WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
- Editor’s Choice
- Key Cybersecurity Drivers
- Global Cybercrime Costs
- Industries Most Targeted by Cyber Threats
- Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- Average Cost of a Data Breach
- Ransomware Trends
- Key Benefits of Partnering with a Security Expert
- Phishing and Social Engineering Data
- Cybersecurity Workforce Shortages
- Cybersecurity Rule Adoption by UK Businesses
- Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
- Small Business Cybersecurity Impact
- How SMBs Expect AI to Strengthen Cyber Defense
- IoT and Endpoint Security Risks
- Spending on Cybersecurity Solutions
- AI Security Procedures by Organization Size
- Role of AI and Automation in Cyber Defense
- Cybersecurity Compliance and Regulatory Trends
- Regional Breakdown of Cyber Incidents
- Recent Developments in Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
- Sources
In early 2025, a small tech startup in Austin, Texas, discovered its customer database had been silently siphoned off over a period of three months. The breach wasn’t sophisticated—it was a simple phishing email that bypassed outdated filters. But the consequences were staggering: legal fees, compliance penalties, and reputational damage tallied over $1.3 million. This isn’t an isolated case. Across sectors and geographies, cyber threats have become a pressing business risk, no longer just an IT issue, but a boardroom concern.
The following statistics offer a data-driven glimpse into the state of cybersecurity in 2025, helping decision-makers understand where the greatest vulnerabilities and threats lie and where to focus efforts for defense.
Editor’s Choice
- Global cybercrime is expected to cost $13 trillion in 2025.
- In 2025, 63% of organizations reported at least one data breach, a 12% increase from the previous year.
- The average time to detect a breach has dropped to 189 days, reflecting growing investments in detection technologies.
- Ransomware incidents rose by 21% year-over-year, with targeted sectors including education, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- 92% of malware is now delivered via email, making phishing the most prevalent initial attack vector.
- Cybersecurity spending is projected to reach $223 billion globally in 2025, driven by endpoint security and cloud protection tools.
- The shortage of qualified cybersecurity professionals stands at 4.1 million globally, with nearly 540,000 in the US alone.
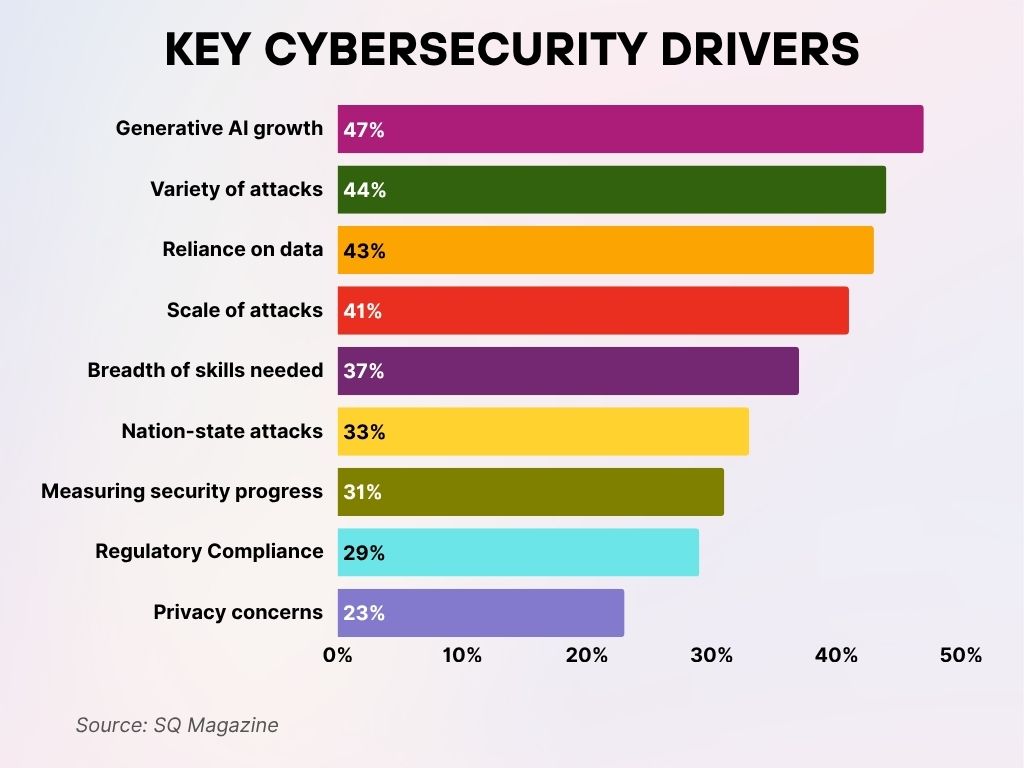
Key Cybersecurity Drivers
- Generative AI growth is the top cybersecurity driver, cited by 47% of respondents as a major influence on security strategies.
