WHAT WE HAVE ON THIS PAGE
- Editor’s Choice
- Top Causes Behind Cyber Insurance Claims
- Familiarity and Experience with Cyber Insurance
- Premium Costs and Coverage Trends
- Cybersecurity Insurance Market Growth Outlook
- Frequency and Severity of Cyber Insurance Claims
- Types of Cyber Insurance Claims
- Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- Top Insured Cyber Risks and Threat Types
- Regional Penetration and Market Leaders
- Average Cost of a Data Breach by Industry
- Impact of Regulatory Changes on Policy Demand
- SME vs. Enterprise Cyber Insurance Uptake
- Industries Most Targeted by Cyber Attacks
- Key Drivers for Policy Adoption
- Common Exclusions and Coverage Gaps
- Cyber Insurance Adoption Trends in Companies
- Role of AI and Data Analytics in Underwriting
- Recent Developments in the Cyber Insurance Industry
- Conclusion
- Sources
In the early hours of a chilly January morning, a small manufacturing company in Ohio found itself locked out of its systems. A ransomware attack had paralyzed operations. Yet, unlike many similar victims, they bounced back, quickly and cleanly. Why? Cyber insurance.
In 2025, stories like this have become increasingly common as businesses of all sizes scramble to shield themselves from ever-evolving digital threats. Cyber insurance is no longer a niche consideration; it’s a critical line item in modern risk management. This article breaks down the latest statistics that define the state of cyber insurance in 2025, helping you understand where the industry is heading and why it matters more than ever.
Editor’s Choice
- 65% of U.S. businesses now have cyber insurance policies in place in 2025.
- The global cyber insurance market is expected to reach $28.4 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 20.5% since 2021.
- In 2025, the average claim payout for cyber incidents has risen to $228,000, reflecting increased threat sophistication.
- Ransomware continues to top the list of claim types, making up 31% of all cyber insurance claims in 2025.
- 85% of cyber insurance underwriters in 2025 utilize AI and predictive analytics during policy issuance and renewal.
- Healthcare is the highest-risk insured industry, accounting for 22% of all policy payouts in 2025.
- The average premium for a U.S. mid-sized firm has climbed to $17,600 annually as of 2025, up 12% year-over-year.
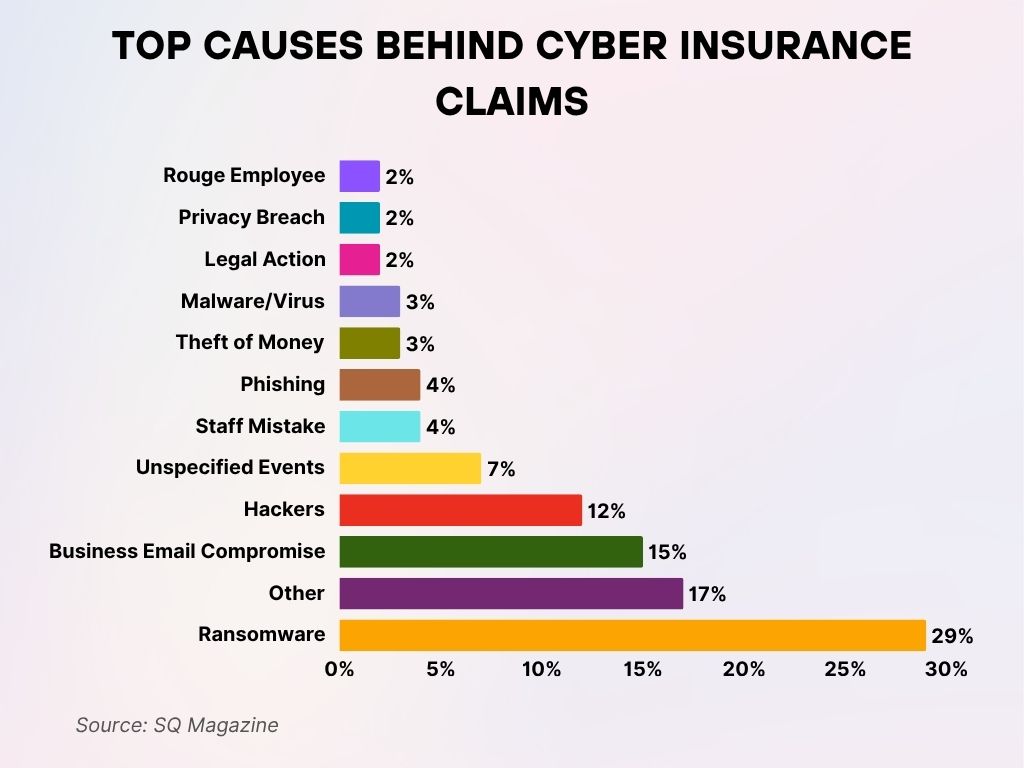
Top Causes Behind Cyber Insurance Claims
- Ransomware tops the list, accounting for 29% of all cyber insurance claims, making it the most costly cyber threat.
