- The cost of downtime due to cyber incidents now averages $21,250 per minute.
- Insurance premiums for cybersecurity coverage have surged by 22% YoY, driven by increased claims and complex risk environments.
- Supply chain breaches cost businesses an estimated $1.3 million per incident due to both direct and collateral impacts.
- Phishing-related frauds alone accounted for more than $2.9 billion in financial damages globally in the first five months of 2025.
- Legal fees and regulatory fines now represent 15%–18% of post-breach costs, especially under GDPR and U.S. state privacy laws.
- Reputational damage costs (brand equity loss, PR recovery, customer churn) are estimated to add another $750,000 per breach on average.
- Cybersecurity budgeting has increased in 79% of Fortune 1000 companies, with a median annual investment now at $8.2 million.
Most Targeted Industries by Cyber Attacks
- Manufacturing tops the list with 24% of all cyber attacks, highlighting its vulnerability due to automation and supply chain integration.
- Finance & Insurance follows closely, accounting for 19% of attacks, as cybercriminals target sensitive financial data and transactions.
- Consumer Businesses are hit by 15% of attacks, reflecting risks tied to customer-facing platforms and e-commerce operations.
- The Education sector faces 10% of attacks, often due to outdated systems and increasing reliance on digital learning tools.
- Healthcare experiences 7% of attacks, with cyber threats aimed at patient data, medical devices, and hospital infrastructure.

Ransomware Attack
- Ransomware attacks have decreased by 7% YoY, but the average payout surged to $1.26 million.
- Double extortion tactics (data encryption + leak threats) are used in 72% of ransomware incidents in 2025.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) offerings now dominate the underground market, used in over 60% of campaigns this year.
- Education and healthcare sectors continue to be primary ransomware targets, with a combined 40% of all attacks.
- LockBit and BlackCat remain the most active ransomware groups, responsible for nearly 1 in 4 attacks globally.
- 85% of organizations hit by ransomware experienced repeat attacks within six months, often from different threat actors.
- Only 41% of victims successfully recover all data, even after paying ransoms.
- The average downtime due to ransomware attacks has increased to 24 days, disrupting business continuity and trust.
- Encryption success rate by ransomware groups is now at 76%, showing improved attacker sophistication.
- 50% of ransomware attack entry points originate from exploited remote desktop protocols (RDP) and misconfigured VPNs.
Phishing and Social Engineering Trends
- Phishing attacks remain the top cyber entry point, making up 31% of all initial compromises in 2025.
- Deepfake voice phishing (vishing) incidents increased by 18% YoY, often targeting finance and HR departments.
- Quishing (QR code phishing) now accounts for 1 in 8 phishing campaigns, exploiting mobile-first users.
- Social engineering scams on LinkedIn and WhatsApp surged by 25%, primarily affecting professionals and freelancers.
- AI-generated phishing emails have a 31% higher open rate compared to traditional phishing due to improved realism.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) caused $3.2 billion in estimated losses worldwide in just the first quarter of 2025.
- Cloud-based collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams and Slack have become phishing targets, with a 19% rise in malicious link sharing.
- Impersonation of internal executives (“CEO fraud”) remains common, with 68% of large organizations reporting at least one attempt.
- Smishing (SMS phishing) grew by 11%, fueled by retail and shipping-themed scams.
- Credential harvesting from phishing kits deployed on compromised websites increased by 21% YoY.
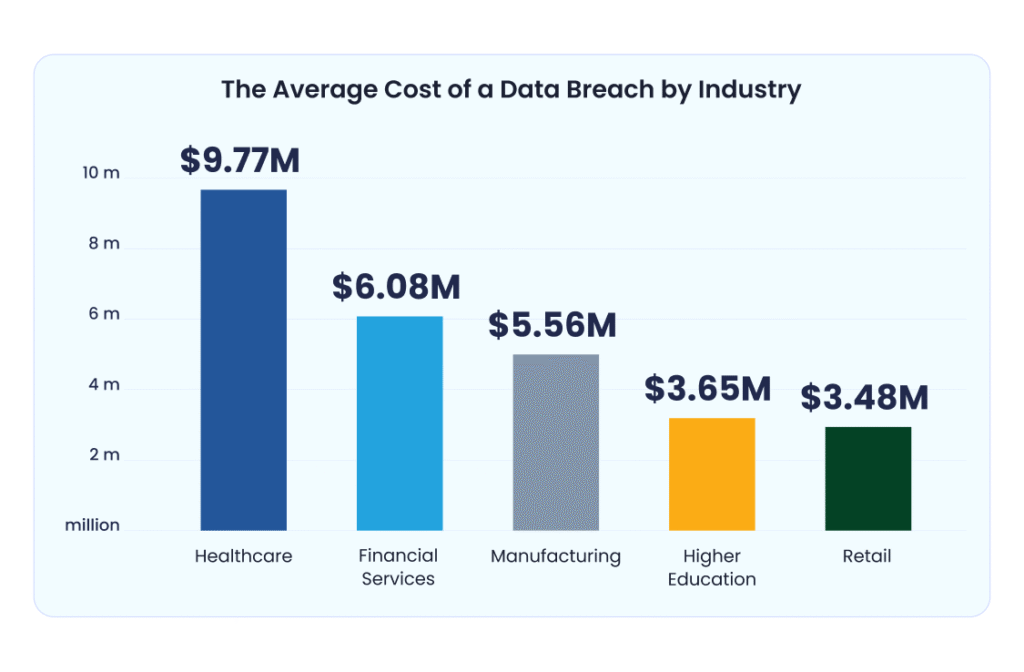
Average Cost of a Data Breach by Industry
- Healthcare tops the chart with an average data breach cost of $9.77 million, making it the most expensive industry to be targeted.
