WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
Introduction
Sleep is a vital part of health and well-being. Getting adequate, high-quality sleep can improve concentration, productivity, physical health, mental health, and overall quality of life. With the increasing demands of modern life, many people suffer from poor sleep. Understanding the latest sleep statistics is key to assessing and addressing this important public health issue. This in-depth statistical report examines the current research on sleep patterns, trends, and correlations in 2023.
Editor Choice
- Worldwide, over 45% of the population gets less than the recommended 7 or more hours of sleep per night.
- Insomnia affects approximately 7-30% of the global population.
- Obstructive sleep apnea affects at least 936 million adults worldwide.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness affects 15-30% of the general global population.
- Approximately 1.5 billion people globally suffer from some form of sleep deprivation.
- Shift work sleep disorder affects 10-40% of night and rotating shift workers around the world.
- Noise pollution globally causes an estimated 1.8 million years of healthy life lost due to sleep disturbance.
- About 19% of road traffic accidents worldwide are attributed to fatigue and drowsy driving.
- Sleep disorders and sleep loss account for over $280 billion per year in economic losses worldwide.
- Melatonin use has risen globally by 150% between 2016 and 2020 as a sleep aid.
- Google searches for “insomnia” doubled worldwide between February and March 2020 during the Covid-19 pandemic.
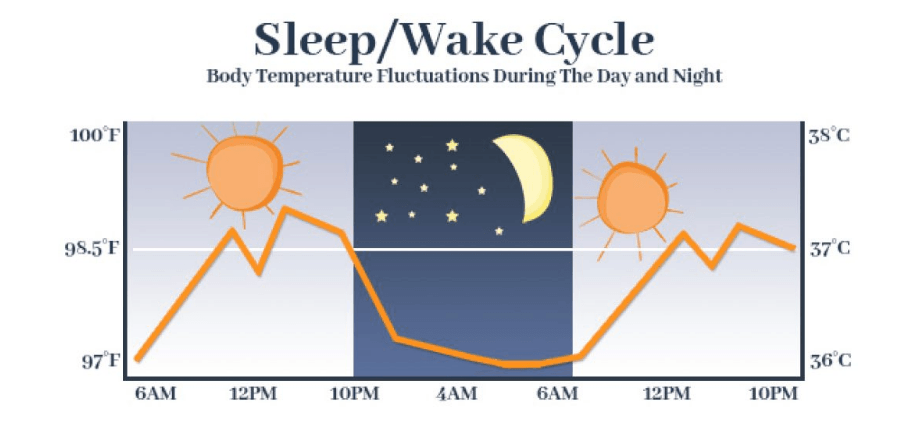
Key Findings In U.S.
- 35% of adults in the U.S. get less than the recommended 7 hours of sleep per night.
- Adults over 60 are the most likely age group to get enough sleep, while those aged 18-60 are the least likely.
- Insomnia affects an estimated 22% of adults in the U.S.
- Using technology before bed is associated with worse sleep outcomes.
- Lack of sleep is estimated to cost the U.S. economy $411 billion per year in lost productivity.
- Between 50-70 million U.S. adults suffer from a sleep disorder.
- Sleep deprivation increases risks for chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, obesity, and depression.
Sleep Duration
How Many Hours of Sleep Do Adults Need?
The National Sleep Foundation recommends that healthy adults get between 7-9 hours of sleep per night. However, individual sleep needs vary, and some adults may require more or less sleep than this range. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that adults get at least 7 hours of sleep per night regularly to promote optimal health.
What Percentage of Adults Are Not Getting Enough Sleep?
- 35% of U.S. adults report typically getting less than the recommended 7 hours of sleep per night.
- Less than 31% of adults meet the sleep duration recommendations from the National Sleep Foundation.
- Over 20% of adults in the U.S. get 6 or fewer hours of sleep per night.
These statistics suggest that 1 in 3 American adults are not getting the amount of sleep they need for optimal performance and health. The prevalence of inadequate sleep highlights the importance of improving sleep hygiene practices across the population.
