A quiet morning in Atlanta turned chaotic for a mid-sized healthcare provider. Every computer screen across the facility suddenly went dark, replaced by a single message: “Your data has been encrypted.” Operations froze. Appointments were canceled. And the cost of recovery reached into the millions.
Unfortunately, this isn’t a rare event anymore; it’s part of a growing digital crisis. As we move through 2025, cyber threats are no longer fringe risks; they’re mainstream hazards. In this article, we break down the latest cyber threat statistics, giving you a clear and data-backed view of where the world stands today.
Editor’s Choice
- 78% of organizations worldwide reported at least one cybersecurity incident in the past 12 months.
- 38% of global ransomware attacks in 2025 targeted the United States, the highest share of any country.
- $5.2 million is the average cost of a data breach in the financial sector, the highest across all industries.
- 91% of successful attacks in 2025 started with a phishing email.
- 30 billion records were exposed in data breaches globally during the first half of 2025.
- 62% of CISOs reported AI-driven threats as their top concern in 2025, marking a shift from malware to automation-based attacks.
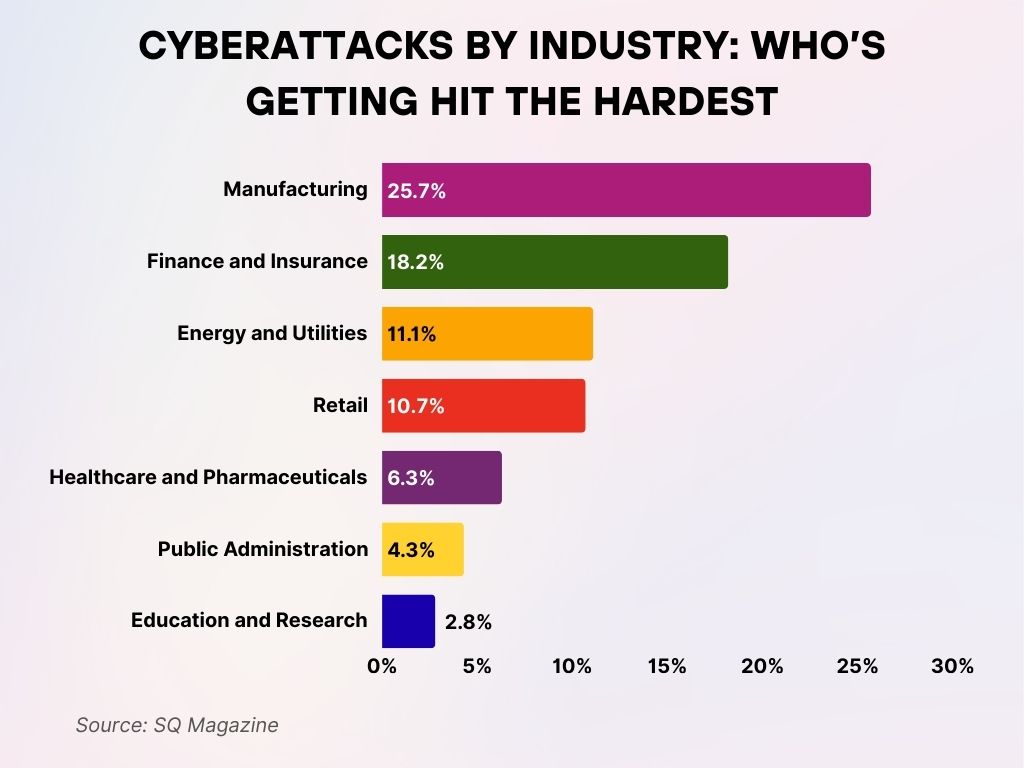
Cyberattacks by Industry: Who’s Getting Hit the Hardest
- Manufacturing is the top target, accounting for 25.7% of all cyberattacks, highlighting the sector’s growing digital vulnerabilities.
- The Finance and Insurance industry follows, facing 18.2% of attacks, reflecting its high-value data and financial assets.
- Energy and Utilities infrastructure experienced 11.1% of total attacks, underscoring critical risks to national infrastructure.