- A diverse range of cyberattacks is pushing organizations to adapt, with 44% highlighting the variety of attacks as a key concern.
- 43% of cybersecurity professionals are driven by the increasing reliance on data, underscoring data protection as a critical priority.
- The scale of cyberattacks continues to grow, with 41% identifying it as a significant pressure point.
- A shortage in expertise remains a challenge, as 37% point to the breadth of skills needed to defend against modern threats.
- Nation-state attacks are a growing worry, influencing the cybersecurity agenda for 33% of respondents.
- 31% of organizations struggle with measuring security progress, highlighting the need for better metrics and visibility.
- Regulatory compliance remains a strong driver, with 29% emphasizing its impact on cybersecurity planning.
- Privacy concerns, while still important, rank lower, mentioned by 23% as a primary driver for cybersecurity efforts.
Global Cybercrime Costs
- Cybercrime costs are forecasted to reach $13 trillion by the end of 2025.
- Losses from business email compromise (BEC) exceed $3 billion globally, marking it as one of the costliest attack types in 2025.
- The cost of cyber insurance premiums increased by 28% year-over-year, reflecting the higher risk landscape.
- Identity theft cases grew by 17%, largely due to data from previous breaches being repurposed in new scams.
- Cryptojacking incidents increased by 34%, as threat actors target cloud infrastructure for mining operations.
- State-sponsored cyberattacks accounted for 12% of total cybercrime costs in 2025.
- The estimated cost of downtime due to cyberattacks reached $1.5 trillion, impacting both large enterprises and mid-market companies.
Industries Most Targeted by Cyber Threats
- Healthcare remains the top-targeted industry in 2025, with 37% of all ransomware attacks aimed at hospitals and medical networks.
- Manufacturing surpassed finance as the second most attacked sector, due to its reliance on outdated systems and IoT devices.
- The education sector saw a 22% increase in reported cyberattacks, many linked to unsecured virtual learning platforms.
- Financial institutions experienced a 13% drop in successful breaches, attributed to stronger encryption and fraud monitoring.
- Retail faced a 28% rise in credential stuffing attacks, targeting e-commerce portals.
- The government sector reported a 16% rise in insider threats and nation-state attacks.
- Media and entertainment firms saw a 19% increase in digital rights theft and streaming service credential hacks.
- Energy providers experienced a 26% surge in SCADA-targeted malware, especially in regions with aging infrastructure.