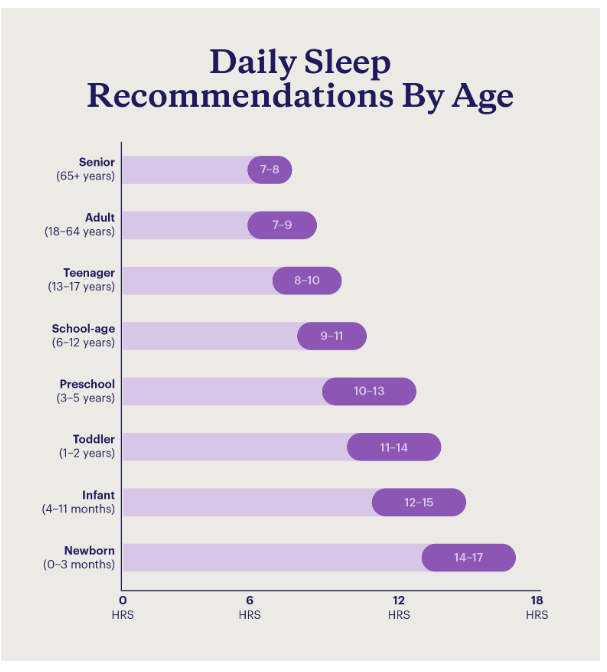
How Does Sleep Duration Vary by Age?
Sleep needs and patterns change as we age. Sleep statistics show differences in duration by age group:
- Age 18-60: The least likely age group to get enough sleep. Around 35-40% get less than 7 hours.
- Age 26-64: Report the least amount of sleep, with an average of 6 hours 42 minutes.
- Over age 60: Most likely age group to get at least 7 hours of sleep, with 67% meeting sleep duration recommendations.
As we age, sleep often becomes lighter and more fragmented. However, older adults require about the same amount of sleep as younger adults. The discrepancy in sleep duration between younger and older adults may be due to altered sleep regulation, fewer work and social obligations, and/or poorer overall sleep quality in older adults.
Sleep Quality
Sleeping for an adequate duration is just one component of healthy sleep. High-quality sleep is also critical for waking up feeling rested and restored. Many factors can interfere with sleep quality, including:
- Stress
- Underlying health conditions
- Environmental factors like noise, light, and temperature
- Consumption of caffeine, alcohol, or heavy meals before bed
- Inconsistent sleep schedule
- Use of electronic devices before bed
What Percentage of People Experience Insomnia Symptoms?
Insomnia, defined as persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep, is the most common sleep disorder.
- An estimated 22% of U.S. adults experience symptoms of insomnia.
- About 14% meet the criteria for a clinical diagnosis of insomnia disorder.
- Insomnia is more prevalent in women, with nearly 1 in 4 affected compared to 15% of men.
Left untreated, insomnia takes a major toll on mental and physical health, productivity, and quality of life. Expanding access to cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia could help address this highly prevalent sleep problem.
How Does Technology Use at Night Affect Sleep Quality?
Statistics clearly demonstrate that nighttime use of phones, tablets, computers, and TVs interrupts sleep:
- 90% of Americans use some type of electronic device in the hour before bed at least a few nights per week.
- 75% keep their cell phone next to their bed while sleeping.
- Those who use tech at night are 3x more likely to feel unrested despite sleeping for at least 7 hours.
- Using e-readers before bed reduces REM sleep by 3-5%.
Experts recommend avoiding bright screens for 1-2 hours before bedtime. The blue light emitted can suppress the sleep hormone melatonin and make it harder to fall asleep. Turning off notifications and setting phones in Do Not Disturb mode can also improve sleep.
Health Impact of Sleep
Adequate high-quality sleep is a pillar of overall health and wellness. Unfortunately, many adults unknowingly compromise their health through poor sleep habits.
What Are the Economic Costs of Insufficient Sleep?
Skimping on sleep takes a major toll on the economy through lost workplace productivity.
- Insufficient sleep among US workers costs businesses more than $400 billion per year in lost productivity.
- Workers who sleep fewer than 6 hours per night have lower productivity levels equivalent to 8 days per month of lost work.
- Lack of sleep leads to an extra 5 days per month of presenteeism (being present at work but functioning sub-optimally).
Encouraging healthy sleep among employees could save billions for the economy through boosted performance and productivity.
How Does Sleep Affect the Risk of Chronic Diseases?
Research clearly links lack of sleep to increased risks of some of the leading causes of death and disability:
- Adults sleeping fewer than 7 hours per night have a 12% higher risk of dying from any cause compared to those getting 7-8 hours.
- Short sleep duration is associated with a 45% increased risk of developing diabetes.
- Sleeping 5 hours or less per night doubles the risk of heart attack and stroke.
- Insufficient sleep raises the risk of obesity by 23% in children and 55% in adults.
Prioritizing healthy sleep duration should be part of preventive healthcare strategies to reduce population risks for chronic diseases.
What Percentage of Adults Have a Sleep Disorder?
