Bing is Microsoft’s search engine platform and a key part of the firm’s AI, cloud, and digital advertising architecture. Today, it continues to evolve rapidly amid surging interest in AI, changing market share dynamics, and workforce shifts. Companies use Bing to power search integrations, deliver advertising at scale, and support digital assistants; industries from e-commerce to education rely on its search infrastructure. In this article, we’ll examine what is known about how many people work at Bing, who they are, and how this workforce is changing.
How Many People Work At Bing?
- Microsoft employs ~228,000 people globally as of mid‑2024.
- Among these, the U.S. workforce accounts for about 120,000 employees.
- Datacenter roles in Microsoft grew 23.9% globally in 2024; in the U.S., growth was 28.9%.
- Women make up 31.6% of Microsoft’s core workforce in 2024, up from 31.2% in 2023.
- Microsoft announced layoffs amounting to ~4% of its workforce (~9,100 employees) in mid‑2025 as part of cost‑control amid AI investments.
- ~78% of business leaders surveyed are considering hiring for AI‑specific roles over the next 12‑18 months.
- Microsoft’s total headcount shows slow growth, from ~221,000 (2023) to ~228,000 (2024).
Recent Developments
- In mid‑2025, Microsoft announced a ~4% workforce reduction (~9,100 employees) to reorganize under its ongoing AI investment strategy.
- Earlier in 2025, Microsoft cut ~3% of its workforce (~7,000 employees), focusing especially on management layers.
- New AI roles are becoming a priority; 78% of leaders say they plan to hire for AI‑specific roles, for “Frontier Firms,” that figure rises to 95%.
- Microsoft’s datacenter workforce is expanding rapidly, 23.9% growth globally in 2024 and 28.9% growth in the U.S. for those roles.
- The “Work Trend Index” emphasizes hybrid human‑AI teams and evolving workplace structures as part of Bing’s parent company’s strategy.
- Microsoft has published more detailed global diversity & inclusion (D&I) data recently, showing incremental increases in the representation of women.
- There is evidence of relatively stable overall headcount despite departures and hires balancing out.
Bing’s Current Team (Key People)
- Mikhail Parakhin served as CEO of Bing and Microsoft Advertising (WebXT) until March 2024, after which he transitioned into a different role following a leadership reshuffle.
- As of April 2024, Mustafa Suleyman, co-founder of DeepMind and former CEO of Inflection AI, leads Microsoft’s Consumer AI division, which includes Bing, Edge, and Copilot.
- Karén Simonyan, also from Inflection AI, joined Microsoft AI’s Chief Scientist and works closely on foundational models that power Bing’s AI experiences.
- Yusuf Mehdi, Microsoft’s Consumer Chief Marketing Officer, has played a critical public-facing role in promoting Bing Chat and Copilot integration into the search experience.
- Rangan Majumder has led Bing’s core Search and AI relevance initiatives, focusing on AI-driven ranking systems and large language model integration.
- Tanner Clark, a Principal Product Manager, has been instrumental in shipping AI features within Bing and its web services.
- The broader WebXT organization, which includes Bing, employs thousands of engineers, researchers, and product leads, many of whom work closely with Microsoft Research and Azure AI teams.
- Cross-collaboration between OpenAI’s API teams and Microsoft’s Bing product group continues to influence product development direction, especially around Copilot in Search.
- Many AI research scientists and applied ML engineers from Microsoft Research are embedded within Bing’s ranking, safety, and personalization teams.
