In January 2025, a small fintech startup in Austin discovered it had fallen victim to a cyberattack. At first glance, the breach looked like a typical case of credential stuffing. But it wasn’t. The attacker had used an AI-driven system that mimicked the behavioral patterns of employees, learning login habits, keyboard rhythms, and even Slack communication styles. What once took hackers days or weeks to orchestrate, AI now executes in real time.
This isn’t science fiction, it’s today’s reality. As artificial intelligence advances, so does its exploitation by malicious actors. From weaponized deepfakes to autonomous phishing bots, AI-enabled threats are not only evolving, they’re escalating.
Editor’s Choice
- 68% of cyber threat analysts report that AI-generated phishing attempts are harder to detect in 2025 than in any previous year.
- The number of reported AI-enabled cyber attacks rose by 47% globally in 2025.
- Financial services ranked as the most targeted industry in 2025, experiencing 33% of all AI-driven incidents.
- In 2025, the average cost of an AI-powered data breach reached $5.72 million, a 13% increase over the previous year.
- 41% of ransomware families now include AI components for adaptive payload delivery as of 2025.
- Synthetic media attacks, including deepfakes, grew by 62% year-over-year in 2025, with most targeting enterprise verification systems.
- North America experienced the highest regional spike in AI-related breaches, recording a 39% year-over-year increase in 2025.
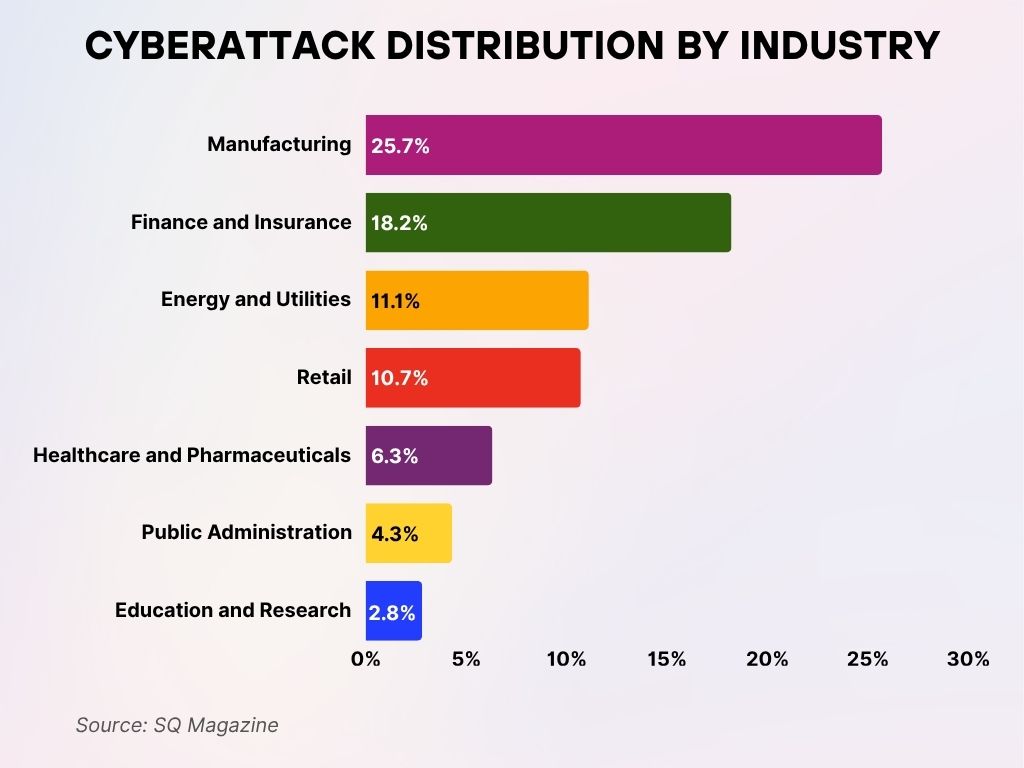
Cyberattack Distribution by Industry
- The Manufacturing sector is the most targeted, accounting for 25.7% of all cyberattacks, more than a quarter of total incidents.
- Finance and Insurance follow closely, experiencing 18.2% of the attack share, underscoring the sector’s vulnerability due to sensitive data and assets.
- Energy and Utilities industries face 11.1% of attacks, reflecting increasing threats to critical infrastructure.