- Other causes represent 17%, indicating a wide range of miscellaneous or unclassified incidents.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) is responsible for 15% of claims, highlighting the financial risks of compromised communications.
- Hackers account for 12% of reported claims, underlining the persistent threat from external cyber attackers.
- Unspecified Events make up 7%, showing there are still many cyber incidents with unclear origins.
- Phishing and Staff Mistakes each contribute 4%, pointing to the role of human error and deceptive tactics.
- Malware/Virus and Theft of Money are behind 3% of claims each, showing ongoing risks from software-based attacks and financial theft.
- Privacy Breach, Legal Action, and Rogue Employee all share the lowest impact at 2% each, but still represent critical internal and legal risks.
Familiarity and Experience with Cyber Insurance
- 78% of IT decision-makers in U.S. companies report being “very familiar” with cyber insurance in 2025, up from 62% in 2022.
- 51% of small and mid-sized businesses (SMBs) have held a policy for more than 3 years as of 2025.
- In 2025, 24% of cyber-insured firms have filed a claim at least once, reflecting increased engagement with the process.
- 41% of businesses chose their provider based on incident response services, making it a leading selection factor in 2025.
- Only 9% of organizations report dissatisfaction with their cyber insurer, down from 15% two years prior.
- 95% of respondents in a 2025 industry survey say they would renew their policy, a sign of growing trust and necessity.
- Education and awareness training are now included in 61% of cyber insurance packages in 2025.
- The average global premium for cyber insurance policies in 2025 is $12,300.
- Premium increases averaged 14% in 2025, with the largest hikes seen in the finance and retail sectors.
- In 2025, 64% of policies cover business interruption, a jump from 49% in 2021.
- Extortion coverage is included in 92% of policies issued in 2025, becoming nearly universal.
- The median coverage limit for mid-sized enterprises rose to $4.5 million in 2025.
- 75% of new policy buyers in 2025 opted for higher deductibles to manage premium costs.
- Telehealth and cloud service providers saw the steepest premium increases, with rates up by 22% in 2025.
- Bundled services (policy + security tools) now account for 33% of all new policy sales in 2025.
- 60% of underwriters in 2025 now require mandatory cybersecurity assessments before issuing coverage.