Bing Employee Overview
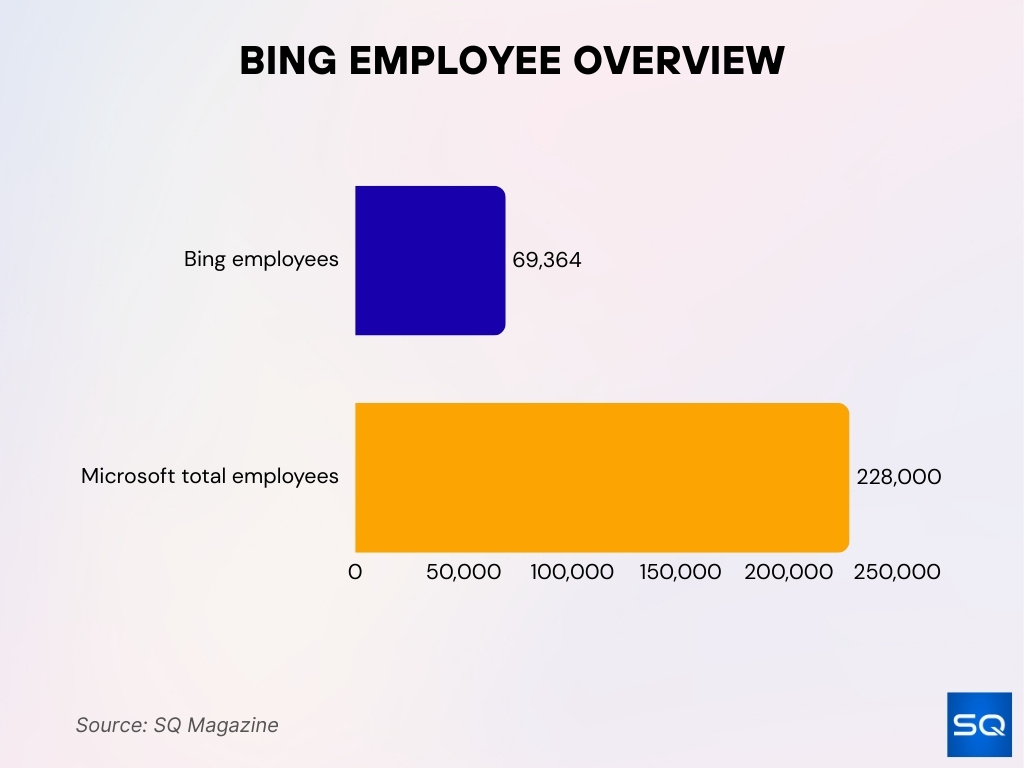
- A data profile suggests Bing has 69,364 employees as of early to mid‑2025.
- Microsoft overall has ~228,000 employees globally.
- There is no reliable public breakdown confirming exactly what share of Microsoft’s workforce is dedicated purely to Bing (search, advertising, R&D, Edge/Copilot, etc.).
- Bing‑related teams likely overlap with Microsoft’s larger R&D, AI, and cloud operations; many employees may not be exclusively “Bing staff.”
- Recent Microsoft layoffs impact roles across ad tech, cloud, and AI infrastructure, which may include Bing‑adjacent employees.
- Microsoft’s reporting focuses more on broader divisions (such as datacenters, product groups, and engineering) rather than “Bing only” units in its public disclosures.
Workforce Growth Trends
- Microsoft’s total headcount grew from ~221,000 in 2023 to ~228,000 in 2024.
- Datacenter employee populations more than tripled since 2020 in some locales, global datacenter workforce grew ~23.9% in 2024.
- In the U.S., datacenter staff grew near 28.9% in 2024.
- AI‑specific hiring is accelerating, survey data indicates ~95% of frontier firms plan AI‑role hiring.
- Although layoffs have occurred, they have been offset by hiring in high‑priority areas like AI, cloud, and infrastructure.
- Microsoft maintains a relatively stable headcount overall despite turnover (hires vs departures near balance).
- Some growth is concentrated in technical infrastructure roles (datacenters, servers, cloud) rather than in fewer non‑technical staff.