- The Retail sector saw 10.7% of attacks, likely driven by consumer data theft and online payment systems.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals were hit in 6.3% of cases, emphasizing the sensitive nature of patient data.
- Public Administration accounted for 4.3% of attacks, pointing to government systems as another key target.
- Education and Research institutions faced 2.8% of cyberattacks, as digital learning platforms and research data remain exposed.
Financial Impact of Cybersecurity Breaches
- The average cost of a data breach globally reached $4.67 million in 2025.
- In the United States, the average cost per breach is significantly higher, at $9.6 million.
- Ransomware payouts in 2025 have hit a record $1.76 million per incident, with many organizations still choosing to pay.
- Downtime due to cyberattacks costs businesses an average of $350,000 per hour in lost revenue and productivity.
- The healthcare industry saw total breach costs of $11.3 billion in 2025, the most of any sector.
- Insurance premiums for cyber liability rose by 23% as underwriters adjust to higher incident frequency.
- 70% of SMBs that experienced a significant breach in the past year reported financial loss exceeding $250,000.
- 46% of affected enterprises lost customer trust, resulting in measurable drops in churn-sensitive industries like SaaS and e-commerce.
- Publicly traded companies experiencing a major breach saw their stock drop by 5.7% on average within 30 days.
- Compliance fines under GDPR and similar global regulations totaled over $2.9 billion globally in the first half of 2025.
- The combined economic impact of cyberattacks across the top 10 U.S. sectors is expected to surpass $1.4 trillion this year.
Cybersecurity Readiness and Spending Trends
- Global cybersecurity spending is projected to reach $215 billion in 2025.
- 72% of organizations increased their cybersecurity budgets this year, prioritizing detection and response.
- SMBs, however, spend only 14% of their IT budget on cybersecurity on average, leaving them vulnerable.
- Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) saw a 28% increase in demand as companies outsource cyber defense.
- Zero Trust architecture adoption has grown to 61% of large enterprises in 2025.
- Cyber insurance uptake rose to 62% of mid-to-large-sized firms, a 9-point jump from last year.
- Investment in security AI and machine learning tools is up 33% globally.
- 38% of companies have hired full-time threat hunters or red teams internally.
- CISOs report that 43% of their security budgets now go toward cloud and endpoint protection solutions.
- DevSecOps integration is accelerating, with 56% of agile teams now including security specialists.
- Gartner predicts that by 2027, over 50% of enterprise software contracts will include specific cybersecurity SLAs.
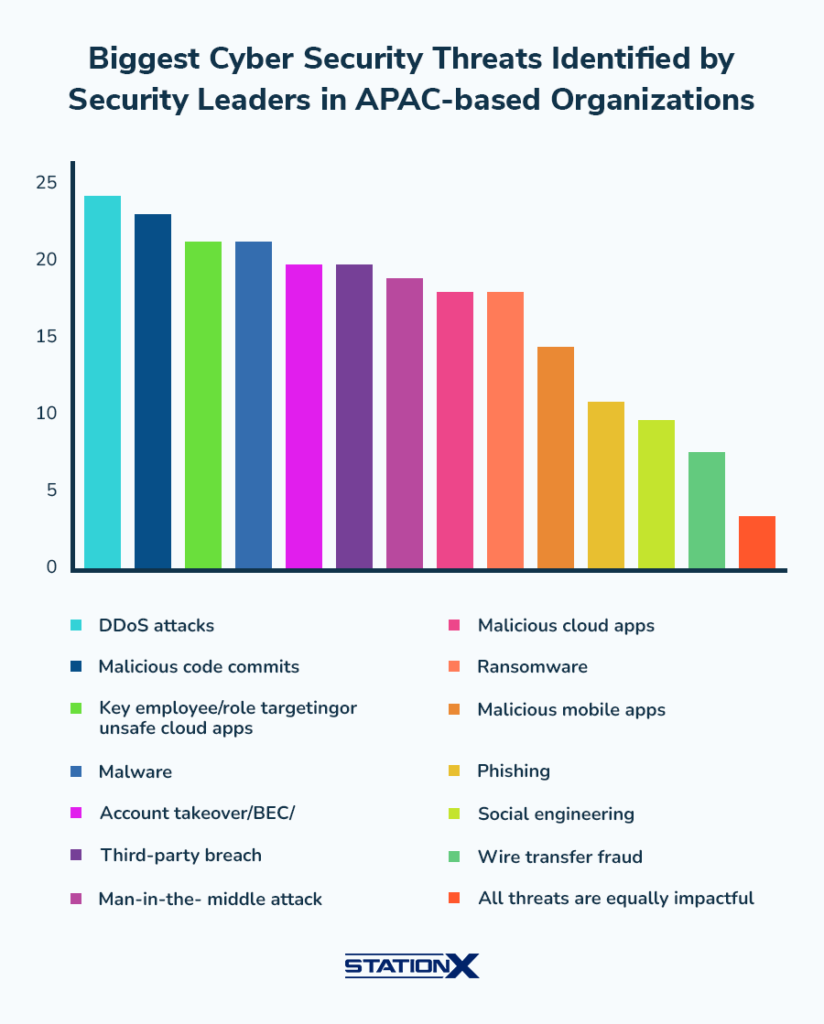
Top Cybersecurity Threats Faced by APAC Organizations
- DDoS attacks were the most cited threat, identified by over 24% of security leaders in the APAC region.
- Malicious code commits are closely followed, flagged by around 23% of respondents.