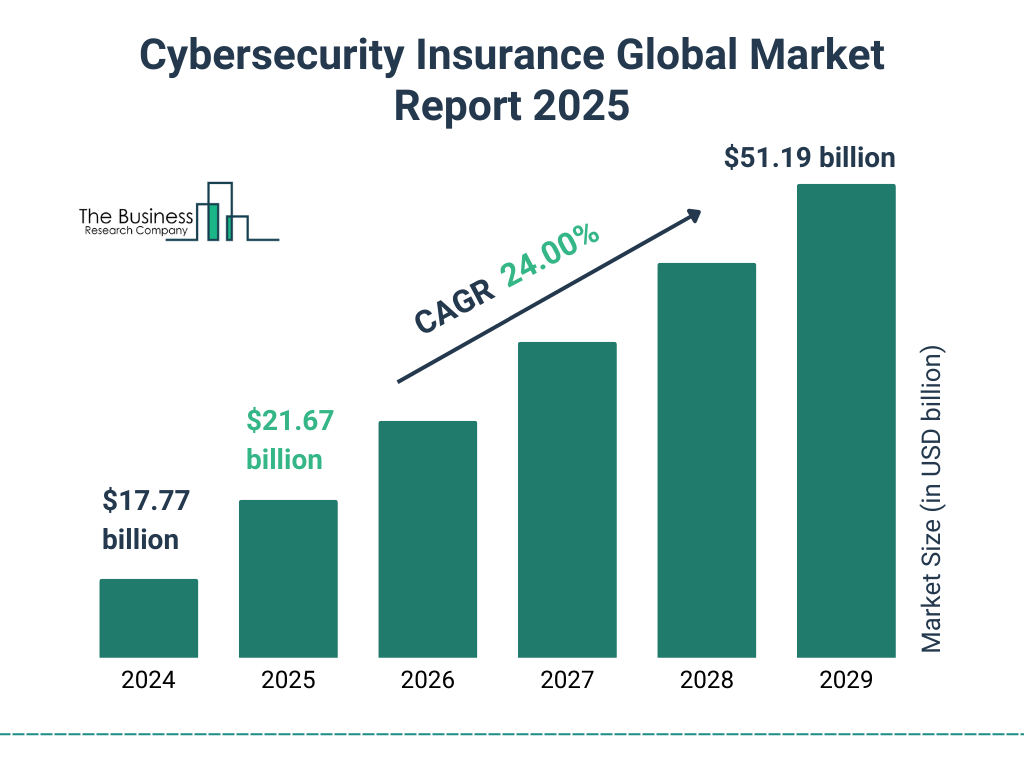
Cybersecurity Insurance Market Growth Outlook
- The global cybersecurity insurance market is projected to grow from $17.77 billion in 2024 to $51.19 billion by 2029.
- This reflects a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 24.00%, signaling robust demand for digital risk protection.
- In 2025, the market is expected to reach $21.67 billion, showing strong year-on-year growth.
- The forecast indicates a nearly 3x increase in market size over a 5-year period.
Businesses are accelerating investments in cybersecurity coverage amid rising threats and compliance pressures.
Frequency and Severity of Cyber Insurance Claims
- 1 in 5 policyholders filed a cyber insurance claim in 2025, the highest claim rate ever recorded.
- Ransomware payouts averaged $492,000 per incident in 2025.
- Phishing-related breaches are behind 28% of all claims in 2025, up from 23% in the prior year.
- Legal and regulatory costs per claim jumped by 18% in 2025, reflecting stricter data protection enforcement.
- Data restoration accounted for 21% of total claim costs on average in 2025, often overshadowing ransom demands.
- Supply chain attacks made up 13% of claims in 2025, doubling their share from two years prior.
- Average resolution time for a claim reached 41 days in 2025.
- 94% of ransomware-related claims in 2025 involved the involvement of law enforcement or third-party negotiators.
- The top three industries by claim volume in 2025 were healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
Types of Cyber Insurance Claims
- In 2025, ransomware attacks remain the most frequent type of cyber insurance claim, representing 31% of all claims.
- Phishing and social engineering incidents account for 22% of total claims.
- Business email compromise (BEC) now makes up 15% of all claims filed in 2025.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks were involved in 7% of claims this year.
- Insider threats, both malicious and accidental, are behind 11% of all covered events in 2025.
- System misconfigurations and human errors led to 9% of reported incidents covered by policies in 2025.
- Third-party vendor breaches are responsible for 13% of claims filed under cyber insurance in 2025.
- Cloud data breaches made up 10% of all policy claims in 2025, highlighting cloud security concerns.
- In 2025, data theft and IP theft accounted for 8% of claim types across major industries.
- Emerging threats like deepfake fraud now represent 1.5% of total claims, a growing but still niche risk.