Distribution by Department
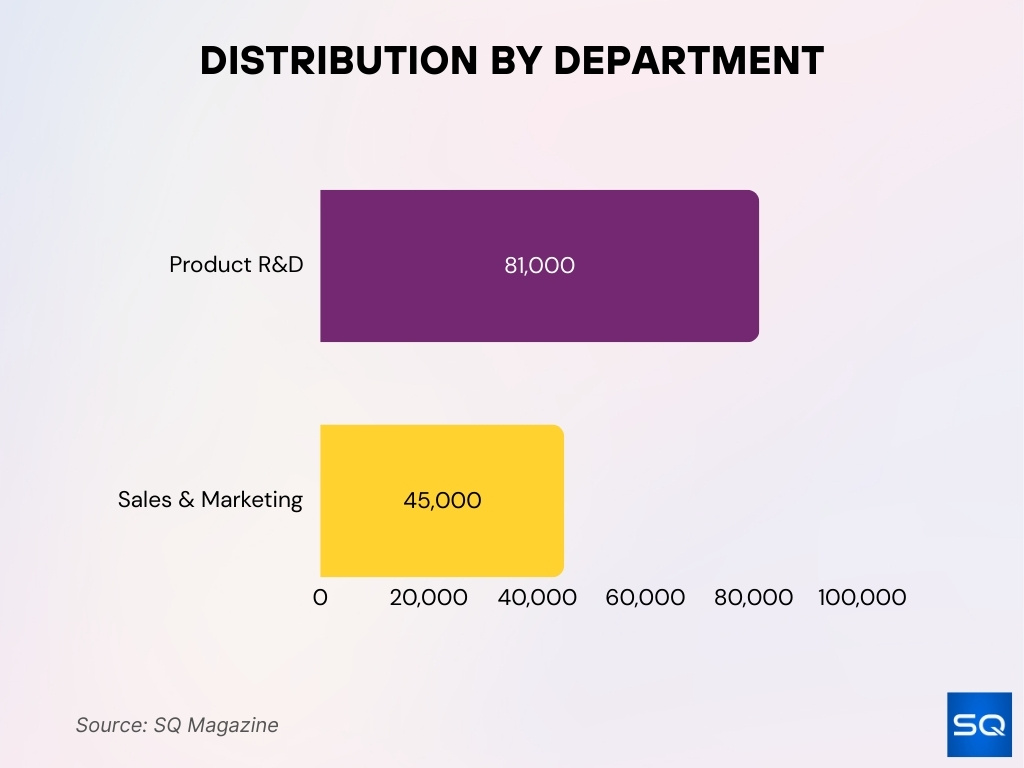
- Engineering & R&D roles make up a large share of Microsoft’s staff, at last count ~81,000 employees in product R&D.
- Sales and Marketing is another notable division, though its precise size for Bing isn’t published, Microsoft reportedly had ~45,000 employees in sales & marketing.
- Datacenter operations have seen strong growth (global ~23.9%, U.S. ~28.9% in 2024).
- Leadership/management layers are being trimmed, indicating that current departmental staffing in management is under adjustment.
- Infrastructure (cloud, AI, servers, datacenters) is growing faster than many support or business functions.
- Roles in AI/machine learning, data science, and product management associated with Bing’s evolution are increasingly prioritized.
- Microsoft’s divisions that handle support, operations, and non‑tech functions likely represent a smaller, flatter portion of Bing‑adjacent staffing.
- Contractors vs full‑time staff distribution is not publicly broken out specifically for Bing.
Demographics
- Women comprise 31.6% of Microsoft’s core workforce as of 2024, up from ~31.2% in 2023.
- In technical roles, women make up 27.2%, a rise of 0.5 percentage points from the prior year.
- Representation of racial and ethnic minority groups in Microsoft’s core workforce is 53.9% globally, up ~0.6 points year‑over‑year.
- Globally, 5.7% of Microsoft’s employees in the core business identify as having a disability, up ~0.2 points from the previous year.
- Indigenous employees globally remain at 0.6%, a number that has stayed stable year over year.
- Black / African‑American representation at the Partner + Executive level rose to 4.3%, up ~0.5 points year‑over‑year.