- The Retail sector is also heavily hit, absorbing 10.7% of cyberattacks, likely due to high transaction volumes and customer data exposure.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals represent 6.3% of attacks, as attackers exploit patient data and medical systems.
- Public Administration accounts for 4.3%, showing that government services are not immune to targeted cyber threats.
- Education and Research institutions experience 2.8% of all cyberattacks, with growing risks linked to academic data and open network environments.
Global Rise in AI-Driven Cyber Attacks
- In 2025, global AI-driven cyberattacks are projected to surpass 28 million incidents.
- Enterprises deploying AI-powered defenses still faced breaches in 29% of cases in 2025, showing attackers are keeping pace.
- 92 countries reported AI-related attack activity in 2025, showcasing the widening global impact.
- The average detection time for AI-assisted breaches decreased to 11 minutes in 2025.
- In 2025, 35% of botnet operations incorporated machine learning algorithms to evade detection and adapt in real-time.
- Healthcare, a critical sector, saw a 76% rise in targeted AI attacks in 2025, largely attributed to the automation of ransomware deployment.
- AI-powered distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks reached a record high of 2.1 million unique incidents in 2025.
- 57% of SOC (Security Operations Center) analysts in 2025 reported that traditional threat intelligence is insufficient against AI-accelerated attacks.
- 20% of all cyberattacks in 2025 used AI-enhanced obfuscation, such as synthetic traffic generation or polymorphic code.
- 52% of AI attacks in 2025 utilized public LLMs to generate phishing content or script payloads.
- 14% of major corporate breaches this year were fully autonomous, meaning no human hacker intervened after the AI launched the attack.
Common Types of AI-Enabled Cyber Attacks
- AI-generated phishing emails rose by 67% in 2025, becoming more personalized through behavioral mimicry and context-aware writing.
- Voice cloning attacks, particularly used for business email compromise (BEC), increased by 81% in 2025.
- Autonomous malware capable of adapting based on host response environments accounted for 23% of malware payloads in 2025.
- In 2025, AI-powered keyloggers were used in 19% of high-profile attacks, using behavior analysis to mask input logging.
- Synthetic identity fraud, often generated using AI-driven data synthesis tools, surged 62% in 2025.
- Credential stuffing bots trained via reinforcement learning bypassed CAPTCHA and MFA protections in 48% of tests in 2025.
- AI-enhanced social engineering tactics, such as real-time emotion detection, featured in 29% of data breach investigations in 2025.
- Polymorphic malware that rewrites itself using AI evasion logic has grown to represent 22% of advanced persistent threats in 2025.
- AI-authored ransomware notes showed a 40% increase in conversion rates (payment compliance) in 2025, owing to a more persuasive tone and structure.
- Self-mutating phishing kits with AI capabilities are now used by 1 in 5 phishing groups as of 2025.
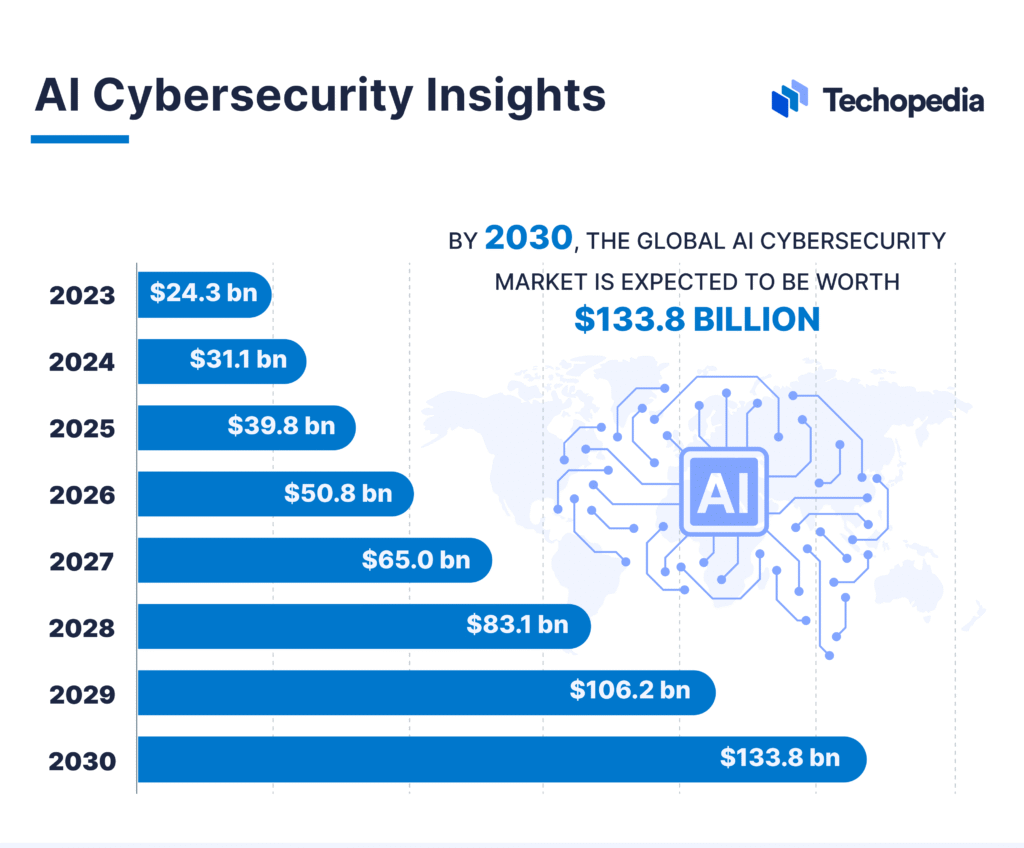