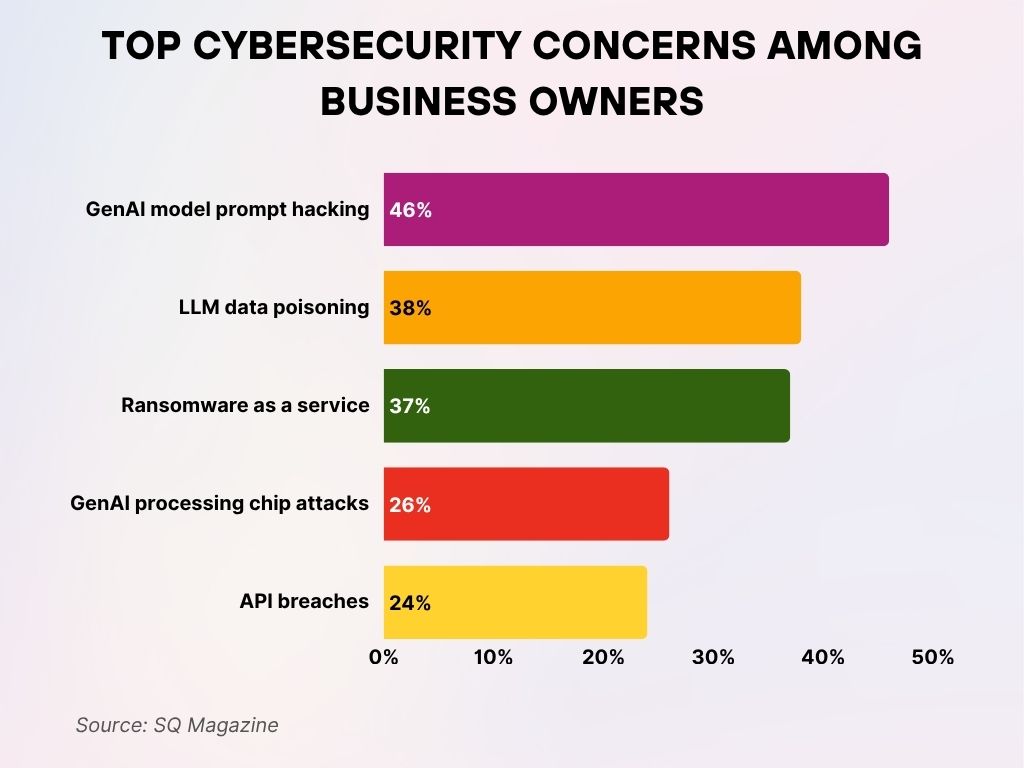
Top Cybersecurity Concerns Among Business Owners
- 46% of business owners cited GenAI model prompt hacking as their top cybersecurity concern, reflecting rising fears around AI misuse.
38% are worried about LLM (Large Language Model) data poisoning, signaling the risks of corrupted AI training data. - 37% identified Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) as a major threat, highlighting the growing accessibility of cybercrime tools.
- 26% expressed concern over GenAI processing chip attacks, pointing to fears of hardware-level vulnerabilities in AI systems.
- 24% of respondents are alarmed by API breaches, emphasizing the importance of securing digital integrations and interfaces.
Top Insured Cyber Risks and Threat Types
- Ransomware is the top-insured threat, explicitly covered in 97% of cyber policies in 2025.
- Phishing scams and credential harvesting are insured risks in 89% of policies in 2025.
- System downtime and business interruption are included in 81% of policies, showing high demand in 2025.
- Data exfiltration and theft coverage appear in 84% of current policy frameworks.
- Regulatory fines and penalties are insurable under 72% of enterprise policies in 2025.
- Supply chain risk is addressed in 66% of policies, a notable rise from 52% in 2022.
- Zero-day vulnerabilities are covered in 58% of policies, up from 41% two years prior.
- Malware infections and their aftermath are covered in 76% of all policies in 2025.
- Cloud service failures are explicitly listed in 63% of 2025 insurance plans as insurable risks.
- Social media account takeovers are covered in 39% of niche or specialized business policies.
Regional Penetration and Market Leaders
- The United States remains the largest cyber insurance market globally, with a market share of 54% in 2025.
- Europe holds the second spot, making up 28% of global premiums written in 2025.
- Asia-Pacific continues its rapid adoption, now contributing to 12% of the global cyber insurance revenue.
- Germany, France, and the UK lead Europe’s cyber insurance uptake with a combined growth of 14% YoY in 2025.
- Singapore saw the highest year-over-year growth in Asia, with policy uptake increasing by 38% in 2025.
- In 2025, California remains the top U.S. state by cyber policy count, accounting for 11% of total policies.