Many adults suffer from diagnosable sleep disorders that disrupt sleep quality and health:
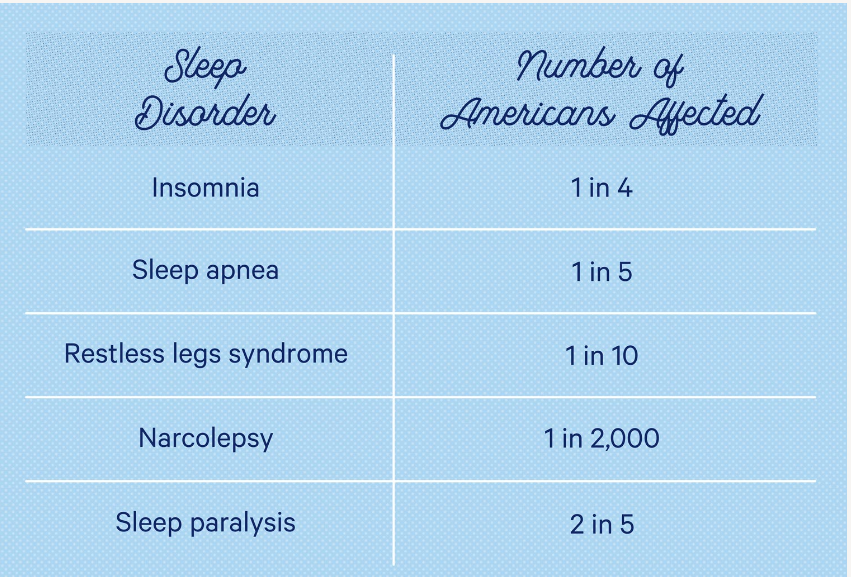
- An estimated 50-70 million US adults have a sleep disorder such as insomnia, sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, etc.
- Sleep apnea affects 22 million adults in the US.
- Up to 20% of adults may have undiagnosed sleep apnea.
- Approximately 8.5% of adults have restless leg syndrome, an uncomfortable urge to move the legs during sleep.
With high prevalence of sleep disorders, increasing access to sleep specialists and diagnostics could help more people achieve restorative sleep.
Sleep Statistics FAQs
What percentage of car accidents are caused by drowsy driving?
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration estimates that 2.5% of fatal motor vehicle accidents, and 2.3% of all accidents with injuries, involve drowsy driving. This equals over 6,400 deaths and 50,000 injuries per year caused by drowsy drivers.
How does mental health correlate with sleep quality?
Poor sleep has a very strong association with mental health issues. Adults with insomnia have a 17-fold increased risk of major depression compared to those sleeping over 7 hours per night. Getting adequate sleep can help improve symptoms of anxiety, depression, bipolar disorder, and more.
Do naps improve health?
Naps are generally healthy. One study found a 30% lower risk of heart disease among adults who nap periodically compared to non-nappers. Naps can enhance alertness and performance on cognitive tasks. However, long or late-day naps may negatively affect nighttime sleep quality.
Is snoring bad for your health?
Frequent snoring may indicate sleep apnea or other health issues. Snoring itself is not inherently harmful. But snoring that occurs with breathing pauses and chronic fragmented sleep can lead to daytime fatigue and increase risks for high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes, and more.
What is the link between sleep and weight gain?
Insufficient sleep alters the release of hunger hormones like ghrelin and leptin, increasing cravings for high-calorie foods. Just a single night of restricted sleep can increase calorie consumption by 500 extra calories the next day. Over time, chronic lack of sleep promotes weight gain and obesity risk.
How much are sleep medications used in the US?
Sleep medications are common but not recommended for long-term use. Survey data indicates around 5% of US adults use prescription sleep medications. Total spending on sleep medication tops $2 billion per year, with over 29 million prescriptions filled annually for medications like Ambien, Lunesta, and Sonata.
Conclusion
This statistical report highlights the importance of sleep for health, well-being, productivity, and public safety. Significant portions of the population sleep fewer than the recommended 7-9 hours per night, contributing to risks for chronic diseases, traffic accidents, and mental health issues. Avoiding technology before bed, adhering to consistent sleep schedules, and practicing other good sleep hygiene habits can help many people achieve improved sleep health. Ongoing research and public health initiatives are needed to promote adequate high-quality sleep as a vital component of overall health.
ABOUT AUTHOR
Yogesh Shinde is a passionate writer, researcher, and content creator with a keen interest in technology, innovation and industry research. With a background in computer engineering and years of experience in the tech industry. He is committed to delivering accurate and well-researched articles that resonate with readers and provide valuable insights. When not writing, I enjoy reading and can often be found exploring new teaching methods and strategies.