- Financial Services ranks second with $6.08 million in average breach costs, reflecting the high value of sensitive financial data.
- Manufacturing incurs an average loss of $5.56 million per breach, underlining growing cyber risks in industrial operations.
- Higher Education faces average breach costs of $3.65 million, due to increasing digitization and legacy system vulnerabilities.
- Retail has an average breach cost of $3.48 million, driven by customer data exposure and e-commerce attacks.
Data Breaches and Information Theft Metrics
- Over 1.7 billion records have been exposed through data breaches globally in the first four months of 2025.
- Misconfigured cloud storage remains a top cause, contributing to 24% of total breach volume.
- The average detection time for a breach is about 207 days, with containment taking an additional 78 days.
- Credential theft is responsible for 46% of data breaches, often linked to poor password reuse and MFA gaps.
- Healthcare breaches accounted for 18% of records leaked.
- Government databases saw an increase of 33% in breach volume, much of it attributed to politically motivated actors.
- 75% of breached companies reported secondary incidents due to stolen data being sold or reused.
- Dark web listings for PII and PHI increased by 21%, with full identity kits fetching up to $120 per set.
- APIs are increasingly exploited, responsible for 14% of unauthorized data access in enterprise environments.
- Data breach notification regulations have resulted in a 9% increase in public disclosures in the U.S. alone.
Nation-State and Geopolitical Cyber Threats
- 22% of high-profile attacks in 2025 show indicators of nation-state involvement, often tied to espionage or infrastructure sabotage.
- U.S. federal agencies reported a 17% increase in suspected state-backed intrusions compared to early 2024.
- Critical infrastructure, including power grids and water utilities, remains a key target, with over 50 documented probes in 2025 so far.
- Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea continue to be the most active APT actors based on TTP patterns and threat intel.
- Hybrid warfare, blending kinetic and cyber tactics, is rising, with incidents tied to regional conflicts and elections.
- DDoS campaigns from politically affiliated groups have increased by 29%, especially targeting financial news and defense portals.
- Credential dumps linked to state activity have been traced back to at least 17 campaigns, mostly through spear phishing and supply chain breaches.
- Cyber mercenaries and private contractors now play a role in 34% of government-related attacks, complicating attribution.
- Advanced malware like wipers and rootkits is increasingly deployed for destructive impact in state-sponsored operations.
- Multinational defense contractors have reported a 12% rise in targeted intrusions, often through cloud collaboration platforms.