- Texas and New York follow with 9% and 8.5% of cyber insurance policies, respectively, in 2025.
- Canada holds steady with 2.7% of global market share and growing adoption among SMBs.
- The Middle East and Africa region remains underpenetrated, holding just 1.6% of the global market in 2025.
- London continues to be a major underwriting hub, with Lloyd’s syndicates writing over $3.2 billion in cyber premiums in 2025.
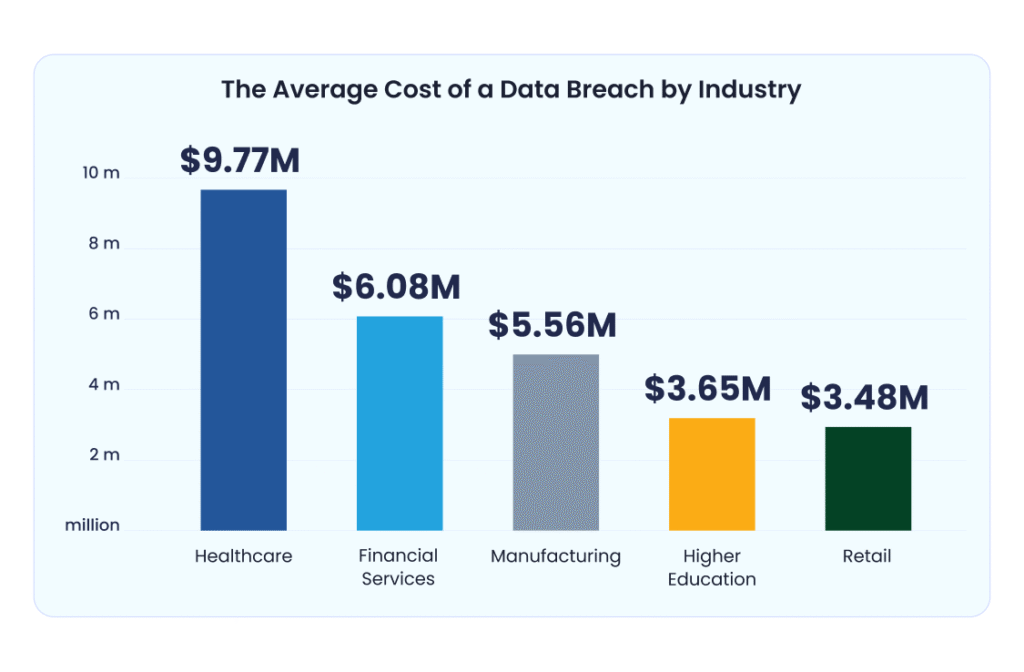
Average Cost of a Data Breach by Industry
- Healthcare suffers the highest breach costs, averaging $9.77 million, making it the most expensive industry for data breaches.
- Financial Services ranks second with an average breach cost of $6.08 million, reflecting the high stakes of compromised financial data.
- Manufacturing faces average costs of $5.56 million, showing that industrial systems are also high-value targets.
- Higher Education sees breach costs averaging $3.65 million, due to sensitive student and institutional data.
- Retail has the lowest average at $3.48 million, but still represents significant financial and reputational damage.
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Policy Demand
- 81% of companies cite data privacy regulations as a key reason for adopting or increasing cyber coverage in 2025.
- The U.S. Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act has driven 20% growth in related policies in 2025.
- In 2025, GDPR enforcement fines exceeded €1.6 billion, prompting a surge in regulatory risk coverage.
- California’s CPRA contributed to a 25% rise in demand for breach response coverage in 2025.
- Australia’s Privacy Act reforms triggered a 41% spike in commercial cyber policy adoption by mid-2025.
- Mandatory reporting laws now exist in 36 countries, pushing organizations to proactively secure cyber insurance.
- 80% of legal and compliance teams in large firms are involved in cyber policy purchasing decisions in 2025.
- Regulatory technology integration is included in 48% of enterprise-grade cyber insurance solutions.
- The introduction of automated regulatory audits has increased insurer demand for evidence-based underwriting.
- International data transfer policies have led multi-national firms to raise their coverage limits by an average of 19% in 2025.