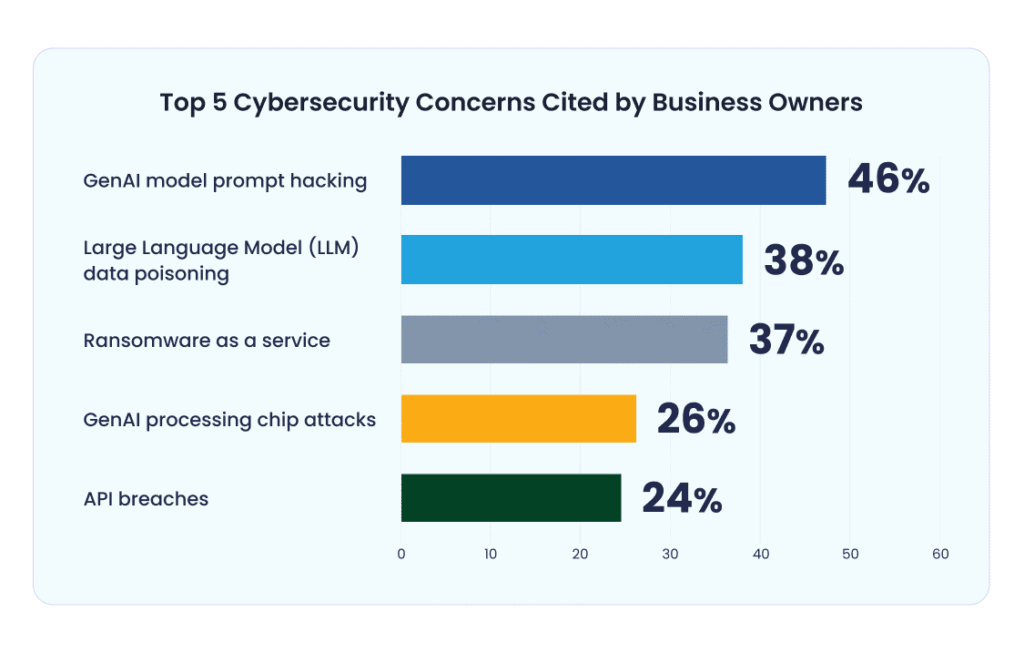
Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- 46% of business owners are most concerned about GenAI model prompt hacking, making it the leading cybersecurity threat.
- Large Language Model (LLM) data poisoning is the second-highest concern, cited by 38% of respondents.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) follows closely, with 37% seeing it as a major risk.
- 26% express worry over GenAI processing chip attacks, highlighting hardware-related vulnerabilities.
- API breaches are flagged by 24% as a critical concern in today’s interconnected systems.
Average Cost of a Data Breach
- The average cost of a data breach in 2025 is $4.62 million.
- For US-based companies, that figure jumps to $9.5 million on average, making it the most expensive country for breach recovery.
- Healthcare breaches cost an average of $11 million, the highest among all sectors.
- Organizations with zero-trust frameworks saved an average of $1.76 million per breach compared to those without.
- Detection and escalation costs account for 41% of the total breach expense.
- Legal and regulatory fines make up 13% of post-breach costs in highly regulated industries.
- Organizations using AI-based security tools reduced breach costs by 23%, highlighting the ROI of automation.
Ransomware Trends
- Ransomware attacks surged 21% in 2025, with attackers now focusing on data exfiltration over encryption.
- The average ransom demand exceeded $1.8 million, while the average payment made was approximately $850,000.
- 42% of victims paid the ransom, but only 68% of them recovered full access to their data.
- Double extortion tactics—stealing data before encryption—were used in 73% of ransomware cases.
- Healthcare and education sectors remain the most targeted, due to time-sensitive operations and legacy systems.
- RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service) kits are being sold on the dark web for as low as $50, enabling low-skill actors.
- Small to midsize enterprises (SMEs) accounted for 61% of all ransomware reports.
- Ransomware dwell time (the time between breach and activation) was shortened to 5.2 days.