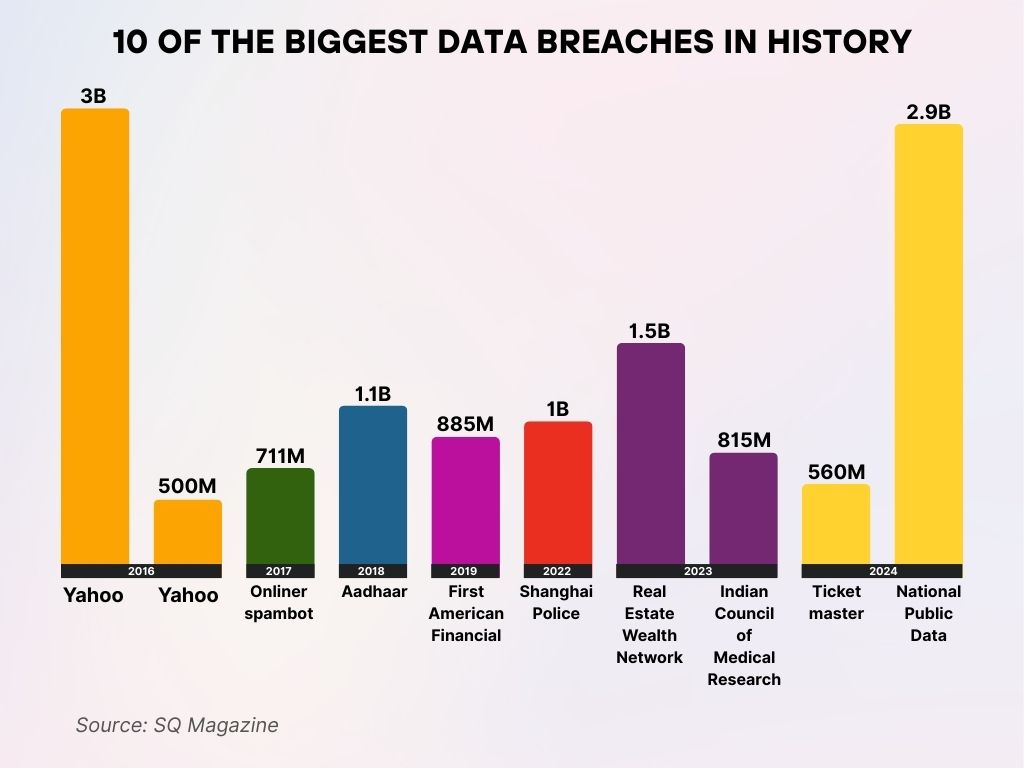
10 of the Biggest Data Breaches in History
- Yahoo (2016) tops the list with 3 billion records compromised, marking the largest data breach ever recorded.
- A second Yahoo breach (2016) exposed an additional 500 million accounts.
- The Onliner spambot (2017) breach affected 711 million email addresses, used to deliver massive spam campaigns.
- India’s Aadhaar (2018) database breach compromised 1.1 billion citizen records, raising major privacy concerns.
- First American Financial (2019) leaked 885 million sensitive real estate documents due to poor security controls.
- The Shanghai Police (2022) breach exposed 1 billion citizens’ records in one of the largest leaks of government data.
- Real Estate Wealth Network (2023) saw 1.5 billion records compromised, highlighting risks in property tech platforms.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (2023) faced a breach affecting 815 million health-related records.
- Ticketmaster (2024) suffered a breach of 560 million user records, impacting customer trust and security.
- The National Public Data breach (2024) exposed 2.9 billion records, ranking as the second-largest breach ever.
Emerging Threat Vectors and Techniques
- AI-powered malware usage has increased by 43% YoY, enabling more adaptive and evasive attack behaviors.
- Quantum decryption threats are still theoretical, but have prompted 15% of Fortune 500 companies to begin quantum-resilient encryption pilots.
- Fileless malware attacks are up 29%, often leveraging PowerShell and memory-only payloads to evade detection.
- Synthetic identity fraud is rising, with fraud rings creating over 110,000 fake identities per month using mixed data sources.
- Adversarial AI attacks on machine learning models have increased by 26%, mostly affecting fraud detection and spam filters.
- Shadow IT vulnerabilities continue to climb, with unauthorized app usage accounting for 21% of successful breaches.
- Living off the land (LotL) techniques, where attackers exploit legitimate admin tools, are used in 64% of advanced attacks.
- Third-party SaaS integrations have been exploited in 13% of corporate data leaks due to token and API mismanagement.
- Malicious browser extensions and plug-ins are gaining traction, with a 16% increase in detection events.
- Smart contract exploits in Web3 environments resulted in over $487 million in crypto-related losses in just Q1 2025.
Cybersecurity Response and Detection Times
- The average detection time in 2025 is 207 days, with containment taking an average of 78 additional days.
- Real-time detection using AI-based tools is now employed by 47% of global enterprises, a 12% YoY increase.
- 60% of companies with automated incident response report attacks within 12 hours, compared to 29% without it.
- SMBs without a dedicated security team took an average of 282 days to detect breaches in early 2025.
- Intrusion detection via SIEM systems caught 38% of early-stage attacks, while EDR platforms intercepted 21%.
- Mean time to remediation (MTTR) is currently 4.7 days, down from 6.3 days in 2024 for major U.S. organizations.
- Attack dwell time has dropped slightly overall, but remains high in supply chain intrusions (average 92 days).
- 22% of organizations still lack an incident response plan, with many citing budget or complexity as primary barriers.
- The use of deception technology (honeypots, honeytokens) rose by 17%, aiding in quicker containment and forensic accuracy.
- Cyber incident reporting within the first 48 hours is now mandatory in 19 U.S. states, boosting early containment metrics.
Cybersecurity Compliance Stats by Company
- 66% of companies say compliance mandates are driving spending, highlighting regulatory influence on security budgets.
- 78% expect annual increases in regulatory requirements, signaling a growing compliance burden.
- 15% of companies have over 1 million files accessible to every employee, posing a massive data exposure risk.