SME vs. Enterprise Cyber Insurance Uptake
- 94% of enterprises (1,000+ employees) now have cyber insurance in 2025, compared to 66% of SMEs.
- The SME cyber insurance market grew by 17% YoY, reaching $5.2 billion globally in 2025.
- Cost remains the biggest barrier for 43% of SMEs without coverage in 2025.
- Microbusinesses (1–10 employees) saw a 19% increase in policy purchases this year.
- 72% of enterprise policies in 2025 include bespoke clauses, while only 28% of SME policies offer this flexibility.
- SMEs in regulated industries, like healthcare and finance, are 4x more likely to buy insurance than non-regulated peers.
- Self-assessment portals are used by 61% of SMEs in 2025 to qualify for tailored premiums.
- Managed Service Providers (MSPs) bundled cyber insurance in 22% of their service packages for SMEs in 2025.
- 60% of enterprises now require supply chain partners to hold cyber coverage as of 2025.
- Bundled policies with business interruption are twice as popular among enterprises compared to SMEs in 2025.
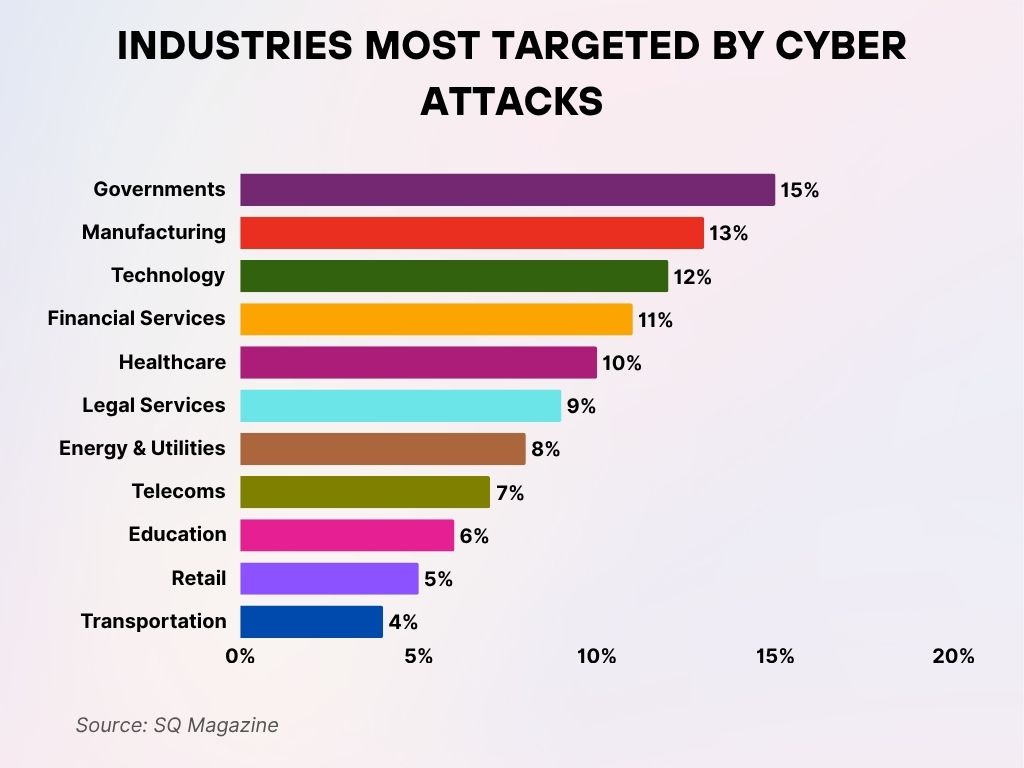
Industries Most Targeted by Cyber Attacks
- Governments were the most targeted sector, accounting for an estimated 15% of all cyber attacks.
- Manufacturing followed closely with 13%, reflecting increasing vulnerabilities in industrial systems and supply chains.
- The Technology sector saw 12% of attacks, underlining its attractiveness as a high-value target.
- Financial Services made up 11% of incidents, driven by the sensitive nature of financial data.
- Healthcare faced 10% of cyber attacks, putting patient data and care operations at significant risk.