AI Cybersecurity Market Growth Forecast
- In 2023, the global AI cybersecurity market was valued at $24.3 billion.
- By 2024, the market is projected to grow to $31.1 billion.
- In 2025, it’s expected to reach $39.8 billion, showing rapid adoption of AI security tools.
- The value increases to $50.8 billion by 2026, highlighting continued industry investment.
- By 2027, the market is set to grow further to $65.0 billion.
- In 2028, it will climb to $83.1 billion, showing accelerated demand.
- The market is projected to reach $106.2 billion in 2029.
- By 2030, the global AI cybersecurity market is forecasted to hit $133.8 billion, marking more than a 5x increase from 2023.
Geographic Distribution of AI Cyber Incidents
- In 2025, North America experienced the highest volume of AI-driven cyberattacks globally, with 39% of all reported incidents.
- Europe followed closely, accounting for 28% of AI-related breaches in 2025, with Germany and the UK as top targets.
- Asia-Pacific saw a 56% rise in AI-enabled attacks in 2025, with financial and e-commerce platforms most affected.
- The Middle East region reported a 31% increase in AI-assisted espionage campaigns during 2025, especially targeting oil and energy systems.
- In 2025, Latin America became a growing target zone, recording a 19% increase in AI-enabled banking malware attacks.
- Africa saw the introduction of AI-powered misinformation campaigns in 2025, primarily around elections and political movements.
- Russia and China were linked to 42% of AI-based state-sponsored incidents tracked in 2025, according to global intelligence estimates.
- India recorded a 71% rise in AI-generated phishing incidents in 2025, mostly targeting digital payment platforms.
- Australia and New Zealand reported that AI-related threats doubled in 2025 compared to the previous year.
- Scandinavian countries saw a 38% surge in AI-fueled deepfake usage for business impersonation scams in 2025.
Economic Impact of AI-Driven Cybercrime
- The total global cost of AI-driven cybercrime in 2025 is projected to exceed $193 billion.
- The average cost per AI-related breach reached $5.72 million in 2025, a 13% increase from the prior year.
- Small-to-midsize enterprises (SMEs) spent 27% more on cyber incident response in 2025 due to AI-specific threats.
- In 2025, insurance payouts for AI-driven attacks rose by 22%, straining cyber liability insurers globally.
- Ransomware campaigns using AI-generated negotiation bots led to faster payment cycles, reducing average negotiation time to 3.4 days in 2025.
- Organizations using legacy security tools incurred an average 42% higher cost per incident in 2025 compared to AI-resilient infrastructures.
- 45% of companies reported budget reallocations in 2025 specifically to address AI-related threat mitigation.
- AI-aided insider threats caused over $2.4 billion in damages in 2025, largely due to machine learning systems identifying exploitable access roles.
- The financial sector alone lost $28.6 billion globally in 2025 to AI-enhanced fraud and data breaches.
- AI-powered fraud detection tools also saved enterprises an estimated $11 billion in potential losses in 2025, indicating the dual-edged impact of AI.