- Key employee/role targeting and unsafe cloud apps each posed serious concerns for 21% of security professionals.
- Malware remains a persistent issue, affecting 21% of organizations.
- Account takeovers and BEC threats impacted nearly 20% of companies.
- Third-party breaches and man-in-the-middle attacks were each recognized by 19% of leaders.
- Malicious cloud apps and ransomware threats were cited by 18% of respondents.
- Malicious mobile apps worried 14%, highlighting mobile security gaps.
- Phishing was identified by 11% of organizations as a top concern.
- Social engineering and wire transfer fraud were flagged by 9% and 8% respectively.
- Only 4% believed that all threats are equally impactful, emphasizing the need for prioritized security strategies.
Human Error and Insider Threat
- 84% of breaches in 2025 involved a human element, either error, misuse, or social engineering.
- Phishing email clicks increased by 7%, with healthcare and education workers being the most frequent victims.
- Insider threats (both accidental and malicious) account for 22% of all breaches.
- 43% of employees admit to having used unsecured personal devices to access corporate networks.
- Remote work continues to be a vulnerability, with 34% of security incidents tied to remote access endpoints.
- Misconfigured cloud settings, often due to human error, led to over 18% of data leaks in 2025.
- Only 49% of organizations conduct phishing simulations or employee security training quarterly.
- Third-party contractors and vendors were involved in 15% of internal breaches, showing external risk convergence.
- Privileged access misuse rose by 21%, with several high-profile breaches traced to IT admin credential abuse.
- 30% of companies still allow default or weak passwords in backend systems, despite industry guidelines.
- Behavioral analytics adoption is growing, with 27% of enterprises using it to identify suspicious internal patterns.
Phishing and Ransomware Incident Rates
- Phishing attacks rose by 39% year-over-year, driven by AI-generated content and hyper-personalization.
- Ransomware attacks surged by 34%, and now affect 1 in every 4 organizations globally.
- Initial access brokers are fueling the rise in ransomware by selling breached credentials to syndicates.
- Email spoofing and business impersonation attempts increased by 31%.
- Education and government sectors experienced the highest phishing incident growth, at 51% and 47%, respectively.
- 91% of organizations report at least one phishing attempt each month.
- 23% of ransomware victims paid the ransom but never regained access to their data.
- AI-generated phishing emails have a 68% open rate, nearly double that of traditional phishing campaigns.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operations expanded by 22%, lowering the barrier to entry for cybercriminals.
- Phishing kits sold on the dark web increased by 36%, often with built-in evasion tools.
- Detection time for phishing threats is improving, now averaging 27 hours, compared to 44 hours last year.