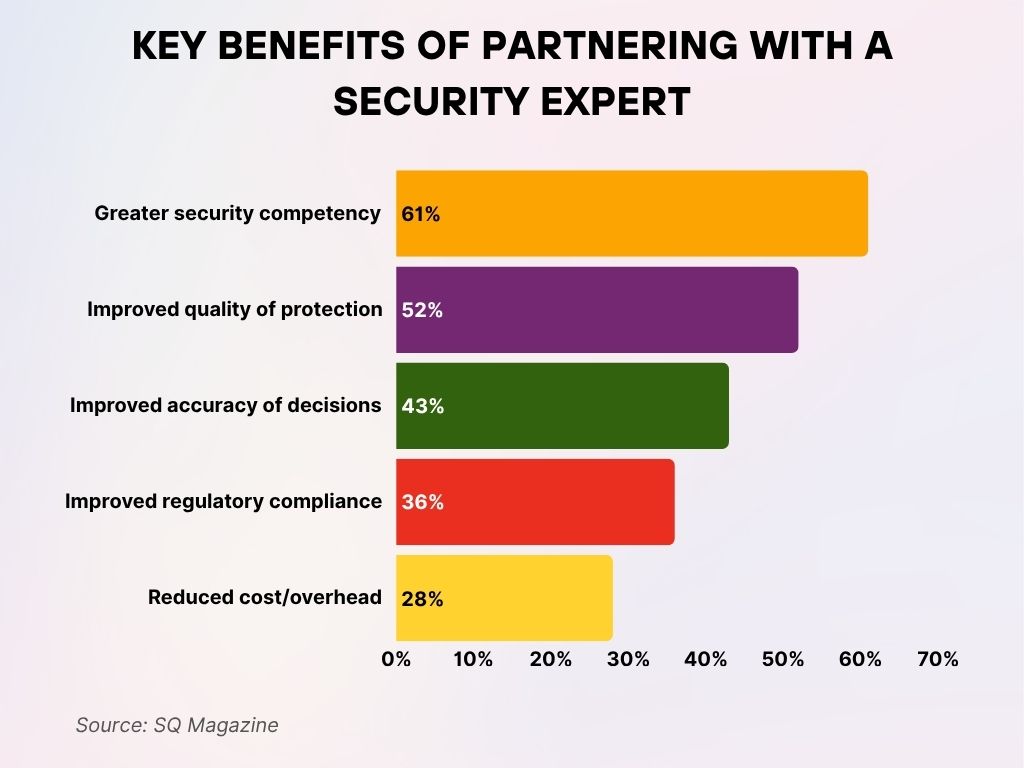
Key Benefits of Partnering with a Security Expert
- 61% of organizations reported greater security competency as the top benefit of working with a security expert.
- Improved quality of protection was cited by 52%, reflecting enhanced defense mechanisms and threat prevention.
- 43% experienced improved accuracy of decisions, indicating better-informed cybersecurity strategies.
- 36% noted improved regulatory compliance, helping meet evolving industry standards.
- 28% benefited from reduced cost and overhead, showing that expert partnerships can also support operational efficiency.
- Email remains the primary vector, delivering over 92% of all malware payloads in 2025.
- Voice phishing (vishing) incidents rose by 38%, especially targeting financial and medical sectors.
- Smishing (SMS phishing) campaigns grew by 41%, often tied to delivery service scams and two-factor code theft.
- Business email compromise (BEC) attacks resulted in $3.2 billion in losses, more than any other social engineering method.
- AI-generated phishing emails now fool recipients 63% of the time.
- Deepfake video and audio scams grew by 55%, targeting high-value executives and political figures.
- Credential harvesting was successful in 57% of phishing attempts where MFA wasn’t in place.
- Spear phishing incidents increased by 29%, with attackers using LinkedIn and other platforms to tailor bait.
Cybersecurity Workforce Shortages
- The global shortage of cybersecurity professionals reached 4.1 million in 2025.
- In the US alone, the gap grew to approximately 538,000 unfilled roles.
- Only 68% of organizations say they have enough staff to respond to security incidents in a timely manner.
- Entry-level roles are particularly difficult to fill, with many positions requiring 3+ years of experience even at junior levels.
- Women make up 27% of the global cybersecurity workforce, signaling slow progress on diversity.
- Average salaries for cybersecurity analysts rose to $113,000 in the US, driven by demand outpacing supply.
- Retention remains a major issue, with 41% of CISOs reporting burnout or turnover in their teams.
- Public sector cybersecurity positions remain vacant the longest, averaging 7.6 months to fill.