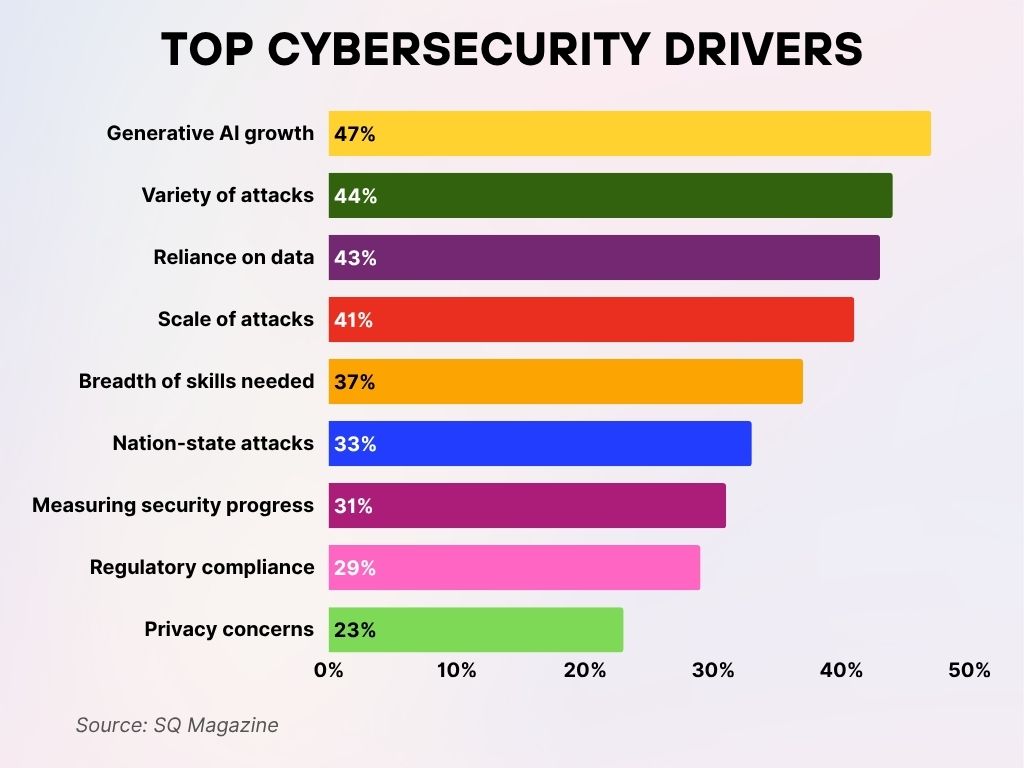
Top Cybersecurity Drivers
- Generative AI growth is the leading driver, cited by 47% of respondents as a key factor shaping cybersecurity priorities.
- A variety of attacks ranks second, influencing 44% of cybersecurity strategies due to the increasing sophistication of threats.
- Reliance on data is a concern for 43%, highlighting the risks tied to data-intensive systems and analytics.
- The scale of attacks drives decisions for 41% of professionals, pointing to the rising frequency and impact of breaches.
- 37% of respondents emphasize the breadth of skills needed, showing a widening cybersecurity skills gap.
- Nation-state attacks are a major concern for 33%, underlining growing geopolitical cyber threats.
- 31% are focused on measuring security progress, reflecting the need for better metrics and accountability.
- Regulatory compliance influences 29%, driven by tightening global data protection laws.
- Lastly, 23% cite privacy concerns as a driver, as consumer awareness and expectations continue to rise.
Role of Generative AI in Phishing and Deepfake Attacks
- Generative AI phishing emails in 2025 had a 72% open rate, nearly double that of traditional phishing attempts.
- Deepfake videos used in CEO fraud cases rose by 83% in 2025, causing an estimated $1.1 billion in direct losses.
- LLMs like open-source GPT variants were used to craft 91% of detected spear-phishing campaigns in 2025.
- In 2025, 37% of large corporations reported at least one instance of a deepfake voice impersonation attempt.
- AI-powered scam call centers leveraged synthetic voices to scale social engineering, resulting in 41% more consumer fraud in 2025.
- Facial animation deepfakes targeting KYC (Know Your Customer) systems bypassed verification in 12% of cases tested in 2025.
- Generative AI phishing kits sold on the dark web increased in value by 61% in 2025, reflecting demand for advanced deception tools.
- 43% of AI-driven phishing campaigns used real-time chatbots to prolong user engagement in 2025.
- AI-written phishing content now mimics emotional tone and urgency, improving response rates by 48% in 2025.