Top Cybersecurity Threats to Watch
- AI-driven malware leads the list, with 43.4% of experts identifying it as the most dangerous cybersecurity threat in 2025.
- AI-enhanced password cracking comes next at 39.2%, reflecting growing concerns about AI’s role in breaking authentication.
- Ransomware as a service remains a critical threat, cited by 38.4% of cybersecurity professionals.
- Supply chain attacks were flagged by 33.6%, showing how third-party vulnerabilities are increasingly exploited.
- Shadow IT, or the use of unauthorized tech, was named by 32.6% as a major risk.
- IoT device vulnerabilities ranked high at 30.2%, highlighting the insecure nature of many connected devices.
- Deepfakes, though newer in the threat landscape, were still identified by 27.5% of experts as a serious concern.

Cloud Security and Data Breach
- 62% of all breaches in 2025 involved cloud assets, up from 45% just two years ago.
- Misconfigured storage buckets remain a leading cause of cloud breaches, contributing to 21% of incidents.
- Data leaks from third-party SaaS apps increased by 37%, especially among marketing and HR tools.
- Zero-trust security adoption in cloud environments reached 58%, up from 42% last year.
- Multi-cloud deployments face 2.4x more breach attempts than single-cloud setups.
- 36% of organizations still store sensitive data in unencrypted form in cloud databases.
- Over 65% of cloud breaches are traced back to poor identity and access management practices.
- Cloud workload protection spending grew by 29%, as firms moved to secure containers and serverless functions.
- Account hijacking incidents in cloud services jumped by 31%, often exploiting OAuth token vulnerabilities.
- 98% of companies using the cloud have experienced at least one misconfiguration-related security event.
- Public cloud providers, such as AWS and Azure, saw increasing attacks targeting APIs, rising by 40% year-over-year.
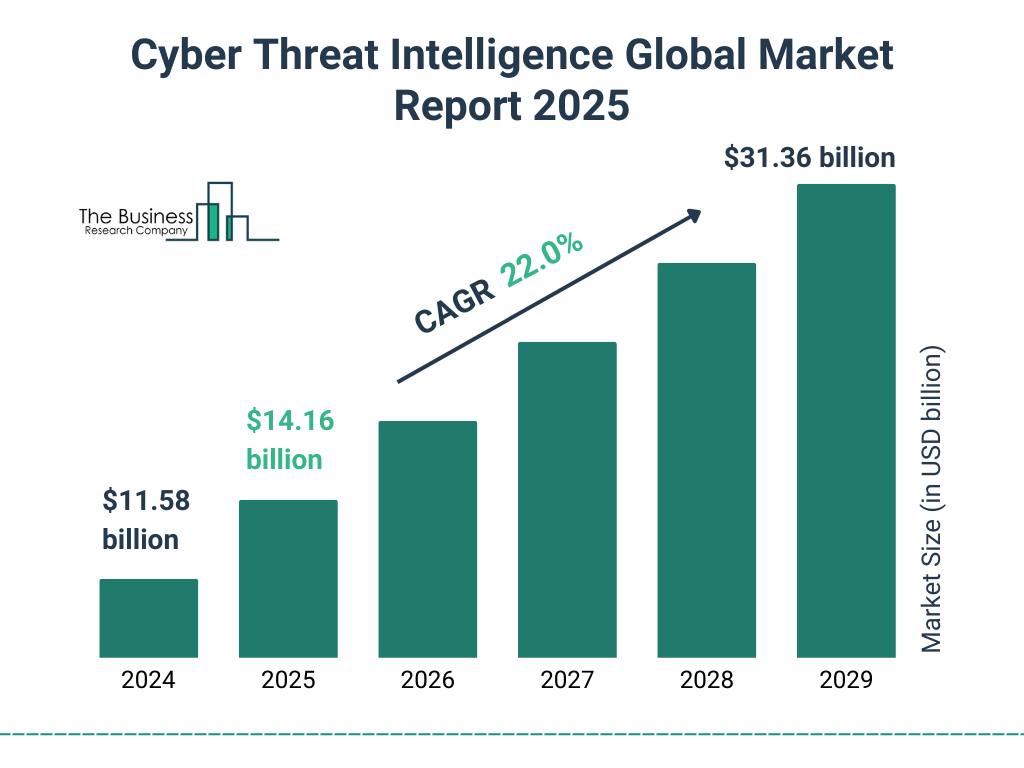
Cyber Threat Intelligence Market Growth Outlook
- The global cyber threat intelligence market was valued at $11.58 billion in 2024.