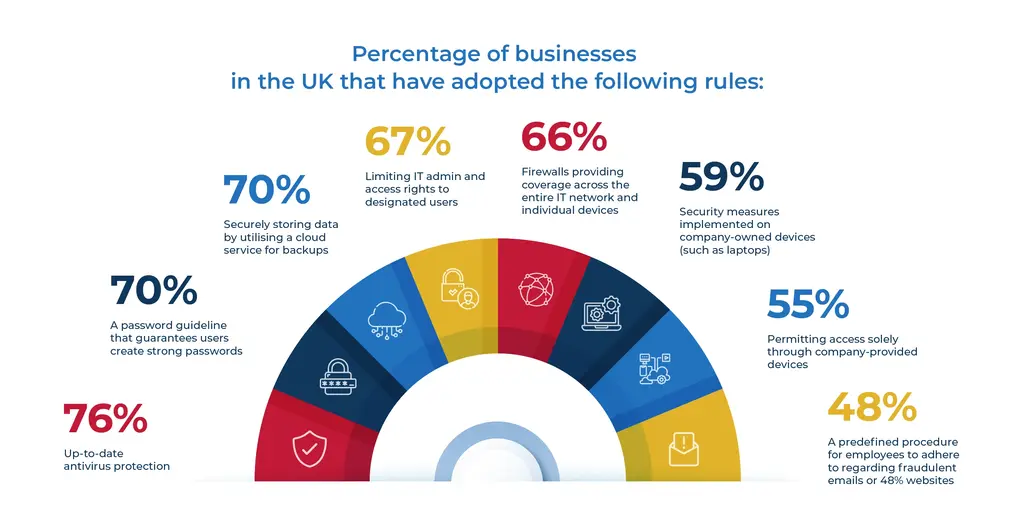
Cybersecurity Rule Adoption by UK Businesses
- 76% of businesses ensure they have up-to-date antivirus protection, making it the most adopted security measure.
- 70% use cloud services for secure data backups and enforce strong password guidelines.
- 67% limit IT admin and access rights to designated users to reduce internal risks.
- 66% implement firewalls across entire networks and individual devices for broader protection.
- 59% apply security measures on company-owned devices, such as laptops.
- 55% permit access only through company-provided devices, enhancing control over endpoints.
- 48% have a predefined employee procedure for handling fraudulent emails and websites.
Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
- Misconfigurations account for 45% of cloud-related data breaches in 2025.
- 81% of organizations experienced a cloud-related security incident in the past 12 months.
- Unauthorized access from compromised credentials led to 31% of all cloud breaches.
- Multi-cloud environments are now used by 78% of large enterprises, increasing complexity and risk exposure.
- Zero trust architecture adoption reached 36% in cloud environments—up 10 points from last year.
- Shadow IT usage is cited in 23% of cloud security alerts, often involving unsanctioned SaaS apps.
- API vulnerabilities have become a top concern, with 27% of breaches traced to insecure APIs.
- Public cloud vendors now offer automated security recommendations, but only 52% of customers actively use them.
Small Business Cybersecurity Impact
- 43% of cyberattacks now target small businesses, often viewed as soft targets with minimal defense budgets.
- 60% of SMBs that experience a cyberattack go out of business within six months, due to reputational and financial losses.
- The average cost of a breach for SMBs in 2025 is $136,000, a 22% increase from last year.
- Only 21% of small businesses have a cybersecurity incident response plan in place.
- Phishing attacks represent 71% of all SMB breach origins, with credential theft being the primary outcome.
- Cloud misconfigurations account for 19% of breaches in small firms that use SaaS platforms.
- Cyber insurance adoption among SMBs rose to 48%, driven by industry-specific mandates and risk awareness.
- Most SMBs spend less than $2,000 annually on cybersecurity, leaving large gaps in protection.
How SMBs Expect AI to Strengthen Cyber Defense
- 55% of SMB owners believe AI will help by identifying cybersecurity threats before they disrupt business operations.
- 49% think AI can assist in detecting phishing emails and texts, a common entry point for attacks.
- Another 49% value AI’s ability to offer real-time threat response recommendations.
- 36% cite secure password options as a key AI-driven defense enhancement.
- 26% expect AI to provide automated software update recommendations, closing gaps caused by outdated systems.

IoT and Endpoint Security Risks
- There are now over 31 billion connected IoT devices, with security coverage lagging far behind.
- 35% of organizations reported a breach caused by an IoT device, such as smart cameras or HVAC controls.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools are deployed in 62% of enterprises.
- Firmware attacks rose by 37%, targeting devices with rarely updated or patched software.
- Wearable tech and medical implants are now emerging vectors, especially in healthcare and elder care.
- Smart home devices accounted for 27% of consumer breaches, often due to weak default credentials.