- Hispanic / Latinx representation at the Executive level rose to 4.6%, up ~0.8 points YoY.
- Microsoft expanded reporting in 2024 to include multiracial, Indigenous, military, and disability categories to increase transparency.
- In leadership levels (excluding Executive), the growth in women and minority representation was positive in almost all categories.
Locations (Global Distribution)
- Microsoft has ~228,000 employees globally in 2024‑2025.
- Around 46% of Microsoft employees are based outside the U.S.
- Microsoft has expanded its datacenter workforce significantly, especially outside the U.S., as part of its global infrastructure build‑out.
- U.S. datacenter employment grew 28.9% in 2024, and global datacenter staff rose 23.9% in the same period.
- Microsoft’s growth in non‑U.S. regions aligns with its cloud, AI, and infrastructure investments in Asia, Europe, and Latin America.
- Remote or hybrid work arrangements are increasingly common, which affects where employees are physically located vs. where roles are based.
- Microsoft’s expansion in global offices is also tied to making leadership more regionally representative.
Bing Users by Education Level
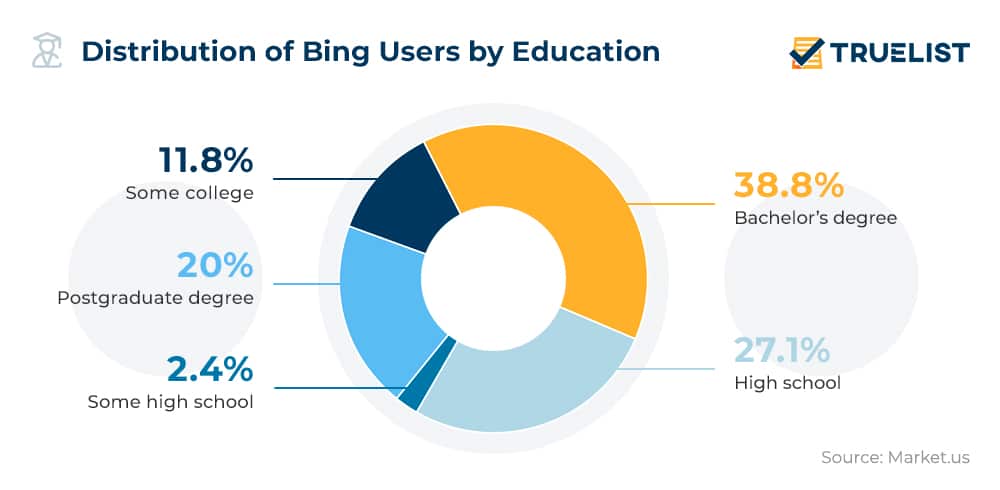
- 38.8% of Bing users have a Bachelor’s degree, making it the largest educational group on the platform.
- 27.1% completed only High school, representing the second-largest segment of users.
- 20.0% hold a Postgraduate degree, showing strong usage among advanced degree holders.
- 11.8% attended some college, indicating partial higher education without a full degree.
- Only 2.4% of users completed some high school, the smallest segment by education level.
Diversity and Inclusion at Bing
- Microsoft’s 2024 report shows 31.6% of its core workforce is women, up from ~31.2% in 2023.
- 27.2% of technical roles are held by women globally, a modest but measurable increase YoY.
- Representation of racial/ethnic minority groups in Microsoft’s broader workforce is 53.9%, up 0.6 percentage points.
- Black / African American leadership (Partner + Executive) is 4.3%, growing ~0.5 points YoY.
- Hispanic / Latinx leadership (Executive level) reached 4.6% after an increase of about 0.8 points.
- Disability self‑identification in the core business is 5.7%, up from ~5.5 in % prior year.
- Employee awareness of the concept of allyship has reached 95.6% globally (as of mid‑2024), rising from ~65% in 2019.
- Employee sentiment surveys show that Microsoft employees globally report a “thriving” score of 76.