- It is expected to rise to $14.16 billion in 2025, showing strong year-over-year momentum.
- A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.0% is projected between 2024 and 2029.
- By 2029, the market is forecasted to reach a substantial $31.36 billion, nearly tripling in just five years.
Small Business Vulnerabilities to Cyber Threats
- 43% of all cyberattacks in 2025 targeted small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs).
- Only 18% of SMBs have a dedicated cybersecurity team or officer in place.
- 75% of SMBs say they would not survive more than three weeks after a severe cyberattack.
- Ransomware is the most common threat, affecting 1 in 5 SMBs this year.
- SMBs experience an average downtime of 21 days following a successful cyber incident.
- 41% of SMBs store customer and payment data without any encryption in their systems.
- Less than 40% of SMBs conduct regular cybersecurity awareness training.
- Only 28% have cyber insurance, leaving many exposed to breach-related costs.
- Website defacements and fake login pages affecting SMBs rose by 34%, especially in e-commerce.
- SMBs using outdated software are 5x more likely to suffer from malware-based attacks.
- Cybersecurity investment per SMB employee averages just $380/year, significantly below enterprise standards.
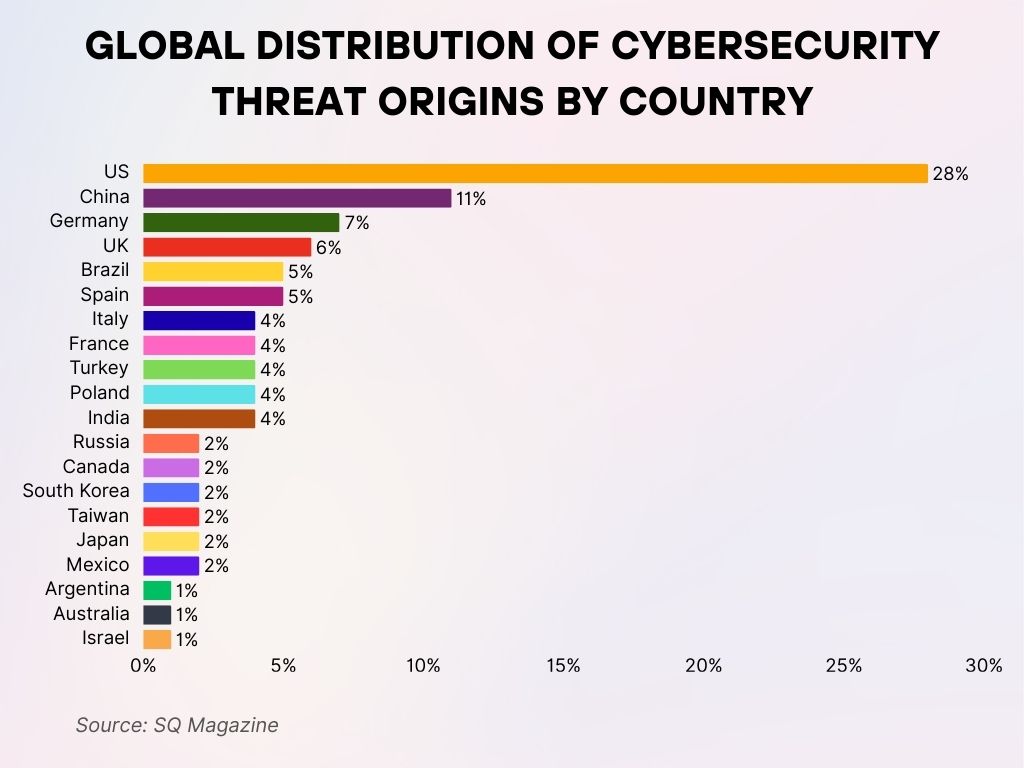
Global Distribution of Cybersecurity Threat Origins by Country
- The US leads significantly, accounting for 28% of global cybersecurity threats.