- Synthetic LinkedIn profiles created using generative AI were used in 29% of corporate infiltration attempts in 2025.
AI Usage in Malware and Ransomware
- In 2025, 41% of all active ransomware families included some form of AI module for adaptive behavior.
- Autonomous ransomware, capable of lateral movement without human oversight, was present in 19% of breaches in 2025.
- AI-crafted malware variants had an 18% higher success rate in bypassing endpoint detection systems in 2025.
- Malware using reinforcement learning adapted to sandbox environments in 11 seconds, down from 22 seconds last year.
- Smart payload delivery, where AI tailors malicious code based on system type, appeared in 24% of cases in 2025.
- In 2025, 18% of Trojans used AI for persistence, avoiding reboots and standard removal tactics.
- AI-embedded steganography was used to conceal payloads in images and video files in 13% of malware campaigns in 2025.
- Code mutation using AI led to an average of 21 unique variants per malware family detected in 2025.
- Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) providers offering AI-driven encryption tools grew by 34% in the underground economy in 2025.
- AI-generated obfuscation layers delayed reverse engineering by an average of 3.2 days in 2025, frustrating forensic teams.
Top Security Measures for Data Protection
- 61% of companies have implemented formal cybersecurity risk assessments as their primary method for protecting sensitive data.
- 48% use network segmentation (logical and/or physical) to contain threats and limit exposure.
- 46% of organizations apply data classification to better manage and secure information based on sensitivity.
- Another 46% have adopted a zero-trust network security model, ensuring that no user or device is inherently trusted.

AI in Nation-State and Espionage Campaigns
- In 2025, 42% of nation-state cyber campaigns used AI to automate reconnaissance and vulnerability mapping.
- Governments with AI cyber capabilities now include 17 countries.
- Russia and China accounted for the majority of advanced persistent threats (APTs) with AI components in 2025.
- AI-powered social media bots ran disinformation campaigns in 31 countries during 2025, with over 9 billion impressions.
- In 2025, AI-enabled espionage tools successfully bypassed two-factor authentication in 15% of state-level intrusions.
- AI-enhanced zero-day exploitation was used in 12% of known government-backed attacks in 2025.
- 5 out of 7 NATO countries reported attempted AI-assisted breaches of military supply chain systems in 2025.
- AI-driven honeypot evasion enabled longer dwell times, averaging 63 days in state-sponsored breaches in 2025.
- Encrypted AI C2 channels (command and control) made detection and tracking 35% harder for national cybersecurity teams in 2025.
- State actors increasingly use AI-generated persona farms to infiltrate civil society and influence discourse undetected in 2025.
AI-Powered Defense vs AI-Driven Attacks
- In 2025, 61% of cybersecurity teams adopted AI-powered threat detection.
- Despite enhanced tooling, 29% of those organizations still suffered AI-based breaches in 2025, indicating an evolving arms race.
- AI-enabled XDR systems (Extended Detection and Response) reduced response times by 44% on average in 2025.
- 48% of global enterprises used AI in SOC automation to reduce analyst fatigue and false positives in 2025.
- AI-driven behavioral analytics identified insider threats 32% faster in 2025 than manual monitoring methods.
- In 2025, organizations using AI for phishing detection reduced click-through rates by 54%, significantly improving resilience.
- 38% of enterprise firewalls were AI-integrated in 2025, up from 24% the previous year.
- Deception technology, powered by machine learning, tricked AI-powered attackers in 19% of honeypot deployments in 2025.
- AI-enabled threat hunting tools uncovered 41% more anomalies in 2025 compared to standard SIEM solutions.
- However, 26% of security vendors in 2025 acknowledged difficulty in keeping pace with AI-driven threat innovation cycles.