- The endpoint security software market hit $18.6 billion in 2025, with growth driven by hybrid work models.
- Edge computing devices added a new layer of risk, with 19% reporting policy enforcement difficulties.
Spending on Cybersecurity Solutions
- Global cybersecurity spending is expected to reach $223 billion in 2025.
- Endpoint protection receives the largest share, accounting for 24% of all enterprise security budgets.
- Spending on cloud security tools has grown by 18%, driven by increased adoption of SaaS and multi-cloud architectures.
- Managed security service providers (MSSPs) saw a 26% rise in demand, particularly among mid-size enterprises.
- Small businesses now allocate 9.3% of their total IT budgets to cybersecurity, a significant jump from 6.8% last year.
- AI and machine learning-based solutions received $12.7 billion in funding, reflecting investor confidence in automated threat defense.
- Security awareness training tools saw a 31% increase in corporate subscriptions.
- Cyber insurance premiums grew by 28%, as more businesses seek coverage and insurers adapt to rising risks.
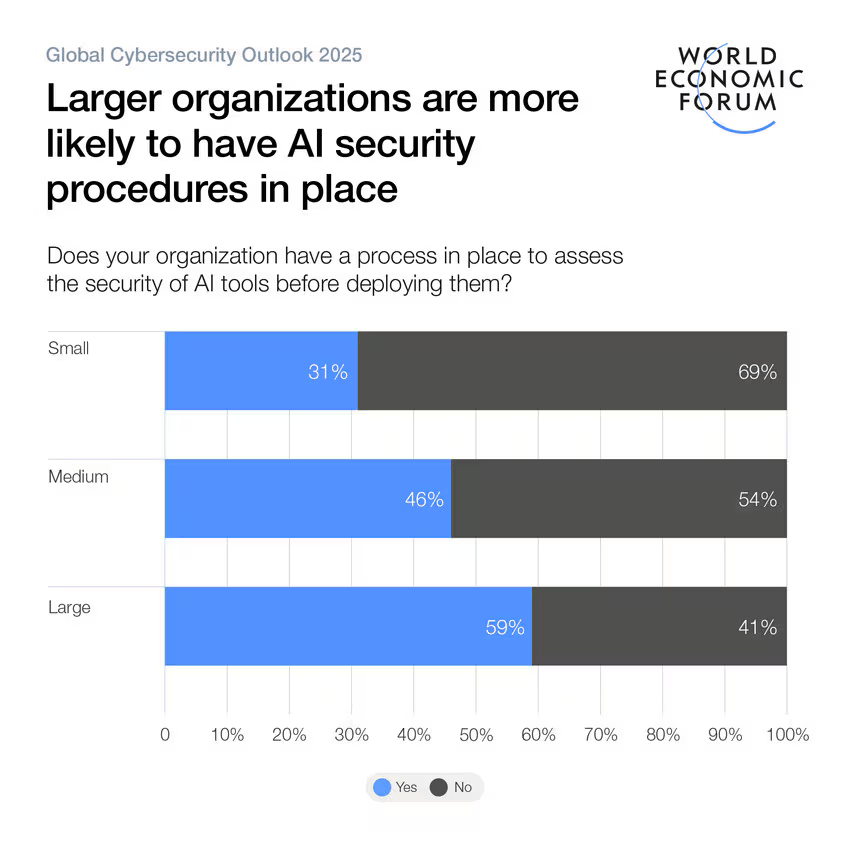
AI Security Procedures by Organization Size
- Only 31% of small organizations have a process in place to assess the security of AI tools before deployment, while 69% do not.
- 46% of medium-sized organizations have implemented such AI security procedures, with 54% lacking them.
- Large organizations lead the way, with 59% confirming they have AI security processes in place, compared to 41% without.
Role of AI and Automation in Cyber Defense
- 89% of large organizations now use AI in their cybersecurity stack.
- Threat detection times have dropped by 46% for companies utilizing AI-powered systems.
- Automated response tools helped reduce breach durations by an average of 31 hours.
- AI is now responsible for triaging 72% of security alerts, significantly reducing analyst workload.