- Legal Services and Energy & Utilities experienced 9% and 8% of attacks, respectively, both critical for infrastructure and confidential data.
- The Telecoms industry accounted for 7%, highlighting threats to communication systems.
- Education saw 6%, with attacks likely focused on data-rich yet under-protected institutions.
- Retail and Transportation were hit with 5% and 4% respectively, pointing to ongoing threats in customer-facing sectors.
Key Drivers for Policy Adoption
- 63% of businesses in 2025 cite ransomware fears as their primary reason for obtaining cyber insurance.
- Compliance mandates are driving adoption in 58% of mid-to-large enterprises.
- Board-level oversight of cybersecurity has increased significantly, with 72% of boards reviewing cyber coverage annually.
- 56% of policyholders** in 2025 purchased coverage after experiencing a cyber incident or near miss.
- Growing reliance on remote work infrastructures influenced 48% of the new policies written this year.
- Third-party risk emerged as a leading concern for 44% of companies seeking coverage.
- Publicly reported breaches in competitor firms influenced 31% of policy decisions in 2025.
- Adoption of cyber insurance incentives tied to cyber hygiene practices is up 36% year-over-year.
- 58% of tech startups cited investor requirements as a key motivator for acquiring cyber insurance.
- 24% of firms added or upgraded policies due to contractual obligations with clients and vendors.
Common Exclusions and Coverage Gaps
- War and nation-state attacks are excluded in 91% of policies in 2025, despite growing geopolitical tensions.
- Known vulnerability exploitation without patching is cited in 83% of denied claims.
- Cryptojacking is explicitly excluded in 67% of SMB-level cyber insurance policies.
- Acts of employee negligence remain a gray area, with exclusions present in 52% of policies.
- Social media defamation claims are excluded in 49% of general cyber policies in 2025.
- Unapproved software use can void coverage in 37% of corporate policies.
- IoT-related risks are excluded or capped in 41% of cyber insurance plans, especially in industrial sectors.
- Coverage for fines related to privacy violations varies widely; only 38% of global policies include it.
- Policy stacking limits (using multiple policies for the same incident) are restricted in 59% of insurers’ clauses.
- Incident response costs can be undercovered by up to 30% in policies with outdated policy terms.
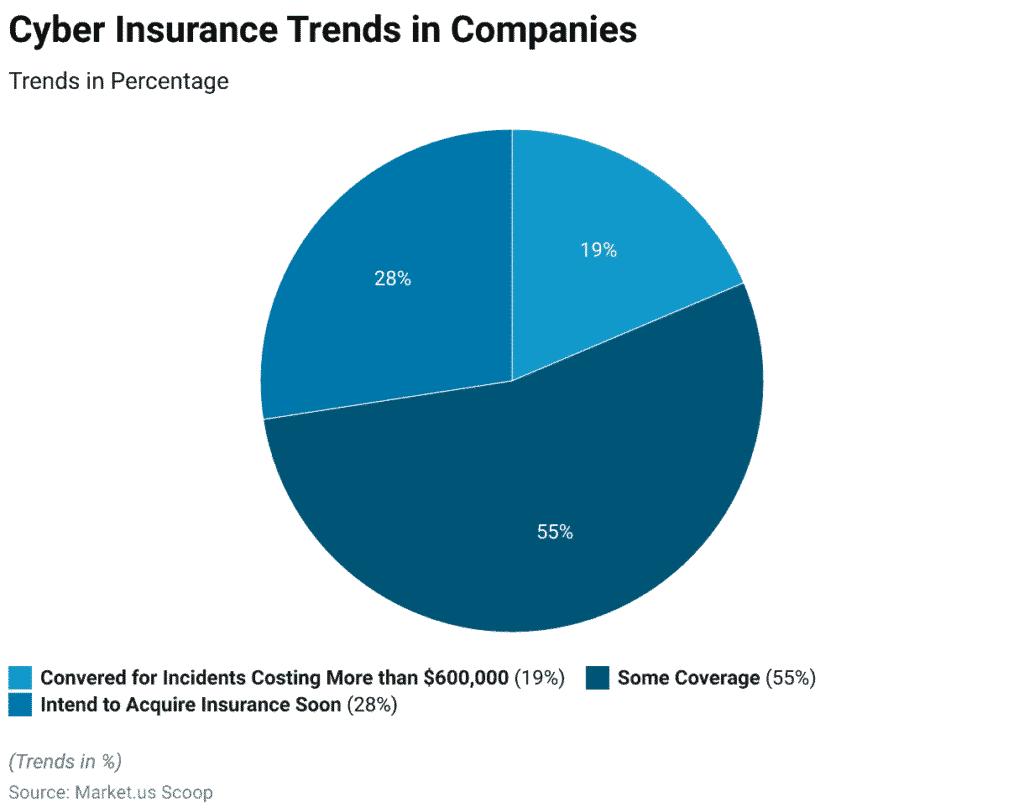
Cyber Insurance Adoption Trends in Companies
- 55% of companies have some level of cyber insurance coverage, showing growing awareness of digital risk protection.