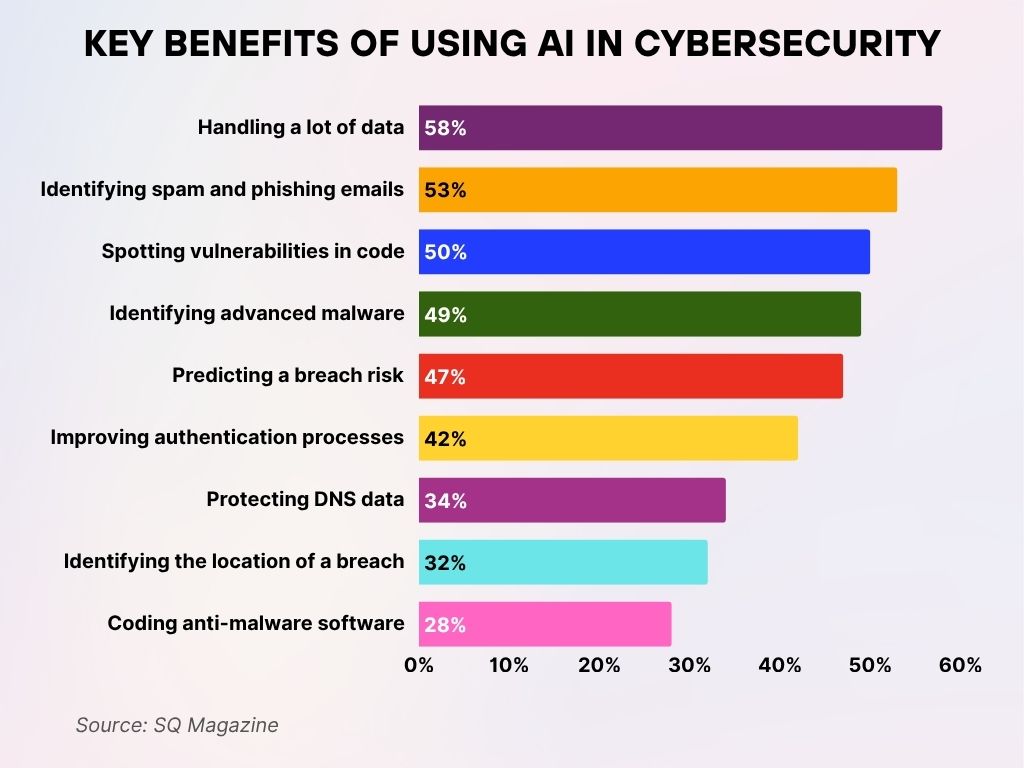
Key Benefits of Using AI in Cybersecurity
- 58% of professionals say AI helps in handling a large volume of data, streamlining analysis, and threat detection.
- 53% find AI effective in identifying spam and phishing emails, reducing the risk of social engineering attacks.
- 50% use AI for spotting vulnerabilities in code, improving software security during development.
- 49% rely on AI for identifying advanced malware and detecting sophisticated threats faster.
- 47% believe AI is valuable in predicting breach risks, enabling proactive defense strategies.
- 42% cite AI’s role in improving authentication processes, strengthening identity verification.
- 34% of respondents use AI for protecting DNS data, helping defend against DNS-based attacks.
- 32% benefit from AI’s ability to identify the location of a breach, aiding faster incident response.
- 28% say AI supports coding anti-malware software, enhancing automated security development.
Reported Incidents and Breach Volumes
- Confirmed AI-related breaches reached 16,200 incidents in 2025, a 49% increase from the previous year.
- Average breach dwell time for AI-driven attacks was 63 days in 2025, versus 72 days for traditional breaches.
- The largest single AI-originated breach in 2025 compromised 228 million records from a global telecom provider.
- Healthcare and finance together accounted for 55% of AI-related breach volume in 2025.
- In 2025, publicly traded companies disclosed AI-related attacks in 12% of SEC filings.
- 72% of surveyed CISOs reported that AI-specific incident tracking had become a standard reporting metric in 2025.
- 21% of breaches in 2025 included multi-stage AI automation, making attribution and containment more complex.
- Cloud service providers reported a 34% uptick in breach volume tied to AI misuse in 2025.
- 41% of all zero-day exploits in 2025 were discovered through AI-aided reverse engineering by attackers.
- The top 5 breached industries in 2025 were finance, healthcare, retail, education, and logistics, in that order.
Regulatory and Legal Responses to AI Cyber Threats
- By mid-2025, 22 countries introduced specific legislation addressing AI misuse in cybercrime.
- The EU AI Act was amended in 2025 to include provisions for autonomous cyberattack attribution.
- In 2025, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) launched the AI Threat Intelligence Sharing Framework.
- California passed a bill in 2025 requiring all companies to report AI-driven cyber incidents within 72 hours.
- The FTC opened 9 major investigations into the misuse of generative AI for consumer scams in 2025.
- Interpol coordinated its first multinational task force focused on AI in cybercrime, leading to 32 arrests in 2025.
- In 2025, Brazil and India proposed AI-specific amendments to their respective national data protection laws.