Workforce Compared to Other Microsoft Divisions
- Microsoft’s ~81,000 employees work in product R&D as of 2024.
- Sales & Marketing headcount has held roughly steady at ~45,000 employees.
- Operations roles have declined slightly, and support/operations headcount dropped from ~89,000 to ~86,000 (~3.37% decline).
- Infrastructure is one of the fastest-growing divisions.
- Bing search, advertising, and AI‑adjacent teams likely share resources with other Microsoft divisions.
- The shift in investment toward AI means divisions such as Azure, AI & Research may be receiving more hiring investment.
- While layoffs have occurred, many are outside core divisions where Microsoft is doubling down.
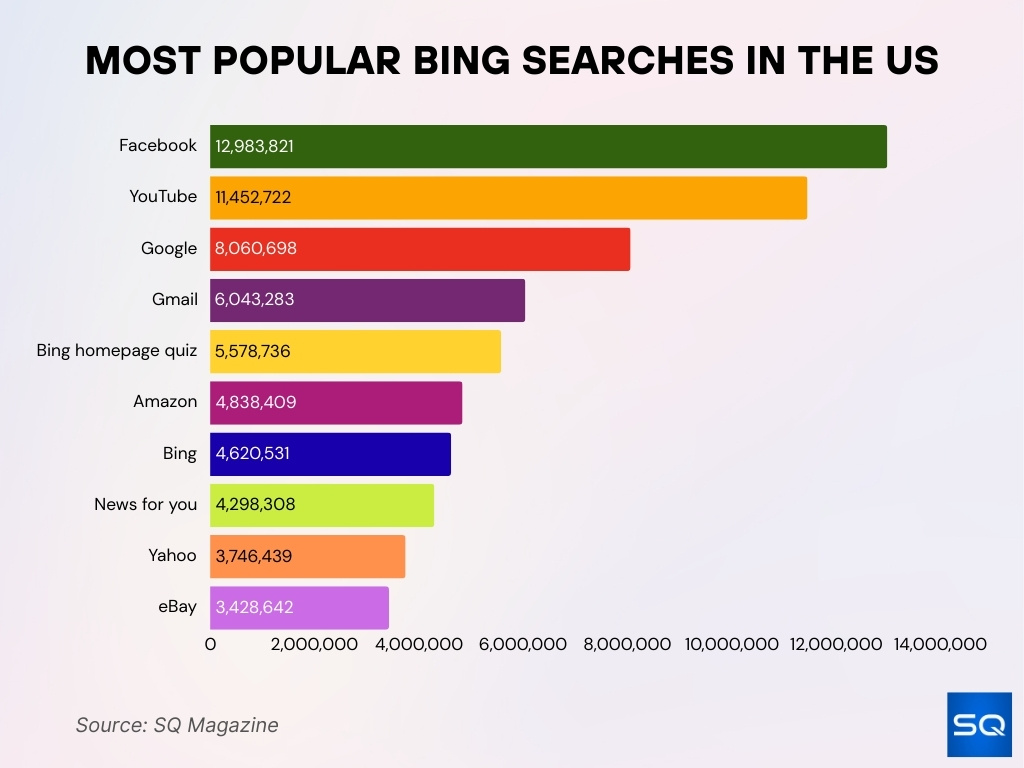
Most Popular Bing Searches in the US
- Facebook tops the list with 12.98 million searches, making it the most searched term on Bing in the US.
- YouTube follows with 11.45 million searches, showing strong user interest in video content.
- Surprisingly, Google ranks third with 8.06 million searches, indicating Bing users often search for a competing search engine.
- Gmail received 6.04 million searches, reflecting widespread use of Google’s email platform.
- Bing homepage quiz generated 5.58 million searches, likely driven by Bing’s daily interactive quiz feature.
- Amazon logged 4.83 million searches, showing strong e-commerce interest among Bing users.
- Bing itself was searched 4.62 million times, possibly by users trying to reset or access the homepage.