- 60% report more than 500 accounts with non-expiring passwords, a serious vulnerability in access control.
- 77% of organizations lack an incident response plan, leaving them unprepared for potential cyber incidents.

Small and Medium-Sized Business Targets
- SMBs accounted for 41% of all cyberattacks in 2025 so far, with phishing and credential theft leading the list.
- Only 34% of SMBs have a full-time IT security staff, leaving many vulnerable to persistent threats.
- One in five SMBs hit by ransomware had to suspend operations temporarily, some permanently.
- 90% of small businesses that suffered a breach cited a lack of employee training as a primary factor.
- SMB-targeted malware campaigns are up 23%, often disguised as software updates or invoice attachments.
- The average breach cost for SMBs is now $96,000, with many struggling to recover within six months.
- Small law firms and private clinics have become prime targets due to their sensitive data and weak cyber hygiene.
- Mobile device compromise among SMBs rose by 28%, driven by BYOD culture and remote workforces.
- Only 11% of SMBs conduct regular penetration testing, increasing the risk of unpatched vulnerabilities.
- Cloud misconfiguration accounted for 18% of SMB breaches, mostly from third-party platforms and misused storage buckets.
Cloud Security and Cyberattack Incidence
- Cloud infrastructure attacks rose by 21% YoY, with identity-based breaches leading the charge.
- Credential compromise is responsible for 52% of cloud-related breaches in 2025.
- Multi-cloud environments were 3x more likely to suffer a breach due to integration complexity and access sprawl.
- 80% of cloud breaches involved human error, often due to poor IAM configurations and a lack of audit logging.
- Serverless application vulnerabilities were exploited in 9% of attacks, often through exposed function endpoints.
- Data exfiltration via misconfigured S3 buckets continues to be a persistent issue, responsible for over 120 million leaked records in Q1 2025.
- Container security incidents increased by 17%, often linked to vulnerabilities in open-source packages and image registries.
- Cloud-native ransomware attacks targeting backup snapshots and block storage volumes rose by 14%.
- Access token theft via OAuth abuse was behind 11% of targeted enterprise cloud breaches this year.
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) adoption reached 37%, indicating progress toward better segmentation and control.
Cybersecurity Insurance Claims Data
- Cyber insurance claims increased by 31% in early 2025, with ransomware and data theft leading the filings.
- 83% of claim payouts were linked to attacks involving human error or social engineering.
- Median claim size has grown to $287,000, driven by legal, notification, and forensic costs.
- Underwriters now require evidence of MFA and endpoint protection for policy renewals.
- Policy exclusions for state-sponsored attacks have become more stringent, often complicating coverage for geopolitical threats.
- More than 60% of U.S. cyber policies now include breach coaching and forensic investigation coverage.
- Business interruption claims account for 23% of payouts, particularly in retail and manufacturing.
- SMBs struggle to secure affordable cyber insurance, with premiums rising 22% YoY and denial rates climbing.
- Bundled policies with cybersecurity software vendors have increased 19%, offering cost-effective protection packages.
- Claims tied to insider threats doubled since 2024, particularly in healthcare and legal sectors.
Recent Developments
- In April 2025, a multi-country task force dismantled one of the largest phishing-as-a-service rings, operating across 18 nations.
- U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) finalized a new rule requiring cyber incident disclosures within 72 hours.
- Apple, Google, and Microsoft jointly announced the default adoption of passkeys over passwords on all devices by year-end.
- A major breach of an AI healthcare platform exposed 11.4 million patient records, prompting HIPAA policy reviews.
- NIST released a 2025 update to its Cybersecurity Framework (CSF), emphasizing supply chain risk and AI defense.
- A new AI-based malware variant (“NeuroStrike”) has emerged, capable of rewriting its code mid-execution.
- GitHub and npm repositories were targeted in a widespread typosquatting campaign, affecting over 5,000 packages.
- The FBI issued a warning on SIM swap scams, which rose by 19% this year, often used to breach multi-factor authentication.
- China and the EU announced new AI-cybersecurity guidelines, focused on responsible model deployment and attack surface minimization.
- Several major banks launched “cyber vault” systems to isolate critical operations in the event of a breach.
Conclusion
The landscape of cyber threats in 2025 is more dynamic, multi-faceted, and aggressive than ever. While organizations globally are investing more in preventive controls and response automation, threat actors are also evolving, leveraging AI, social engineering, and system misconfigurations at scale.
From SMBs to state agencies, the targets have expanded, but so have the tools to fight back. The future of cybersecurity lies not just in defense, but in resilience, developing systems that adapt, recover, and learn.
Whether you’re a business leader, IT manager, or a concerned citizen, understanding these numbers isn’t optional, it’s mission-critical.