- China ranks second with 11%, highlighting its major presence in the threat landscape.
- Germany contributes 7%, the highest among European countries.
- The UK follows with 6%, also representing a major source of attacks.
- Brazil and Spain each account for 5%, reflecting rising activity in Latin America and Europe.
- Countries like Italy, France, Turkey, Poland, and India are tied at 4% each.
- Nations including Russia, Canada, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Mexico are all at 2%.
- Argentina, Australia, and Israel each represent 1% of global cyber threats.
Zero-Day Exploits and Advanced Threats
- Zero-day vulnerabilities exploited in the wild rose by 23% in 2025, reaching a new record.
- Browser and OS-level exploits accounted for 56% of zero-day attacks, especially targeting Chrome and Windows.
- 18 major zero-day flaws were actively used by nation-state actors in Q1 2025 alone.
- APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) campaigns increased by 31%, with a more stealthy dwell time before detection.
- Detection time for zero-day incidents averages 42 days, leaving systems exposed.
- AI is now being used to automate exploit detection, with 38% of security vendors integrating ML-driven threat hunting.
- Attackers now use evasion-aware malware that rewrites itself to bypass endpoint detection tools.
- Email and document-based delivery vectors accounted for 44% of zero-day exploits in 2025.
- Remote work tools, such as collaboration and video conferencing apps, are new high-value targets for zero-day bugs.
- Firmware-level attacks, especially against routers and IoT devices, rose by 19%.
- Bug bounty programs paid out over $45 million globally in 2025 to ethical hackers who reported critical zero-days.
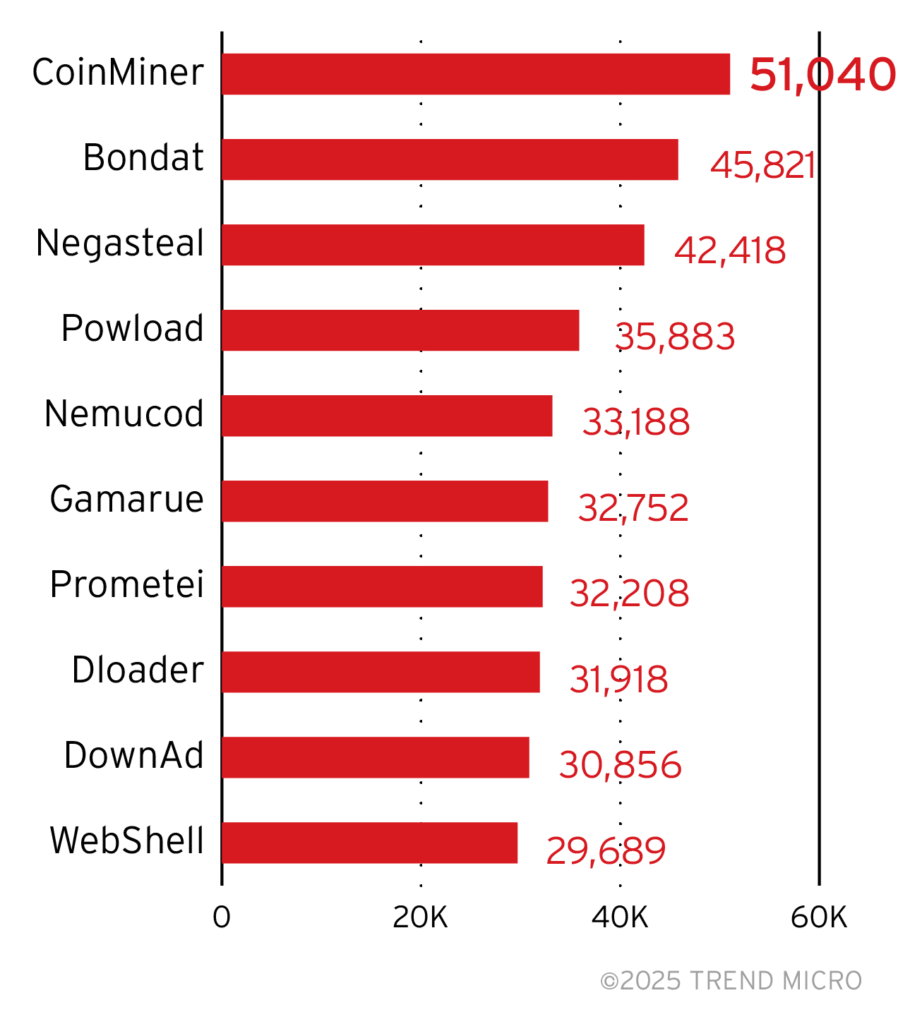
Top Malware Families Detected
- CoinMiner topped the list with 51,040 detections, underscoring the widespread threat of cryptojacking malware.