- 28% of businesses intend to acquire cyber insurance soon, highlighting an upward trend in adoption.
- Only 19% of companies are fully covered for incidents costing over $600,000, indicating a gap in high-cost risk preparedness.
Role of AI and Data Analytics in Underwriting
- 85% of cyber insurers in 2025 use AI to assess applicant risk in real time.
- Predictive analytics tools are used in 76% of policy renewals to adjust premiums dynamically.
- AI-enabled risk scoring algorithms have replaced manual assessments in 70% of large providers.
- 45% of insurers offer discounts based on ongoing telemetry data monitored via endpoint protection tools.
- Machine learning models now forecast claim likelihood with 82% accuracy, up from 64% two years ago.
- In 2025, insurers reduce manual processing time by an average of 65% thanks to AI-assisted workflows.
- NLP-driven data analysis of breach reports is used by 58% of underwriters to inform policy design.
- Customer segmentation models powered by AI help offer customized pricing tiers to SMBs and enterprises alike.
- 34% of policies in 2025 include real-time analytics dashboards for insured clients to monitor risk posture.
- Insurtech startups using full AI-based underwriting grew by 29% in market share compared to traditional insurers.
Recent Developments in the Cyber Insurance Industry
- The global cyber insurance market surpassed $28.4 billion in total value in 2025.
- Consolidation among insurers accelerated, with 5 major mergers recorded this year alone.
- Insurtech investment reached $2.1 billion globally in 2025.
- Parametric cyber insurance models gained traction, with 12% of new policies using automated trigger-based payouts.
- Cyber coverage extensions into OT (Operational Technology) networks expanded in 2025, particularly in manufacturing and energy.
- Digital identity verification integration in underwriting rose by 41% among the top 20 global insurers.
- Public-private insurance frameworks, like cyber catastrophe bonds, were launched in the U.S. and the UK.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting began including cyber resilience metrics in 2025.
- Cyber insurance capacity constraints eased slightly as reinsurers re-entered the market with higher limits.
- Cybersecurity partnerships, such as bundled offerings with endpoint protection vendors, now account for 38% of policy sales.
Conclusion
Cyber insurance has evolved from a specialized risk transfer product into a strategic business essential. In 2025, rising threats, regulatory pressure, and technological advancements continue to reshape the landscape. Enterprises and SMBs alike are not only buying more coverage, they’re demanding smarter, AI-driven, and more responsive policy solutions.
This evolution isn’t just reactive. It’s proactive. With insurers offering tailored protection, predictive risk models, and bundled cybersecurity tools, the cyber insurance market has become a vital player in digital resilience. The trends show no signs of slowing, and neither do the risks. Staying informed is no longer optional; it’s a necessity.
Sources
- https://www.statista.com/topics/2445/cyber-insurance/
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/tip/Cyber-insurance-trends-What-executives-need-to-know
- https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/cybersecurity-insurance-global-market-report
- https://www.cyber-insurance-innovation-eu.com/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/1190800/forecast-cyber-insurance-market-size/
- https://www.theinsurer.com/ti/viewpoint/the-future-of-europes-fast-growing-cyber-insurance-market-2025-02-26/
- https://www.landers.com.au/legal-insights-news/cyber-insurance-trends-shaping-2025-and-beyond