- News for you brought in 4.30 million searches, highlighting demand for curated news.
- Yahoo had 3.75 million searches, suggesting cross-platform usage among legacy web users.
- eBay rounded out the list with 3.43 million searches, maintaining its relevance in online retail.
Organizational Changes
- Microsoft announced a round of layoffs in May 2025 affecting roughly 3% of its global workforce (≈ 7,000 jobs).
- In July 2025, Microsoft cut nearly 4% of its workforce (~9,000 jobs).
- Layoffs have especially targeted management layers in many cases.
- These organizational changes reflect strategy shifts.
- Microsoft has improved transparency in its Diversity & Inclusion reporting.
- Self‑ID categories have been expanded in the 2024 GDI report.
- Microsoft is maintaining pay equity across gender and race globally.
- The company is emphasizing more hybrid and flexible work models.
Hiring and Recruitment Trends
- Microsoft employs ~250,893 people worldwide as of August 2025.
- There were 7,321 new hires and 7,992 departures.
- Engineering remains the largest department with ~104,214 employees.
- Business Management (≈16%) and Sales & Support (~12%) are the next largest functional areas.
- Marketing & Product represent about 8%.
- Hybrid job postings reached ~24% in the U.S., up from ~15% in Q2 2023.
- New postings for fully on‑site roles dropped from 83% to 66% during 2023.
- Hiring in AI, cloud infrastructure, and R&D has been prioritized.
R&D and Engineering Teams
- Engineering accounts for ~104,214 employees within Microsoft globally.
- A large share of investment is being directed towards AI, search, cloud infrastructure, and supporting tools.
- 82% of leaders expect AI agents will be used heavily in the next 12‑18 months.
- Many engineering teams face high work pace, burnout risk, and fragmented work days.
- Productivity‑support functions are growing in proportion.
- Microsoft is investing in global development centers.
- There is increasing cross‑disciplinary collaboration.
Remote Work Statistics
- In 2025, approximately 22% of the U.S. workforce works remotely.
- Globally, hybrid work is preferred by ~83% of workers.
- Employees report that work feels fragmented, with interruptions every ~2 minutes.
- About 48% of employees, and more than half of leaders, say their work is chaotic.
- Remote or hybrid postings are increasing.
- Remote‑only job roles are still less common than hybrid ones.
- ~75% of workers report companies requiring more in‑office presence in late 2024.
- Many Microsoft employees probably fall under hybrid policies.
Employee Retention Rates
- Microsoft had 7,321 hires vs 7,992 departures, showing a slightly negative net change.
- Voluntary turnover rates in the U.S. average ~13.5%.
- “Intent to stay” survey responses are the strongest predictor of voluntary turnover.
- ~65% of Microsoft employees agree there is a reasonable compensation balance.
- Burnout and workload strain contribute to retention risk.
- ~55% of “Frontier Firm” leaders say they can take on more work, compared to ~25% globally.
- Retention is stronger in divisions aligned with strategic AI/cloud initiatives.
- Companies are focusing more on reskilling, mental health, and flexibility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Bing is reported to have ~69,364 employees as of December 2025.
Microsoft’s total global headcount is ~228,000 employees in 2024‑2025.
Microsoft recorded 7,321 hires and 7,992 departures, showing a slight net negative change in overall headcount.
The layoffs of ~9,100 employees represented about 4% of Microsoft’s workforce.
Conclusion
Bing’s exact employee numbers remain mostly private. What we can say with confidence, Microsoft has over 250,000 employees globally as of today, with engineering / R&D playing a central role in its workforce. Hiring is active but nearly balanced by departures, particularly amid strategic shifts toward AI, search, and cloud infrastructure. Hybrid work is now the norm in many parts of tech, including likely Bing‑adjacent teams, while retention leans heavily on employee sentiment, compensation balance, flexibility, and workload manageability.
As Bing continues evolving and as Microsoft redefines its internal units via AI and hybrid working models, tracking future disclosures will be key.