- Bondat followed with 45,821 incidents, continuing to target connected devices for botnet activities.
- Negasteal, known for data theft, was detected 42,418 times.
- Powload registered 35,883 detections, often used to deliver additional malware payloads.
- Nemucod, a Trojan downloader, had 33,188 cases.
- Gamarue, a known worm malware, showed 32,752 detections.
- Prometei, associated with botnet operations, had 32,208 hits.
- Dloader was detected 31,918 times, known for spreading additional threats.
- DownAd, linked to adware and backdoors, had 30,856 detections.
- WebShell infections reached 29,689, posing serious risks to web server security.
AI and Automation in Cyber Threat Detection
- Over 60% of enterprise security teams now use AI-powered tools for real-time threat analysis.
- AI-driven SOC platforms reduced response times by 41%, boosting operational efficiency.
- Machine learning-based anomaly detection helped identify 74% of stealth attacks missed by traditional firewalls.
- Automated patch management tools were adopted by 48% of companies.
- Conversational AI phishing bots are emerging threats, capable of real-time victim interaction and manipulation.
- AI-generated malware, created and deployed without human coding, has grown by 27% since last year.
- Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) systems are deployed by 54% of Fortune 1000 firms.
- False positives in threat detection dropped by 35% due to AI refinements in 2025.
- AI-enabled insider threat detection tools flagged 30% more behavioral anomalies than human analysts.
- Generative AI is also being used by attackers to craft deepfake voicemails and personalized bait.
- Cybersecurity vendors now allocate more than 40% of their R&D budgets to AI-based toolsets.
Recent Developments in Cyber Threat Landscape
- Cybercrime forums on the dark web now sell bundled ransomware kits for under $50, making entry easier for novices.
- Law enforcement globally disrupted 12 major ransomware gangs in the first half of 2025, including affiliates of LockBit and BlackCat.
- Cryptocurrency wallet exploits and smart contract breaches increased by 19%, fueled by rising DeFi adoption.
- Synthetic identity fraud grew by 42%, often blending real and fake data for undetected infiltration.
- State-sponsored attacks on election infrastructure were reported in at least seven countries, including the US and India.
- Social media impersonation scams targeting public figures and CEOs surged by 39%.
- New malware strains in 2025 deploy self-deletion routines to evade forensic analysis.
- Quantum computing risks are now factored into long-term security planning by 22% of Fortune 500 firms.
- Credential phishing using QR codes is up 46%, driven by trust in physical-visual formats.
- Cybersecurity workforce shortages remain critical, with 3.4 million jobs unfilled globally.
- Major vendors, including Microsoft and Google, have launched “Secure by Design” initiatives to harden products at the code level.
Conclusion
As cybercrime grows more industrialized, hyper-targeted, and AI-enhanced, the digital world in 2025 faces unprecedented risk. Organizations of all sizes are under pressure to strengthen their security posture, not just through tools, but through awareness, governance, and rapid response.
What’s clear is this: cyber threats are no longer occasional disruptions; they’re ongoing, evolving battles. By understanding the trends and preparing accordingly, businesses and individuals alike can build resilience in a landscape that’s only getting more complex.