- SOAR platforms (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) adoption hit 42%, growing across finance and healthcare.
- ML-based behavioral analytics prevented 28% of insider threats that traditional methods missed.
- Bias in AI models was cited in 13% of false positive incidents, pushing demand for explainable AI (XAI).
- AI-driven security solutions have a projected CAGR of 21% through 2028, reflecting long-term growth expectations.
Cybersecurity Compliance and Regulatory Trends
- 77 countries now have active data protection laws, with 11 new regulations introduced in 2025 alone.
- US federal agencies are required to adopt zero-trust architecture by Q4 2025, per updated Executive Order mandates.
- Fines for GDPR violations totaled €2.2 billion in the past 12 months.
- The PCI DSS 4.0 compliance deadline passed in March 2025, affecting all businesses handling cardholder data.
- SOX compliance violations due to cybersecurity lapses rose 14%, especially in the energy and finance sectors.
- HIPAA-related cybersecurity fines in the US exceeded $250 million, mostly related to breaches of protected health information (PHI).
- China’s new CSL (Cybersecurity Law) updates introduced tiered penalties, ranging from $75,000 to $2 million.
- Cross-border data transfer restrictions affected 32% of multinational cloud deployments in 2025.
Regional Breakdown of Cyber Incidents
- North America remains the most targeted region, accounting for 34% of all global cyberattacks in 2025.
- Europe saw a 19% increase in state-sponsored intrusions, particularly in critical infrastructure and defense.
- Asia-Pacific experienced a 27% rise in phishing scams, primarily targeting the fintech and telecom sectors.
- Latin America reported a 15% increase in mobile malware infections, with Brazil and Mexico as hotspots.
- The Middle East recorded a 12% rise in oil & gas sector attacks, attributed to geopolitical tensions.
- Africa’s financial institutions saw a 22% increase in cyber fraud, largely driven by mobile banking growth.
- Australia implemented a national cybersecurity levy, helping fund improved infrastructure after a year of major breaches.
- Russian and Chinese-originated APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) activity increased by 14%, according to global intelligence reports.
Recent Developments in Cybersecurity
- Quantum-resistant encryption protocols began early-stage deployment in 2025 across the banking and defense sectors.
- The US National Cyber Strategy 2025 emphasizes public-private collaboration and expanded breach reporting rules.
- Decentralized identity frameworks using blockchain are in pilot phases with major tech companies.
- The SEC finalized its cybersecurity disclosure rules, requiring public companies to report breaches within four business days.
- AI-generated malware is now detectable by only 62% of traditional antivirus engines, raising concerns among security vendors.
- Cybersecurity mesh architecture (CSMA) adoption hit 19%, integrating security across diverse digital assets.
- Passwordless authentication saw a 33% uptick in adoption, especially through FIDO2 standards.
- Security startups raised over $9.3 billion in venture capital funding, with a focus on autonomous defense and cloud-native tools.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in 2025 isn’t just a technical challenge; it’s a global business imperative. From rising ransomware threats and phishing campaigns to workforce shortages and cloud vulnerabilities, organizations face mounting pressure to invest smartly, comply rigorously, and respond swiftly. As technology evolves, so too must the defenses that protect our data, privacy, and digital infrastructure. The statistics outlined above highlight not only the scale of the threat landscape but also the promising strides being made through AI, automation, and regulatory clarity. Vigilance, adaptability, and collaboration will define the most resilient organizations in this ever-changing digital era.
Sources
- https://www.statista.com/outlook/tmo/cybersecurity/worldwide
- https://industrialcyber.co/threat-landscape/uk-spending-review-2025-backs-ai-cybersecurity-and-intelligence-modernization/
- https://kpmg.com/in/en/insights/2025/03/cybersecurity-considerations-2025/government-public-sector.html
- https://www.statista.com/topics/1712/cybersecurity/
- https://www.bworldonline.com/spotlight/2025/05/26/674700/gogolook-underscores-ais-role-in-cybersecurity-at-gen-ai-summit-2025/
- https://www.virusbulletin.com/blog/2025/06/what-cybersecurity-experts-are-talking-about-2025/