- 40% of legal tech providers in 2025 offered services addressing AI-based digital forensics and litigation support.
- Cyber insurance contracts in 2025 began including AI-specific exclusions, complicating claims in ambiguous breach cases.
- Global consensus on defining “malicious autonomous AI” remains unresolved as of 2025, despite mounting pressure from the UN’s digital security council.
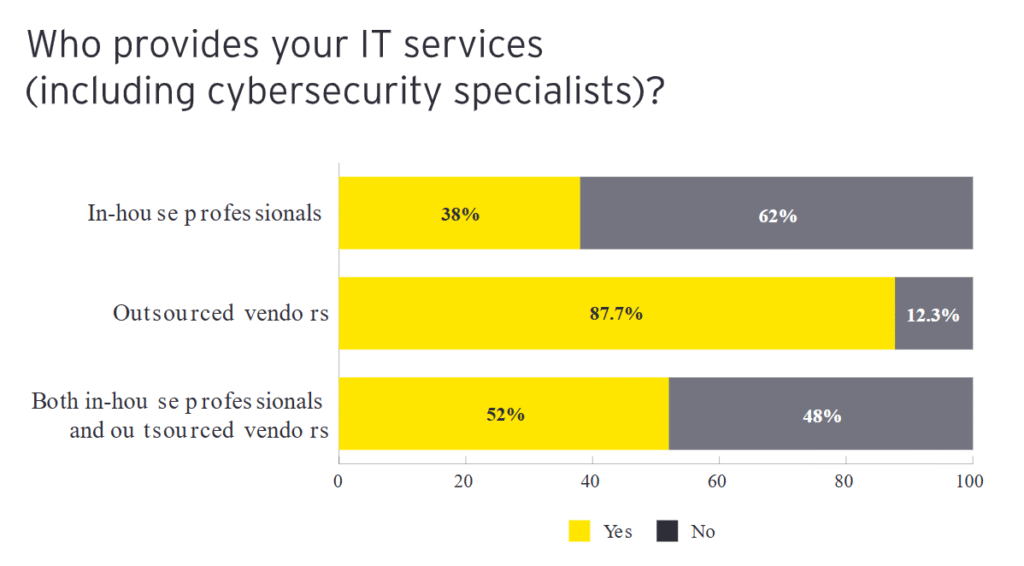
IT Service Providers in Cybersecurity
- 38% of companies rely solely on in-house professionals for IT and cybersecurity services, while 62% do not.
- A significant 87.7% use outsourced vendors, making third-party providers the most common source of IT support.
- 52% of organizations leverage a hybrid model, combining both in-house teams and external vendors for comprehensive cybersecurity coverage.
Recent Developments in AI and Cybersecurity Trends
- In 2025, AI Red Teaming emerged as a mainstream enterprise practice, used by 31% of Fortune 1000 companies.
- Open-source AI threat modeling frameworks saw a 73% increase in adoption among cybersecurity startups in 2025.
- Synthetic data poisoning was identified as a new attack vector in 19% of enterprise security audits in 2025.
- Quantum-augmented AI tools for cryptanalysis gained visibility in early 2025, though large-scale usage remains speculative.
- 2025 saw a surge in AI security certifications, with over 5,400 professionals completing new AI-specific tracks.
- AI integration with blockchain monitoring tools improved crypto fraud detection accuracy by 43% in 2025.
- Dark web marketplaces specializing in AI-malware tools expanded by 29% in 2025, introducing subscription-based exploit kits.
- Microsoft, Google, and IBM launched collaborative AI threat intelligence exchanges in 2025 to fight large-scale autonomous attacks.
- Behavioral fingerprinting models trained on multimodal data (voice, typing, location) reached 89% accuracy in spoof detection by 2025.
- The emergence of AI disarmament proposals at the World Economic Forum in 2025 signaled growing concern over unchecked AI weaponization.
Conclusion
AI’s presence in cybersecurity is no longer a future concern; it’s the defining force of 2025. While it enables powerful defenses, its role in enabling sophisticated, fast-moving, and autonomous threats has reshaped the cyber threat landscape. Industries once shielded by human oversight now face adversaries that learn, evolve, and deploy attacks in seconds.
The statistics from this year highlight both the scale of the threat and the urgency of action. Regulatory bodies, corporations, and security providers are racing to adapt, but the margin for error is narrowing. The AI arms race is here, and it’s already rewriting the rules of digital warfare.